13. Entry to be registered: (1) A person, firm or company importing a motor vehicle from abroad shall make an application to the police office situated in the place of entry of such a motor vehicle into Nepal for the registration of entry of such a motor vehicle.
(2) If an application is made for the registration of entry pursuant to Sub-section (1), the police office shall, upon examining the evidence of purchase of such a motor vehicle and the related documents, register the entry of such a motor vehicle for fifteen days and give a certificate of the entry registration to the person, firm or company having imported such a motor vehicle, and send the description of such a motor vehicle to the concerned Transport Management Office promptly.
14. Motor vehicle to be registered: (1) A person, firm or company purchasing a motor vehicle or importing it from abroad or an agent selling or distributing a motor vehicle shall get the motor vehicle registered with the competent authority no later than fifteen days after the date of bringing it into Nepal upon paying customs duty. (2) No one shall ply or cause to be plied any motor vehicle without getting it registered pursuant to Sub-section (1).
15. Application to be made for the registration of motor vehicle: (1) If a motor vehicle is required to be registered pursuant to Section 14, a person, firm or company or agent who has purchased the motor vehicle shall, where such a motor vehicle has been purchased within Nepal, make an application, accompanied by the evidence of such purchase, and a person, firm or company or agent who has imported such a motor vehicle from abroad shall, where such a motor vehicle has been imported from aboard, make an application, accompanied by the evidence of payment of customs duty of that motor vehicle, and other related documents, to the competent authority in the prescribed format and accompanied by the prescribed fees. Provided that, no registration fee shall be levied for the registration of a motor vehicle with diplomatic facility.
(2) A person who makes an application pursuant to Sub-section (1) shall attach with the application a certified copy of the certificate ofcitizenship of Nepal and his or her three passport size photographs recently taken.
(3) In the case of a governmental motor vehicle, the application shall also be accompanied by a letter of the governmental office in whose name the motor vehicle is going to be registered, and in the case of a motor vehicle with diplomatic facility, it shall also be accompanied by a recommendation letter of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the Government of Nepal. If a motor vehicle with diplomatic facility is to be registered in the name of any person, such a person shall attach a copy of his or her passport or citizenship and three passport size photographs.
(4) If a foreign citizen who carries on any business and transaction within the State of Nepal intends to get any motor vehicle registered for his or her personal use, a recommendation letter of the concerned diplomatic mission shall also be attached, in addition to the matters set forth in Subsections (1) and (2).
(5) If a motor vehicle is required to be registered in the name of a minor, his or her guardian shall, on his or her behalf, make an application, accompanied by three passport size photographs each of the minor and the guardian and a certified copy of citizenship.
16. Motor vehicle registration certificate: (1) If an application is made for the registration of any motor vehicle pursuant to Section 15, the competent authority shall make necessary inquiry into the matter, register such a motor vehicle in the name of the applicant and issue the registration certificate in the form as referred to in Schedule-3. Provided that, any motor vehicle with more than fourteen seats and with gross weight of four tons or more shall not be registered as a private motor vehicle except in the name of a national or international organization
established with social, religious, benevolent and educational purpose or a body corporate established under the laws in force.� (2) In registering a motor vehicle in the name of a minor, the motor vehicle registration certificate shall also contain the guardian’s name and be signed by the guardian, as well. (3) The registration certificate shall contain the total laden weight of a motor vehicle as specified in the technical specification of the motor vehicle issued by its manufacturer as the weight of that motor vehicle; and in so specifying the weight of the motor vehicle, the unladen weight and the laden weight must be separately and clearly specified. (4) The registration certificate shall remain valid for a period of one year after the date of its issuance.
17. Road worthiness certificate to be issued: (1) Prior to registering any motor vehicle pursuant to Section 16, the competent authority shall, subject to the criteria prescribed pursuant to Section 23, examine such a motor vehicle as to whether it is in good condition that it can be plied and register such a motor vehicle only when it is in good condition that it can be plied and issue the certificate of registration. In so issuing the certificate of registration, the certificate of road worthiness of such a motor vehicle shall also be issued to the owner of such a motor vehicle. (2) The road worthiness certificate issued pursuant to Sub-section (1) shall have to be affixed on the motor vehicle.
