Abstract
Key message
This paper describes the development of monosomic alien addition and disomic introgression lines through a cross between autotetraploid indica rice and Oryza punctata toward tapping valuable traits for rice improvement.
Abstract
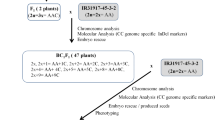
Oryza punctata is a distantly related wild Oryza species having BB genome with untapped genetic resources for rice improvement. Low crossability between the cultivated O. sativa and O. punctata restricts the success of transferring many desirable traits into cultivated rice. Artificially induced autotetraploids of an elite breeding line, IR31917-45-3-2, were produced and crossed with O. punctata. Allotriploid F1 plants were backcrossed to IR31917-45-3-2 and generated progenies with extra chromosomes from O. punctata. Twenty BC1F1 and 59 BC2F1 plants were produced with chromosome numbers ranging from 24 (2n) to 29 (2n + 5) and 2n (24) to 26 (2n + 2), respectively. Eleven monosomic alien addition lines (MAALs) were characterized morphologically and cytologically and designated as MAAL 1–12. MAALs were genotyped using O. punctata genome-specific molecular markers and detected chromosome segments inherited from O. punctata. O. punctata introgressions across all the chromosomes of O. sativa were identified except for chromosome 8. The most frequent introgressions were observed in chromosomes 4, 6, 10, and 11, which could be the recombination hotspots between A and B genomes. Some of the qualitative traits such as black hull, purple coleoptile base, purple stigma, long awn, and short grain size from O. punctata were inherited in some disomic introgression lines (DILs). Several DILs inherited genes from O. punctata conferring resistance to brown planthopper, green leafhopper, and diseases such as bacterial blight and blast. This is the first report on successful gene transfer from O. punctata into O. sativa.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amante-Bordeos A, Sitch LA, Nelson R, Dalmacio RD, Oliva NP, Aswindor H, Leung H (1992) Transfer of bacterial blight and blast resistance from the tetraploid wild rice Oryza minuta to cultivated rice, Oryza sativa. Theor Appl Genet 84:345–354
Ammiraju JSS, Lu F, Sanyal A, Yu Y, Song X, Jiang N, Pontaroli AC, Rombo T, Currie J, Collura K, Talag J, Fan C, Goicoechea JL, Zuccolo A, Chen J, Bennetzen JL, Chen M, Jackson S, Wing R (2008) Dynamic evolution of Oryza genomes is revealed by comparative genomic analysis of a genus-wide vertical data set. Plant Cell 20:3191–3209
Ammiraju JS, Song X, Luo M, Sisneros N, Angelova A, Kudrna D, Kim H, Yu Y, Goicoechea JL, Lorieux M, Kurata N, Brar D, Ware D, Jackson S, Wing RA (2010) The Oryza BAC resource: a genus-wide and genome scale tool for exploring rice genome evolution and leveraging useful genetic diversity from wild relatives. Breed Sci 60:536–543
Angeles-Shim R, Vinarao RB, Marathi B, Jena KK (2014) Molecular analysis of Oryza latifolia Desv. (CCDD genome)-derived introgression lines and identification of value-added traits for rice (O. sativa L.) improvement. J Hered 105:676–689
Arnold ML (2004) Transfer and origin of adaptations through natural hybridization. Plant Cell 16:562–570
Asaga K (1981) A procedure for evaluating field resistance to blast in rice varieties. J Cent Agric Exp Stn 35:51–138
Bamberg JB, Hanneman RE, Palta JP, Harbage JF (1994) Using disomic 4x (2EBN) potato species germplasm via bridge species Solanum commersonii. Genome 37:866–870
Chen M, Presting G, Barbazuk WB, Goicoechea JL, Blackmon B, Fang G, Kim H, Frisch D, Yu Y, Sun S et al (2002) An integrated physical and genetic map of the rice genome. Plant Cell 14:537–545
Chen Y, Wang Y, Wang K, Zhu X, Guo W, Zhang T, Zhu B (2014) Construction of a complete set of alien chromosome addition lines from Gossypium australe in Gossypium hirsutum: morphological, cytological, and genotypic characterization. Theor Appl Genet 127:1105–1121
Cheng Y, Fang S, Lin Y, Chung M (2007) A repetitive sequence specific to Oryza species with BB genome and abundant in Oryza punctata Kotschy ex Steud. Bot Stud 48:263–272
Delourme R, Foisset N, Horvais R, Barret P, Champagne G, Cheung WY, Landry BS, Renard M (1998) Characterization of the radish introgression carrying the Rfo restorer gene for the Ogu-INRA cytoplasmic male sterility in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 97:129–134
Du B, Zhang W, Lui B, Hu J, Wei Z, Shi Z, He R, Zhu L, Chen R, Han B, He G (2009) Identification and characterization of Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to brownhopper in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci Biol 106:22163–22168
