A new hypothesis about the location of the mythical Viking stronghold on Hangman’s Hill near Wolin (West Pomerania) has been put forward by archaeologist Dr. Wojciech Filipowiak.
According to archaeologist Dr. Wojciech Filipowiak from the Institute of Archaeology and Ethnology PAS, Jomsborg was a fortress, and at its foot was the city of Jom.
Wolin is an island at the mouth of the river Oder. It was almost certainly the location which the sagas depict as the home of the Jómsvikings: a band of elite Vikings who sold their services to the highest bidder.
Sagas tell of a magnificent fortress with an artificial harbor that could hold 360 ships. However, archaeological evidence yet does not bear this out. Soon this may change.
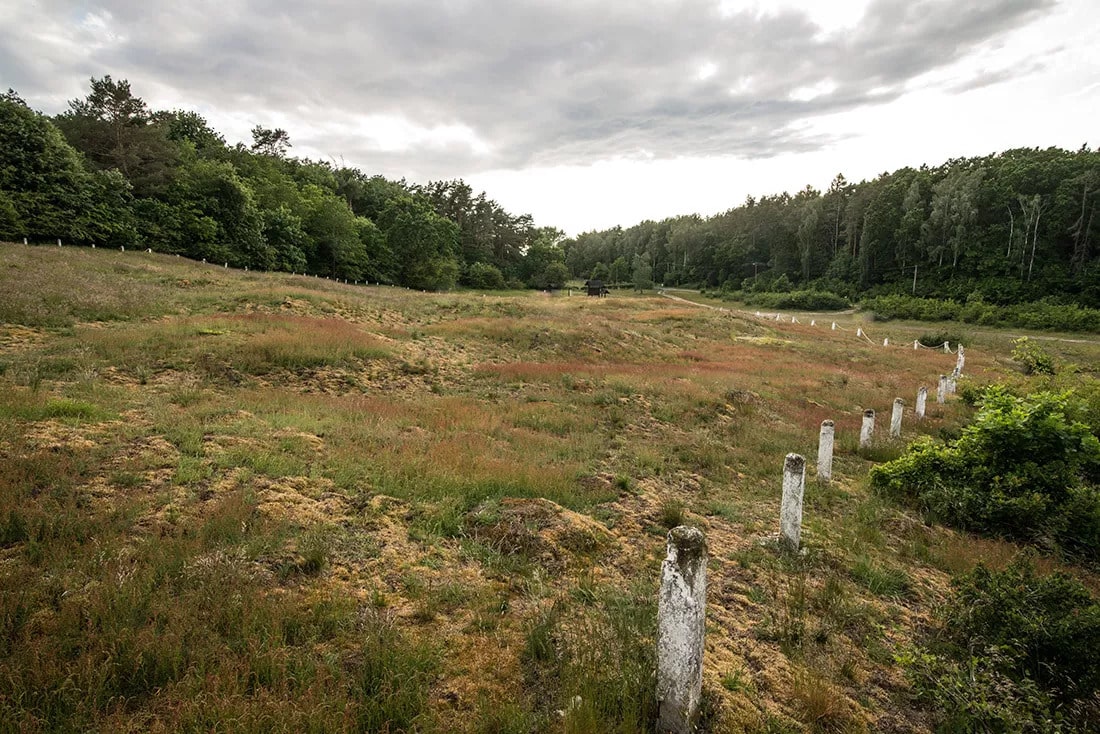
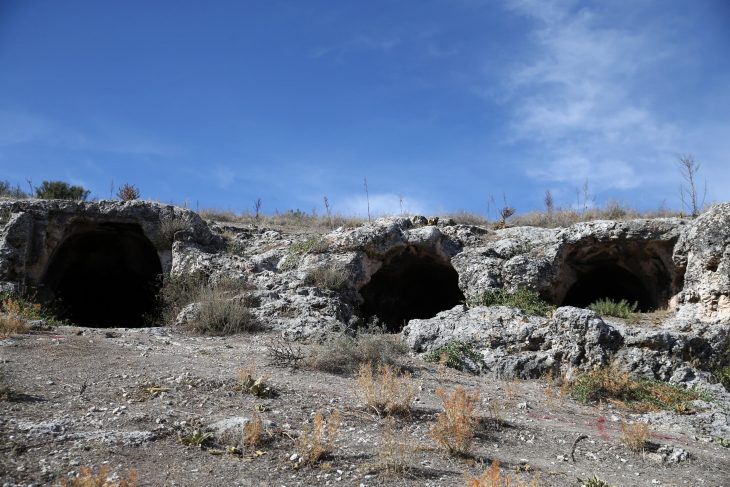
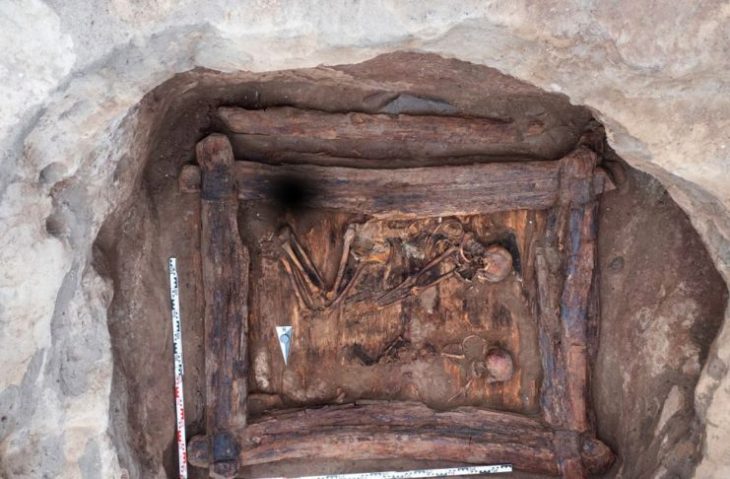
Hangman’s Hill is one of the largest early medieval cemeteries in northern Europe, located south of Wolin.