18. Joint registration: If an application is made by two or more persons to the competent authority pursuant to Section 15 for the joint registration of any motor vehicle, the competent authority shall make necessary inquiry into the matter, register such a motor vehicle jointly in the names of these persons and issue the registration certificate as referred to in Section 16 to them.
19. Provisional registration: Any motor vehicle may be registered provisionally in the following circumstance: (a) if there exists a reasonable reason for the failure of the importer of the motor vehicle to appear to get the motor vehicle registered within the time limit within which it is required to be registered; (b) if it is not possible to immediately produce the imported motor vehicle for registration due to defects in the engine, chassis or any other spare parts of the motor vehicle; or (c) if it is not possible to immediately register the motor vehicle due to the arising of an insurance claim dispute with the manufacturer company or sales agent of the motor vehicle or insurance company owing to the occurrence of the condition set forth in Clause (b).
20. Application for provisional registration: (1) If there occurs any circumstance set forth in Section 19, the importer of a motor vehicle or his or her nearest heir in his or her absence shall make an application, accompanied by the evidence of payment of customs duty of the motor vehicle and other relevant documents, in the prescribed format, along with the prescribed fees, to the competent authority for the provisional registration of the motor vehicle in the name of its importer. (2) In making an application pursuant to Sub-section (1), the applicant shall also attach a certified copy of the certificate of citizenship of Nepal and three copies of recently taken photograph of the person in whose name the motor vehicle is to be registered provisionally.
21. Provisional registration certificate: (1) If any person makes an application for the provisional registration of any motor vehicle pursuant to Section 20, the competent authority shall inquire into whether the motor vehicle can be registered provisionally pursuant to Section 19, register such a motor vehicle provisionally and issue the provisional registration certificate in the form as referred to in Schedule-4.
(2) The provisional registration certificate shall also specify that the word provisional is also to be set down in the number plate of that motor vehicle. (3) The provisional registration certificate may be so issued that it remains valid for a maximum period of six months at one time or at several times.
22. � Motor vehicle to be produced: In making application for the registration of a motor vehicle pursuant to Section 13, 15 or 20, for the transmission of ownership of motor vehicle pursuant to Section 37 and for the alteration in any matter of motor vehicle pursuant to Section 39, the person, firm or company making such an application shall also produce the motor vehicle intended to be so registered, transmitted or altered in any respect.
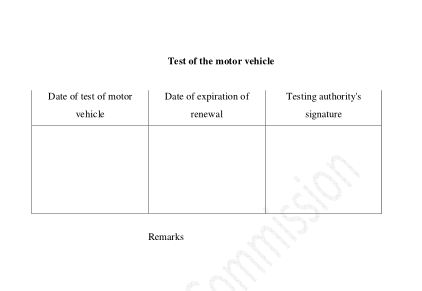
23. Power to specify criteria for examination of motor vehicles: (1) The Government of Nepal may determine and prescribe necessary criteria on the following matters in order to examine and ascertain whether a motor vehicle is capable of being plied: (a) Mechanical condition of the motor vehicle. (b) Length, breadth, height, structure and body of the motor vehicle. (c) Pollution likely to be generated from the motor vehicle. (d) Period during which the motor vehicle can be plied. (2) In issuing the road worthiness certificate after examining whether a motor vehicle is capable of being plied or issuing the test certificate, the competent authority shall make examination subject to the criteria prescribed pursuant to Sub-section (1).
24. Power to refuse to register motor vehicle: (1) If an application is made for the registration of a motor vehicle, and if upon examining, subject to the criteria as specified in Section 23, whether the motor vehicle is capable of being plied, the competent authority considers that such a motor vehicle is not capable of being plied, the competent authority may refuse to register such a motor vehicle.
(2) If it is refused to register any motor vehicle pursuant to Subsection (1), the competent authority shall give a notice thereof, accompanied by the reason for such refusal, to the applicant.
(3) Notwithstanding anything contained in Sub-sections (1) and (2), if the Department is of the opinion that it is reasonable to stop the registration of any type of motor vehicle to be made under Section 14 for public interest owing to environmental pollution, traffic load, condition of roads, difficulty with vehicular movement or similar other reasons, it may issue an order to any or all Transport Management Offices to stop the registration of such a motor vehicle.
