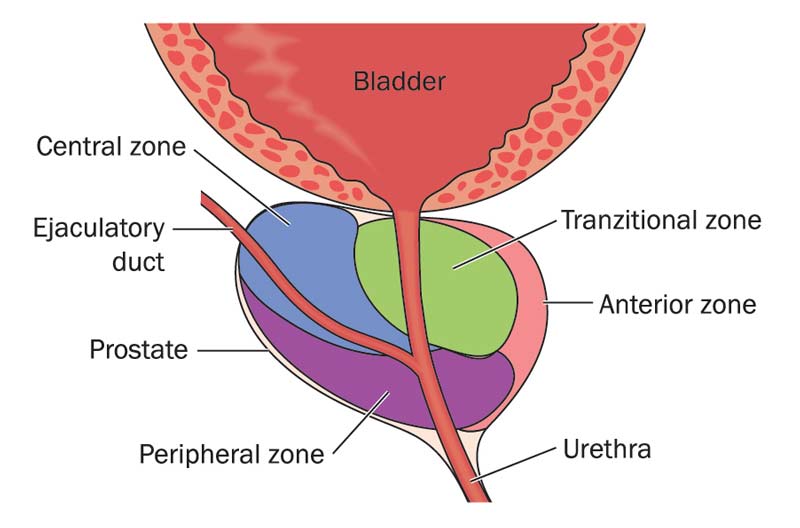
What Is Prostatitis?
Types of Prostatitis
There are four main types, each with distinct characteristics:
1. Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
Acute bacterial prostatitis is caused by a bacterial infection in the prostate gland. It often occurs suddenly and is accompanied by severe symptoms such as fever, chills, lower abdominal pain, frequent urination, and pain during urination. Prompt medical attention and treatment with antibiotics are essential to prevent complications.
2. Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
Chronic bacterial prostatitis is a recurrent infection of the prostate gland. Symptoms are similar to acute bacterial prostatitis but are milder and last for longer periods of time. Antibiotic therapy is necessary to manage the infection and prevent future episodes.
3. Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CP/CPPS)
CP/CPPS is the most common form of prostatitis and accounts for approximately 90% of cases. The exact cause is unknown, but it is believed to be non-bacterial in nature. Symptoms include pelvic pain, discomfort in the genital area, frequent urination, and pain during ejaculation. Treatment involves a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
4. Asymptomatic Inflammatory Prostatitis
Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis is characterized by inflammation of the prostate gland but without noticeable symptoms. It is often diagnosed during medical examinations for other conditions and treatment may not be necessary unless symptoms develop in the future.
Causes and Risk Factors of Prostatitis
The causes can vary depending on the type. Acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis is caused by bacterial infections that may originate from urinary tract infections or sexually transmitted infections. CP/CPPS may be associated with pelvic floor muscle dysfunction, autoimmune factors, or nerve-related issues. Some risk factors include a history of prostate or urinary tract infections, urinary catheter use, unprotected sexual activity, and stress.
Symptoms of Prostatitis
There are many symptoms of prostatitis which may overlap with other urological conditions. Common symptoms include:
- Pain or discomfort in the pelvic region, lower abdomen, or lower back
- Frequent, urgent, or painful urination
- Painful ejaculation or sexual dysfunction
- Blood in the urine or semen
- Fever, chills, and general malaise
Diagnosis of Prostatitis
Diagnosing prostatitis requires a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional. The process may involve some or all of the following steps:
1. Medical History
The first step in diagnosing prostatitis is taking a detailed medical history. The physician will ask about the patient’s symptoms, duration, and any factors that may have triggered or worsened them. They will also inquire about the patient’s sexual history, urinary habits, and past medical conditions.
2. Physical Examination
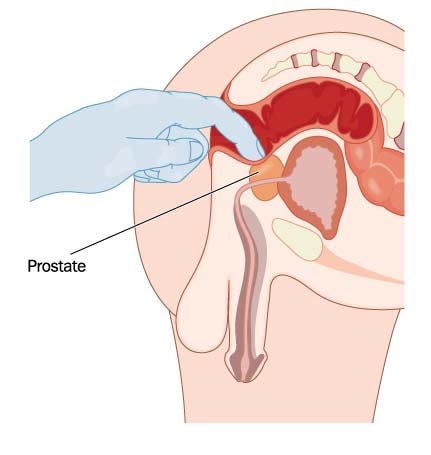
A physical examination is crucial in assessing the patient’s overall health and identifying any signs of prostatitis. The provider will palpate the prostate gland through the rectum (digital rectal exam) to check for tenderness, swelling, or abnormalities. While this part of the examination may be uncomfortable, it is a vital diagnostic tool.