‘During the research, we conducted there in 2021 and 2022, we were surprised to discover almost entire burial mounds under a half-meter layer of sand. The hill was covered with forest until World War II, the sand was carried there by the wind. This means that there may be more objects that still have their original form, but they are not visible on the surface, Dr. Filipowiak tells PAP.
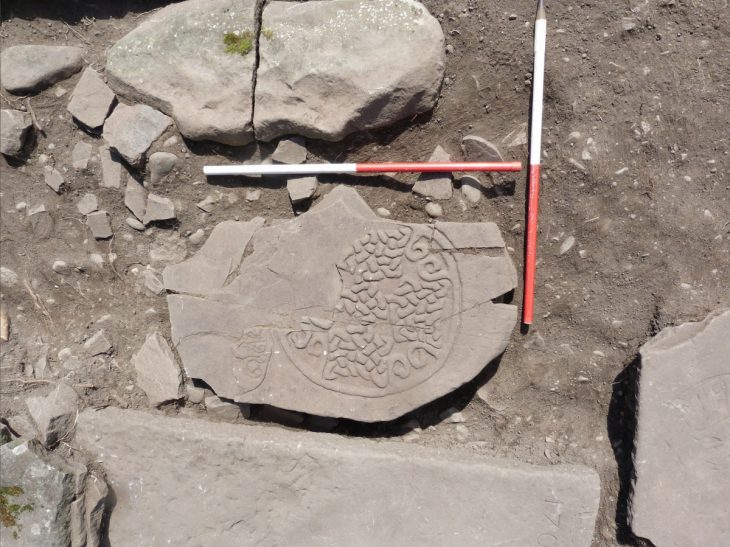
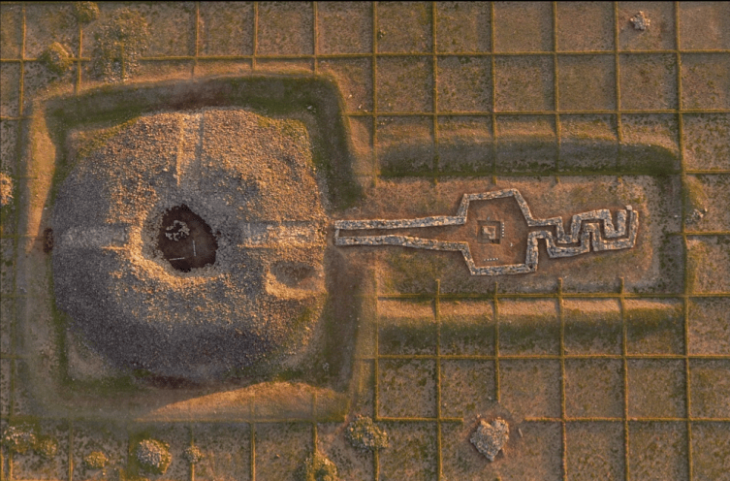
He adds that the archaeologists also found two objects that did not resemble burials. One of them is located on the top of the hill, on the side of the city, and has the shape of a ring(in cross-section there are two embankments). The second one, several meters away, is a linear embankment with burn traces and fragments of wood on both banks.
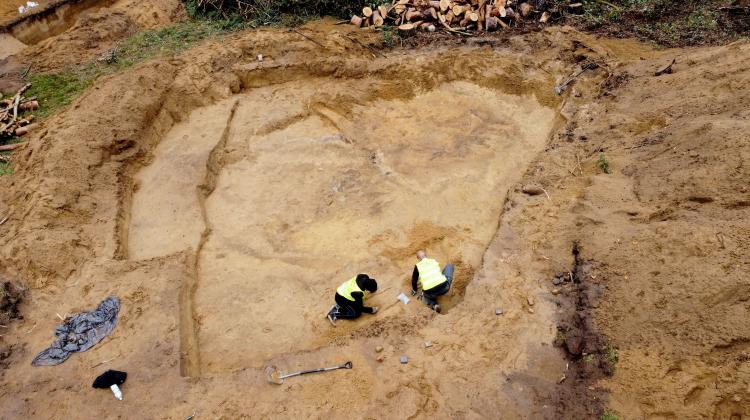

‘They could be a part of a burnt fortification, for example, an embankment,’ says Dr. Filipowiak. He adds that the possible course of the embankments is difficult to determine without further research. The archaeologist explains that he compared the topography of Wolin with two Viking centres – Hedeby in Denmark and Birka in Sweden, and points out that there are great similarities between the three.