Frankel OM, Brown AHD, Burdon JJ (1995) The conservation of plant biodiversity. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
IRRI (1996) Standard evaluation system for rice, 4th edn. International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños
Jena KK (2010) The species of the genus Oryza and transfer of useful genes from wild species into cultivated rice O. sativa. Breed Sci 60:518–523
Jena KK, Khush GS (1989) Monosomic alien addition lines of rice: production, morphology, cytology and breeding behavior. Genome 32:449–455
Jena KK, Khush GS (1990) Introgression of gene from Oryza officinalis Well ex Watt to cultivated rice O. sativa L. Theor Appl Genet 80:737–745
Jena KK, Multani DS, Khush GS (1991) Monosomic alien addition lines of Oryza australiensis and alien gene transfer. In: Rice genetics II. International Rice Research Institute, Philippines, p 728
Jena KK, Kochert G, Khush GS (1992) RFLP analysis of rice (Oryza sativa L.) introgression lines. Theor Appl Genet 84:608–616
Jena KK, Jeung JU, Lee JH, Choi HC, Brar DS (2006) High-resolution mapping of a new brown planthopper (BPH) resistance gene, Bph18 (t), and marker-assisted selection for BPH resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 112:288–297
Kauffman HE, Reddy APK, Hsieh SPY, Merca SD (1973) An improved technique for evaluating resistance of rice varieties to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Plant Dis Rep 57:537–541
Khush GS (1973) Cytogenetics of aneuploids. Academic Press, New York
Khush GS (1979) Genetics and breeding for resistance to brown planthopper. In: International Rice Research Institute (ed) Brown planthopper: threat to rice production in Asia. International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, pp 321–332
Khush GS (2005) What it will take to feed 5.0 billion rice consumers in 2030. Plant Mol Biol 59:1–6
Khush GS (2010) Trisomics and alien addition lines in rice. Breed Sci 60:469–474
Kim HR, San Miguel P, Nelson W, Collura K, Wissotski M, Walling JG, Kim JP, Jackson SA, Soderlund C, Wing RA (2007) Comparative physical mapping between Oryza sativa (AA genome type) and O. punctata (BB genome type). Genetics 176:379–390
Kim SM, Suh JP, Qin Y, Noh TH, Reinke RF, Jena KK (2015) Identification and fine-mapping of a new resistance gene, Xa40, conferring resistance to bacterial blight races in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 128:1933–1943
Kole C (2011) Wild crop relatives: genomics and breeding resources: plantation and ornamental crops. Springer, Germany
Kurokawa Y, Noda T, Yamagata Y, Angeles-Shim R, Sunohara H, Uehara K, Furuta T, Nagai K, Jena KK, Yasui H, Yoshimura A, Ashikari M, Doi K (2016) Construction of a versatile SNP array for pyramiding useful genes of rice. Plant Sci 242:131–139
Liu GQ, Yan HH, Fu Q, Qian Q, Zhan ZT, Zhai WX, Zhu LH (2001) Mapping of a new gene for brown planthopper resistance in cultivated rice introgressed from Oryza eichingeri. Chin Sci Bull 46:1459–1462
Lukaszewski AJ (1995) Physical distribution of translocation breakpoints in homeologous recombinants induced by the absence of the Ph1 gene in wheat and triticale. Theor Appl Genet 90:714–719
Marathi B, Ramos J, Hechanova SL, Oane RH, Jena KK (2015) SNP genotyping and characterization of pistil traits revealing a distinct phylogenetic relationship among the species of Oryza. Euphytica 201:131–148
Mezard C (2006) Meiotic recombination hotspots in plants. Biochem Soc Trans 34(4):531–534
Multani DS, Khush GS, de los Reyes BG, Brar DS (2003) Alien gene introgression and development of monosomic alien addition lines from Oryza latifolia Desv. to rice O. sativa L. Theor Appl Genet 107:395–405
Qiu Y, Guo J, Jing S, Zhu L, He G (2012) Development and characterization of japonica rice lines carrying the brown planthopper-resistance gene BPH12 and BPH6. Theor Appl Genet 124:485–494
Rahman ML, Jiang W, Chu SH, Qiao Y, Ham TH, Woo MO, Lee J, Khanam MS, Chin JH, Jeung JU, Brar DS, Jena KK, Koh HJ (2009) High-resolution mapping of two rice brown planthopper resistance genes, Bph20 (t) and Bph21 (t), originating from Oryza minuta. Theor Appl Genet 119:1237–1246
Renganayaki L, Fritz AK, Sadasivam S, Pammi S, Harrington SE, McCouch SR, Kumar SM, Reddy AS (2002) Mapping and progress toward map-based cloning of brown planthopper biotype-4 resistance gene introgressed from Oryza officinalis into cultivated rice, O. sativa. Crop Sci 42:2112–2117
Sanchez PL, Wing RA, Brar DS (2013) The wild relatives of rice: genomes and genomics. In: Zhang Q, Wing RA (eds) Genetics and genomics of rice. Plant genetics and genomics. Springer, New York, pp 9–26