3. Urine Sample Analysis
A urinalysis checks for white blood cells, red blood cells, and bacteria in the urine. Elevated white blood cells in the urine may indicate an infection or inflammation in the urinary tract, including the prostate gland.
4. Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test
A PSA blood test may be ordered to measure the level of prostate-specific antigens in the blood. Elevated PSA levels can indicate various prostate conditions, including prostatitis. However, it is important to note that PSA levels can also be elevated due to other factors, such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostate cancer.
5. Prostate Fluid Analysis
The healthcare provider may order a prostate fluid analysis to be performed if they suspect bacterial prostatitis. This involves collecting a sample of prostatic fluid during the rectal examination. The fluid is then examined under a microscope to look for signs of infection, such as bacteria or white blood cells.
6. Imaging Studies
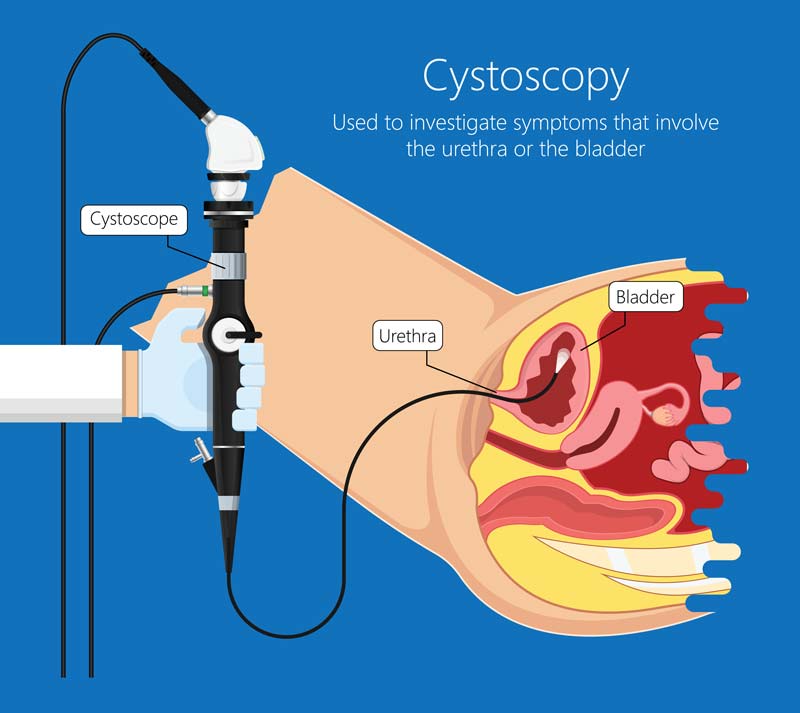
Imaging studies, such as transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may be recommended in certain cases. These tests allow for detailed visualization of the prostate gland and surrounding structures, helping the physician rule out other conditions and identify any abnormalities.
7. Urodynamic Studies
In some instances, urodynamic studies may be performed to assess how the bladder and urethra are functioning during urination. These tests help identify any issues with urine flow and bladder emptying, which may be helpful in diagnosing or ruling out prostatitis.
8. Cultures and Tests for Other Infections
If bacterial prostatitis is suspected, cultures of urine, prostatic fluid, or semen may be done to identify the specific bacteria responsible for the infection. Additionally, tests for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) may be conducted if relevant risk factors are present.
9. Rule Out Other Conditions
Prostatitis symptoms can sometimes mimic those of other urological or pelvic conditions. The urologist will also work to rule out conditions such as urinary tract infections, urinary stones, interstitial cystitis, and prostate cancer.
Treatment Options
The treatment approach for prostatitis depends on the type and severity of the condition. It may involve a combination of the following:
1. Antibiotics
Antibiotics are prescribed for bacterial prostatitis to eliminate the infection. The choice of antibiotics depends on the specific bacteria involved and their susceptibility to different medications. This is determined by performing a culture and sensitivity test on the bacteria causing the infection.
2. Alpha-Blockers
Alpha-blockers are medications that help relax the muscles in the prostate and bladder neck, reducing urinary symptoms such as frequent urination and pain during urination.
3. Anti-Inflammatory Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can provide relief from pain and inflammation associated with prostatitis.
4. Physical Therapy
Pelvic floor physical therapy may be recommended for patients with CP/CPPS to help relax and strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, which can alleviate pain and improve urinary function.
5. Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes such as stress reduction techniques, regular exercise, and avoiding irritants like caffeine and alcohol can help manage symptoms, especially from CP/CPPS.