25. Validity of registration: (1) A motor vehicle registered in any one region pursuant to this Act may also be plied in another region.
(2) Notwithstanding anything contained in Sub-section (1), a motor vehicle registered in any one region shall not be allowed to be plied in another region for more than one year consecutively or at several times. Provided that, this restriction shall not apply to a governmental motor vehicle, corporation motor vehicle, motor vehicle with diplomatic facility and motor vehicle with route permit.
26. Information to be given: (1) If a motor vehicle registered in one region enters another region, the owner or driver of the motor vehicle, as the case may be, shall give information thereof to the nearby police office no later than twenty four hours of such entry. (2) If it is required to ply a motor vehicle having entered pursuant to Sub-section (1) for more than thirty days in that region, the owner or driver of the motor vehicle, as the case may be, shall have to obtain permission from the competent authority no later than seven days of the entry into that region.
27. Transfer registration: (1) If it is required to ply a motor vehicle in a region other than the region in which it has been registered for more than the period as set forth in Sub-section (2) of Section 25, the owner of the motor vehicle shall make an application, accompanied by the registration certificate, three recently taken passport size photographs of him or her and prescribed fees, to the competent authority for the registration of transfer. (2) If an application referred to in Sub-section (1) is made and the competent authority, upon making examination of such a motor vehicle subject to the criteria specified pursuant to Section 23, considers it appropriate to make transfer registration, the competent authority shall register the transfer of that motor vehicle and give the registration certificate to the owner of that vehicle.
28. Records of motor vehicle to be maintained: The competent authority shall cause the details of each motor vehicle registered pursuant to this Act, including the name and address of owner, date of registration, and registration number, of the motor vehicle, name of motor vehicle manufacturer, model, year, engine number, chassis number, type and weight of the motor vehicle to be clearly mentioned in the register and maintain records of motor vehicles in an updated manner. The photograph of the owner of the motor vehicle must also be affixed on the concerned page of such a register.
29. Prohibition on plying foreign motor vehicle without obtaining permission: No motor vehicle registered abroad shall be plied within the State of Nepal without obtaining permission pursuant to the laws in force.
30. Permission to ply foreign motor vehicle: If an application is made for permission to ply a motor vehicle registered abroad within the State of Nepal, the competent authority may, upon collection of the prescribed fees, give permission to ply that motor vehicle for a period not exceeding one month. Provided that, such a motor vehicle must not be permitted to operate the transport service within the State of Nepal.
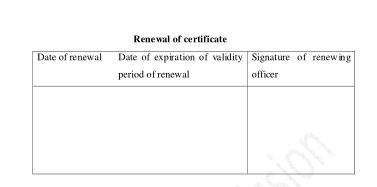
31. Renewal of registration certificate: (1) The registration certificate shall have to be got renewed within three months of the expiration of the time limit set forth in the registration certificate pursuant to Sub-section (4) of Section 16.
(2) The owner of a motor vehicle or a person deputed by him or her shall have to submit the registration certificate, accompanied by the prescribed fees, to the competent authority for the renewal of the registration certificate pursuant to Sub-section (1). Provided that, no fee shall be charged for the renewal of the registration certificate of a motor vehicle with diplomatic facility. (3) If the registration certificate is submitted for renewal pursuant to Sub-section
(2), the competent authority shall have to renew such a registration certificate for other one year.
(4) If the owner of a motor vehicle shows up for the renewal of the registration certificate after the expiration of the time limit referred to in Subsection (1), such a registration certificate shall have to be renewed by collecting from such an owner one hundred percent fees until one year of the expiration of the time limit, two hundred percent fees until two years, three hundred percent fees until three years, four hundred percent fees until four years and five hundred percent fees until five years, in addition to the renewal fees.
32. Power of the competent authority to notify: If the registration certificate of a motor vehicle with diplomatic facility is not submitted for renewal within the period as referred to in Sub-section (1) of Section 31, the competent authority may notify the concerned diplomatic mission, office or person, through the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, to get renewed the registration certificate of such a motor vehicle.
