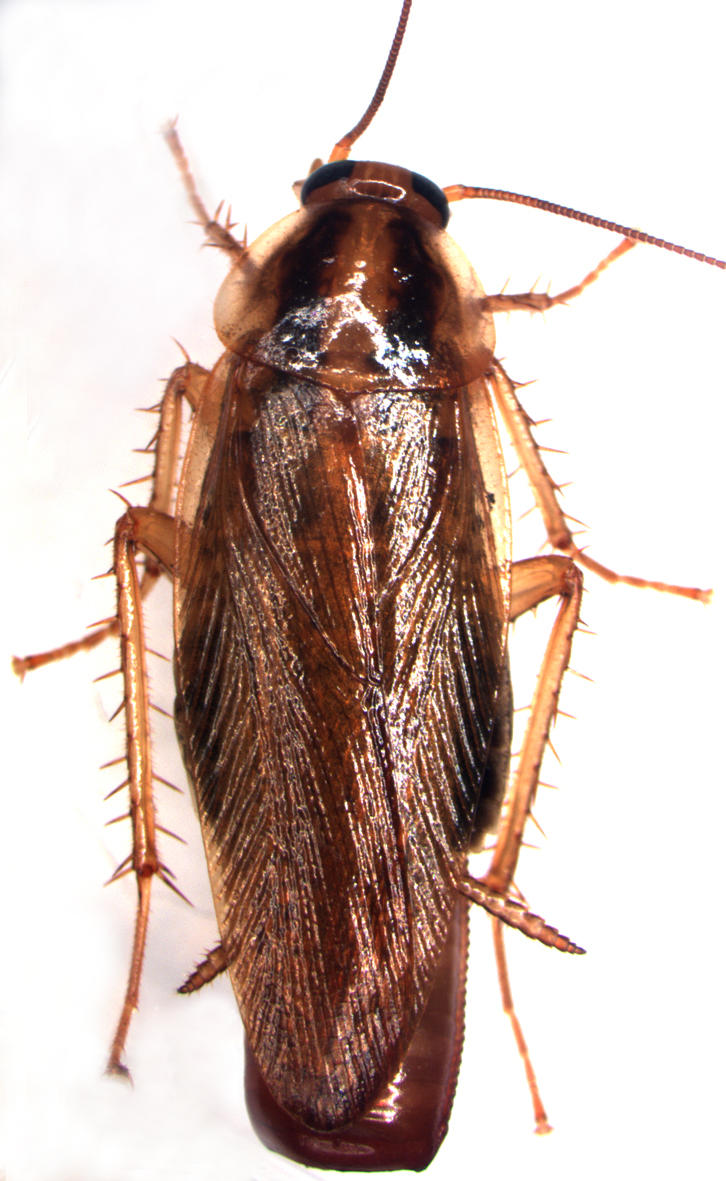
Adult
Size
Up to 20 mm long.
Aspect
Elongate and dorso-ventrally flat, with a soft body; head, thorax, abdomen clearly visible. Long, fine antennae. Well-developed eyes (more than 2,000 facets each) that allow nearly 360° vision.
Among the other cockroach species found in France, German cockroaches are easily recognisable thanks to the 2 black longitudinal stripes on their pronotum
Big wings, longer than the abdomen, yet they do not allow adults to fly long distances. Wings are longer in females, which makes it possible to differentiate them from males, which are also more slender.
There are 2 characteristic cerci at the end of the abdomen. Their tactile hairs are highly sensitive. They can sense sounds and the least vibrations, enabling cockroaches to run away rapidly.
Like other cockroaches, German cockroaches cannot see infra-red light but react quite well to ultra-violet light.
Colour
Dark yellow to dark brown, entirely light-coloured legs.


 Blatte germanique
Blatte germanique  German cockroach
German cockroach  Cucaracha Rubia
Cucaracha Rubia  Deutsche Schabe
Deutsche Schabe