Singh RJ, Nelson RL (2015) Intersubgeneric hybridization between Glycine max and G. tomentella: production of F1, amphidiploid, BC1, BC2, BC3, and fertile soybean plants. Theor Appl Genet 128:1117–1136
Suh JP, Jeung JU, Noh TH, Cho YC, Park SH, Park HS, Shin MS, Kim CK, Jena KK (2013) Development of breeding lines with three pyramided resistance genes that confer broad-spectrum bacterial blight resistance and their molecular analysis in rice. Rice 6:5
Tan GX, Wang QM, Ren X, Huang Z, Zhu LL, He GC (2004) Two whitebacked planthopper resistance genes in rice share the same loci with those of brown planthopper resistance. Heredity 92:212–217
Tateoka T (1962) Taxonomic studies of Oryza II. Several species complexes. Bot Mag 75:455–461
Vaughan DA (1989) The genus Oryza L. current status of taxonomy, IRRI Res Paper Sr 138. International Rice Research Institute, Manila
Vaughan DA (1994) The wild relatives of rice. A genetic resources handbook. IRRI, Manila
Wang YM, Dong ZY, Zhang ZJ, Lin XY, Shen Y, Zhou D, Liu B (2005) Extensive de novo genomic variation in rice induced by introgression from wild rice (Zizania latifolia Griseb.). Genetics 170:1945–1956
Wang X, Wu R, Lin X, Bai Y, Song C, Yu X, Xu C, Zhao N, Dong Y, Liu B (2013) Tissue culture-induced genetic and epigenetic alterations in rice pure-lines, F1 hybrids and polyploids. BMC Plant Biol 13:77
Wu J, Machara T, Shimokawa T, Yamamoto G, Harada C, Takazaki Y, Ono N, Mukai Y, Koike K, Yazaki J et al (2002) A comprehensive rice transcript map containing 6591 expressed sequence tag sites. Plant Cell 14:525–535
Wulff BBH, Moscou M (2014) Strategies for transferring resistance into wheat: from wide crosses to GM cassettes. Front Plant Sci 5:692. doi:10.3389/fpls.2014.00692
Yang HY, You AQ, Yang ZF, Zhang F, He RF, Zhu LL, He GG (2004) High resolution genetic mapping at the Bph15 locus for brown planthopper resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 110:182–191
Yasui H, Iwata N (1991) Production of monosomic alien addition lines of Oryza sativa having a single O. punctata chromosome. In: Rice genetics II. International Rice Research Institute, Philippines. pp 147–155
Yoshida S, Forno DA, Cock JH, Gomez KA (1976) Laboratory manual for physiological studies of rice. International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos
Yu J, Herrmann M (2006) Inheritance and mapping of a powdery mildew resistance gene introgressed from Avena macrostachya in cultivated oat. Theor Appl Genet 113:429–437
Zeigler RS (2014) Food security, climate change and genetic resources. In: Jackson M, Ford-Lloyd B, Parry M (eds) Plant genetic resources and climate change. CAB International, UK, pp 1–15
Zhao Q, Zhang Y, Cheng Z et al (2002) A fine physical map of the rice chromosome 4. Genome Res 12:817–823
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Mr. Patricio Carandang, Mr. Eleazar Manalaysay, and Ms. Janice Sapin for providing excellent technical assistance during the experiment. We thank Dr. Sung-Ryul Kim for assisting in Indel marker development through comparative sequence analysis. We thank the editorial team of IRRI Communication for an accurate editing of the manuscript. We are grateful to the Global Rice Science Partnership (GRiSP) program (Grant No. DRPC 2011-134) for financial support to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest in this study.
Additional information
Communicated by L. Jiang.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
122_2016_2745_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Fig. S1 Physical map of O. punctata-specific 111 markers designed for molecular detection of introgression (TIFF 552 kb)
122_2016_2745_MOESM2_ESM.pptx
Fig. S2 Detection of O. punctata segment in the resistant DILs using genome-specific markers. Banding pattern are as follows: P1-IR31917-45-3-2 (red arrow), P2- O. punctata (green arrow), Lanes 1-14 are DILs in BC2F4 generation, M - 100 bp DNA Ladder. Note the presence of O. punctata genome-specific allele (304 bp) in lanes 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 13 and 14; and 285 bp allele of O. sativa (IR31917-45-3-2) (PPTX 713 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jena, K.K., Ballesfin, M.L.E. & Vinarao, R.B. Development of Oryza sativa L. by Oryza punctata Kotschy ex Steud. monosomic addition lines with high value traits by interspecific hybridization. Theor Appl Genet 129, 1873–1886 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-016-2745-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-016-2745-8