Hybrid Pear Tree
- September 21, 2023
- 0 comment
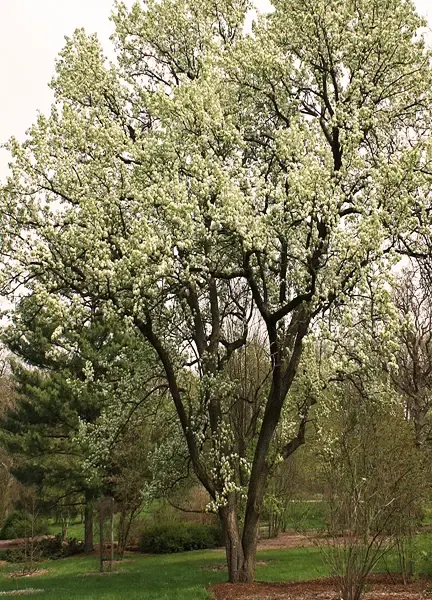

- Common Name: Hybrid Pear Tree
- Botanical Name: Pyrus x hybrida
- Family: Rosaceae
- Plant Type: Deciduous fruit tree
Lumber
Hybrid Pear trees are not primarily grown for lumber production, but they can provide some usable wood. The wood is moderately hard and can be used for small woodworking projects.

Mature Size and Growth Rate
Hybrid Pear trees typically reach a height of 20 to 40 feet (6 to 12 meters) and have a spread of 15 to 30 feet (4.5 to 9 meters). They have a moderate growth rate, with most varieties reaching maturity in 5 to 7 years.
Soil Type
Hybrid Pear trees exhibit a preference for well-draining soil, a characteristic crucial for their optimal growth and development. This preference for well-draining soil is rooted in their need for aeration around the root system. When soil drains effectively, it prevents waterlogged conditions that can lead to root rot and other fungal diseases. This adaptation to well-draining soil is vital for these trees, as it ensures that their root systems have access to both water and oxygen, promoting nutrient uptake and overall tree vigor.


Soil Preferences
Hybrid Pear trees demonstrate a remarkable adaptability to a variety of soil types, but they truly thrive in soils that range from slightly acidic to slightly alkaline on the pH scale. This adaptability allows them to flourish in diverse geographical locations, making them a popular choice for orchards and home gardens alike. The preference for soils within this pH range optimizes nutrient availability to the tree’s roots, enhancing nutrient uptake efficiency. While they can grow in other soil types, such as sandy or clayey soils, they particularly favor loamy soils due to their balanced composition of sand, silt, and clay. Loamy soils offer a perfect blend of water retention, drainage, and nutrient-holding capacity, creating an ideal environment for Hybrid Pear trees to reach their full potential.
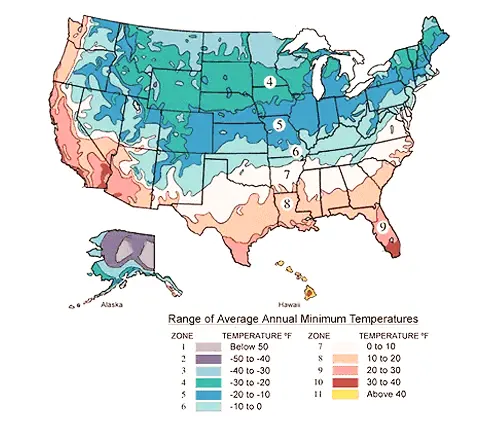
Hardiness Zone
Hybrid Pear trees are hardy in USDA Zones 4-9, although specific varieties may have slightly different zone preferences.
Sun Preference
They prefer full sun, requiring at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily to produce abundant fruit.
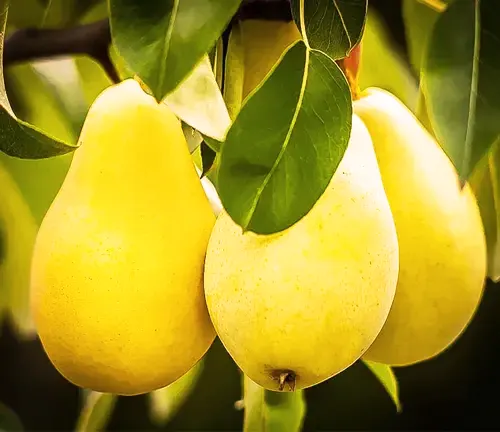

Attributes and Characteristics
Hybrid Pear trees offer a delightful blend of features. They produce sweet and juicy fruit with diverse flavors and textures, ideal for fresh eating, canning, and cooking. In spring, the trees adorn themselves with clusters of white or pink flowers, adding to their visual appeal. Additionally, their oval-shaped, glossy green leaves transition to vibrant yellow, orange, or red in the fall, creating a seasonal spectacle.
Wildlife Value
Hybrid Pear trees provide valuable food sources for wildlife such as deer, squirrels, and various bird species. The flowers attract pollinators like bees and butterflies.
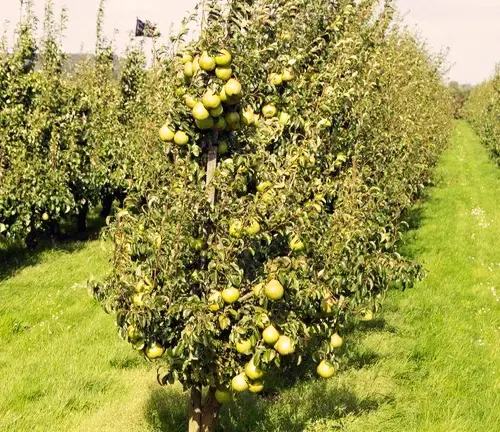