33. Special provision relating to renewal: Notwithstanding anything contained in Sub-section (3) of Section 31, if the owner of a governmental motor vehicle, corporation motor vehicle, motor vehicle with diplomatic facility and private motor vehicle intends to get the registration certificate of his or her motor vehicle renewed for five years at a time and submits the registration certificate, accompanied by the renewal fees chargeable for five years, the competent authority may renew such a registration certificate for five years at a time.
34. Ipso facto revocation of registration certificate: (1) A registration certificate which has not been renewed even within the period as referred to in Sub-section (4) of Section 31 shall ipso facto be revoked. (2) The records of the motor vehicle of which registration certificate has been revoked pursuant to Sub-section (1) shall be crossed off the register. (3) The registration certificate of which records have already been crossed off the register pursuant to Sub-section (2) shall not be renewed.
35. Eligibility for re-registration: If a motor vehicle of which registration certificate has been revoked and records crossed off pursuant to Section 34 is produced for re-registration, such a motor vehicle shall be registered pursuant to Section 16 and another registration certificate shall be given to the motor vehicle owner, by collecting the renewal fees due to be collected pursuant to Section 31 and additional fees as well as a fine that is two-fold of the additional fees referred to in Sub-section (4) of Section 31 for the years after which it has been produced for registration.
36. Information of change in address of motor vehicle owner to be given: (1) In the event of a change in the address of the owner of any motor vehicle registered pursuant to this Act, information thereof, accompanied also by the registration certificate, shall have to be given to the competent authority within one month. (2) Upon receipt of the information as referred to in Sub-section (1), the competent authority shall mention the new address in the registration certificate and also make necessary correction in the register.
37. Transmission of motor vehicle: (1) If the owner of a motor vehicle registered pursuant to this Act transfers his or her ownership in that vehicle to any other person by way of gift or sale or otherwise, the owner shall have to make an application in the prescribed format, accompanied also by the registration certificate and a proof of payment of the motor vehicle tax, to the competent authority for the transmission of that motor vehicle, no later than fifteen days.
(2) The heir whom the ownership in a motor vehicle has to be transmitted to as a consequence of the death of the owner of the motor vehicle shall have to make an application in the prescribed format, accompanied also by an evidence of the death of the owner of the motor vehicle, the registration certificate, a proof of payment of the motor vehicle tax and an evidence proving that he or she is the nearest heir, to the competent authority for the transmission of that motor vehicle, no later than thirty five days after the death of the owner of the motor vehicle.
(3) If an application is made for transmission pursuant to Sub-section (1) or (2), the competent authority shall hold necessary inquiry into the matter and make transmission by indicating the matter of transmission in the registration certificate, and collecting the prescribed fees. Provided that, if an application is made by more than one heir on the equal footing for transmission pursuant to Sub-section (2), the transmission must be made by jointly registering that motor vehicle in the names of all the heirs.
(4) In the event of the transmission of a motor vehicle pursuant to Sub-section (3), the matter that transmission has been made upon the transfer of ownership accordingly must be mentioned in the register. (5) If, in making inquiry in the course of transmitting a motor vehicle pursuant to this Section, the competent authority finds that there is any lawsuit pending as to the title to the motor vehicle, that motor vehicle must not be transmitted to the name of any one pending the final settlement of such a lawsuit.
38. Prohibition on changing registration: Notwithstanding anything contained elsewhere in this Act, the registration certificate must not be issued in such a manner as to change the registration of a motor vehicle having obtained the registration certificate upon being registered as a goods motor vehicle into a passenger motor vehicle.
39. Prohibition on alteration without obtaining approval:
(1) The owner of a motor vehicle owner shall not make any such alteration in the motor vehicle as to change its color, number of seats, � structure, engine or chassis, without obtaining approval of the competent authority. Provided that this Sub-section shall not be deemed to prevent the making of a normal change of spare parts in a motor vehicle.
(2) If a request is made for approval to make an alteration pursuant to Sub-section (1), the competent authority shall make necessary inquiry into the matter, and may, if it thinks appropriate to give approval for such an alteration, give such an approval. Provided that, no approval shall be so given as to change the specification made by the motor vehicle manufacturing company in relating to the structure of the motor vehicle.⊗
(2a)⊗ In giving approval for alteration pursuant to Sub-section (2), there shall be charged the fee which is fifty percent of the fees chargeable for the registration of the motor vehicle.