In Hedeby, there is Hochburg Hill covered with burial mounds to the north of the centre, and there is also a small rampart dating back to the Viking period. ‘According to one theory, there was a garrison on the hill that controlled the city,’ says Dr. Filipowiak.
To the south of the center of the trade center Birki, on a rock, surrounded by a 350-meter semi-circular embankment, there is the Borgen Fortress. Next to it, on the terrace, there was (as confirmed) a garrison of warriors.
Hangman’s Hill is located south of the city, at the mouth of the Zalew Szczeciski to Dziwna, i.e. on the main shipping route to Wolin; it provides a panoramic view of the entire city. As the archaeologist pointed out, this is an ideal location for a fortress controlling a trading center.
He explains that after formulating the hypothesis, he also looked at the earlier findings of researchers (work on the hill had been carried out since the 19th century) and written sources about Jomsborg.
The only alleged Scandinavian burial under the barrow is at Hangman’s Hill. A skeletal grave without a head and tied hands was also discovered nearby; it was previously associated with the hill’s name and interpreted as a convict’s grave. The archaeologist speculates that the Vikings may have performed a ritual burial here.
One of the arguments for the location of Jomsborg on Hangman’s Hill is the topography.
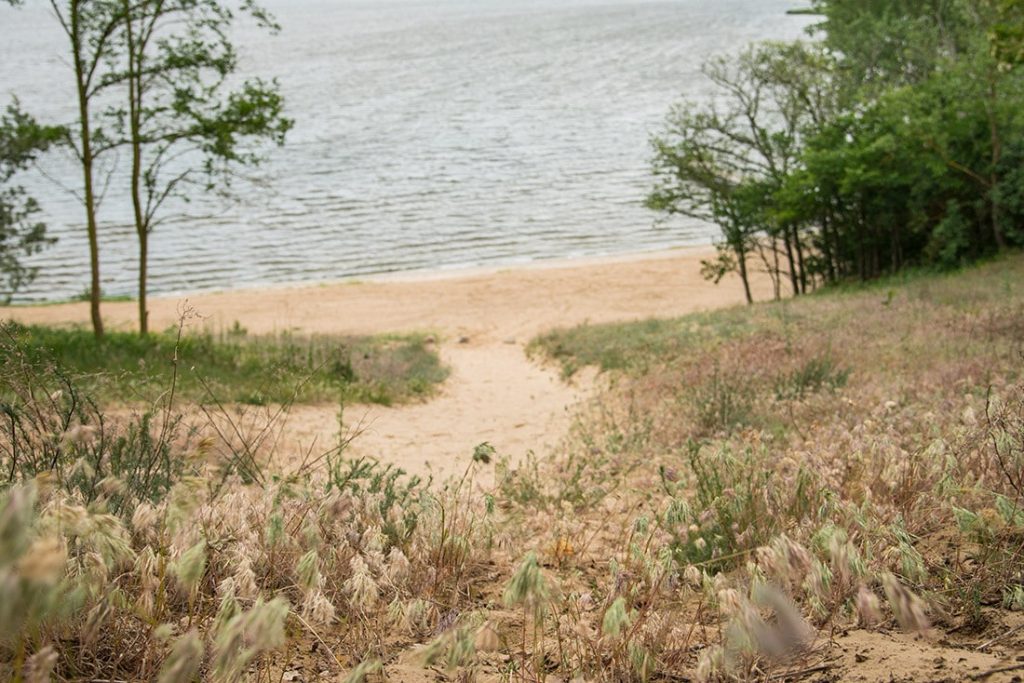

‘The power of Wolin was based on sea trade. The main route to it runs not through Dziwna from the north and through Świna and Piana from the west. Controlling the entrance to Wolin would therefore be most effective from Hangman’s Hill,’ Filipowiak says.
He adds that in the sources there is also the name ‘Jom’, which caused interpretation problems for chroniclers, skalds, and researchers. The proximity of the fortress and the city may have been the reason for confusing the names Jom and Jomsborg. The archaeologist extended the hypothesis to include this issue, pointing out that Jomsborg is a fortress on Hangman’s Hill, and the city at its foot is Jom, after which the entire region was also named.
He also says that in his opinion, the establishment of the fortress in the place of burials was neither accidental nor dictated only by defensive value.
‘I think there was also symbolic violence at play here. Placing military force literally on the graves of ancestors must have carried a huge message for the local population,’ he says.
Researchers are currently planning an extensive project, consisting of several stages, including large excavations in the city center and Hangman’s Hill, which could clarify the relationship between the city and the fortress (if it did exist).
Cover Photo: Hangman Hill Barrows. Wolin Museum