Care
Proper care includes regular pruning to maintain shape and improve fruit production, adequate watering, and protection from pests and diseases.
Benefits
- Fruit Production: Hybrid Pear trees yield delicious and versatile fruit that can be enjoyed fresh or used in various culinary applications.
- Ornamental Value: These trees offer aesthetic appeal with their spring blooms and fall foliage.
- Wildlife Attraction: Attract beneficial wildlife to your garden while providing a food source for them.
Invasive
Hybrid Pear trees are not considered invasive in most regions. However, some self-seeding may occur.
Lifespan
Under proper care, Hybrid Pear trees can live for 20-50 years, depending on the variety and environmental conditions.
Disadvantages
Hybrid Pear trees come with certain challenges, notably their susceptibility to diseases like fire blight, apple scab, and pear psylla, necessitating consistent monitoring and care to prevent and manage these issues. Moreover, the tree’s maintenance, including pruning to shape and manage growth, can be time-intensive, particularly as it matures, demanding dedication from caretakers.
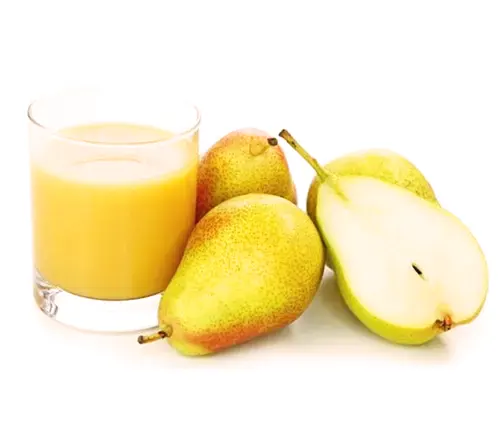

Edible or Not
The fruit of Hybrid Pear trees is edible and highly sought after for its sweet, juicy flavor.
Name of Origin
Hybrid Pear trees are the result of crossbreeding different pear species. They have been cultivated for centuries, with origins dating back to China and Europe.
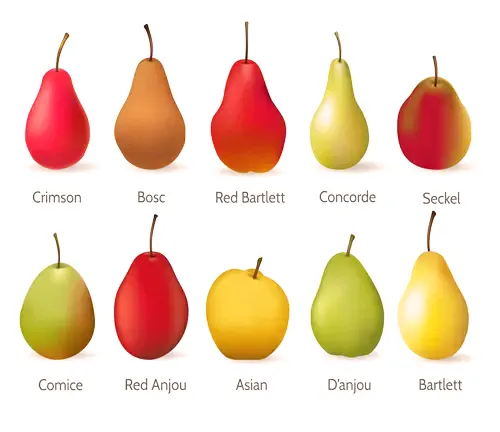

Varieties
There are numerous pear varieties within the hybrid category, including Bartlett, Anjou, Bosc, and Comice, each with its distinct characteristics.
Pruning
Regular pruning is necessary to maintain tree shape, remove dead or diseased branches, and promote fruit production. Prune during the dormant season to minimize stress on the tree.
Propagating
Hybrid Pear trees are typically propagated through grafting or budding onto rootstock. This ensures the desired characteristics of the parent tree are passed on to the new tree.

Common Pests & Diseases
Hybrid Pear trees face common pest issues like aphids, pear psylla, and codling moths, requiring regular inspection and pest control measures. They are also susceptible to diseases such as fire blight, apple scab, and pear rust, which can be managed with proper care like routine pruning and opting for disease-resistant varieties.y.
Experience the distinction today by exploring our array of Forestry Services. Don’t overlook the chance to enhance your experience!
Fun Facts
- The pear is one of the world’s oldest cultivated fruits, with evidence of cultivation dating back over 4,000 years.
- Pear wood has been used historically to make musical instruments, such as flutes and harps.
- The phrase “to go pear-shaped” originates from the pear’s tendency to develop a rounded bottom as it ripens, leading to its use as a metaphor for things going awry.
FAQs
- When is the best time to plant a Hybrid Pear tree?
The best time to plant these trees is in late winter or early spring when they are still dormant but the soil is workable. - How do I prevent diseases in my Hybrid Pear tree?
Regularly prune and provide proper air circulation. Choose disease-resistant varieties when possible and use organic or chemical treatments if necessary. - Do I need multiple pear trees for pollination?
Some pear varieties are self-pollinating, but having multiple trees can increase fruit production. Be sure to choose compatible pollinators if needed. - How long does it take for Hybrid Pear trees to bear fruit?
Most varieties will start bearing fruit in 3-5 years after planting, although this can vary depending on growing conditions and tree health.
In conclusion, Hybrid Pear trees offer a delightful addition to gardens and orchards, gracing them with sweet and juicy fruit, ornate spring blooms, and vibrant fall foliage. While they require diligent care to combat pests and diseases, their versatility and beauty make them a valuable asset for fruit enthusiasts and landscape lovers alike. With proper attention, these trees can thrive and provide years of delicious harvests and aesthetic charm.





Leave your comment