40. Power to suspend registration certificate:
(1) The competent authority may, in any of the following circumstances, issue an order suspending the registration certificate of any motor vehicle for a period not exceeding the following period:
(a) If it appears that the plying of a motor vehicle may cause a loss of or damage to the body or property of the general public because the motor vehicle is out of order, for a period until the motor vehicle is repaired and maintained satisfactorily, and
(b) If the owner of motor vehicle plies the motor vehicle without fulfilling any terms required to be fulfilled under this Act or any order issued by the competent authority subject to this Act or the ambit of Rules framed under this Act, for a period not exceeding six months.
(2) In issuing an order to the owner of motor vehicle, thereby suspending the registration certificate pursuant to Sub-section (1), the competent authority shall also clearly assign the reason for such suspension.
(3) In the event of suspension of the registration certificate pursuant to Sub-section (1), the competent authority shall have to give information thereof to the concerned police office.
(4) In the event of suspension of the registration certificate pursuant to Sub-section (1), the owner of motor vehicle shall have to surrender the registration certificate to the competent authority no later than seven days of the order issued by the competent authority.
(5) The competent authority shall have to return the registration certificate surrendered by the owner of motor vehicle pursuant to Sub-section (4) after the expiration of the period of suspension of the registration certificate. (6) In returning the registration certificate to the owner of motor vehicle pursuant to Sub-section (5), the competent authority shall cause to be clearly specified the period of suspension and the reason for suspension in the registration certificate and the records thereof to be mentioned also in the register.
41. Revocation of registration certificate: (1) If any motor vehicle registered pursuant to this Act is destroyed in any manner or becomes out of order as not being capable of plying or taken outside Nepal permanently, the owner of such a motor vehicle shall have to make an application, in the prescribed format, accompanied by the registration certificate, to the competent authority for crossing off the records of such a motor vehicle no later than thirty days. Provided that, if it is required to take outside Nepal any motor vehicle which is important archaeologically or any spare parts of such a motor vehicle, its owner shall have to obtain prior approval of the competent authority. (2) If an application as referred to in Sub-section (1) is made, the competent authority shall, if the contents are found true upon necessary inquiry made into the matter, revoke such a registration certificate, mention that matter in the register and cross off the record of such a motor vehicle.
42. Remission of renewal fees: If any motor vehicle registered pursuant to this Act is not capable of plying or being plied for a period exceeding one year because of being seized for any reason or being out of order due to an accident or otherwise and the owner of motor vehicle makes an application setting out that matter, accompanied by the registration certificate and an evidence thereof, the competent authority may seize the registration certificate of such a motor vehicle and remit the renewal fees required to be paid by that motor vehicle owner� for a period until the motor vehicle becomes capable of being plied.
43. Issuance of duplicate copy of registration certificate: (1) If the registration certificate is lost or illegible because of being torn or defaced or is destroyed in any other manner, the owner of motor vehicle shall have to make an application, in the prescribed format, accompanied by the prescribed fees, to the competent authority no later than fifteen days after the date of such loss, illegibility or destroy. (2) If the contents are found correct upon necessary examination made in relation to the application made pursuant to Sub-section (1), the competent authority shall have to issue a duplicate copy of such a registration certificate to the owner of motor vehicle. (3) The competent authority shall give information of the issuance of a duplicate copy of the registration certificate pursuant to Sub-section (2) to the concerned police office.
44. Details to be submitted: (1) Any firm, company or agent who imports motor vehicles from abroad shall have to submit the details of the model, engine number, chassis number of each motor vehicle, the type of and name of manufacturer of such a motor vehicle, and also indicating which of such motor vehicles has been sold to whom and when and how many of the motor vehicles imported by him or her are in stock, to the competent authority each month.
(2) The competent authority may demand any other necessary details and documents relating to the import and sale and distribution of motor vehicles, in addition to the details set forth in Sub-section (1) from any firm, company or agent who imports motor vehicles from abroad. It shall be the duty of such a firm, company or agent to provide the details and documents so demanded immediately.