Abstract
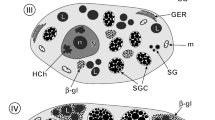
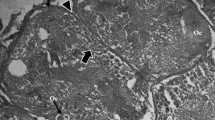
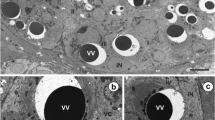
This study of the fish blood fluke Aporocotyle simplex represents the first detailed transmission electron microscopical (TEM) investigation of the vitellarium of an aporocotylid digenean blood fluke. It revealed some unusual characteristics in the cytoarchitecture of the vitelline follicles and demonstrated modifications of the vitelline granules for eggshell formation. The vitelline follicles consist of vitellocytes at different developmental stages surrounded by sarcoplasmic processes of myocytes which occur throughout each follicle. Sites of intimate contact occur between the vitellocytes and the myocytes. Individual vitelline globules (0.1–0.2 μm in diameter) accumulate in quite small clusters of 10–20 and have a dense, heterogeneous matrix possessing central and peripheral regions with a greater density. Modifications of the vitelline globules take place within the clusters and are first apparent when the vitellocytes reach the lumen of the vitelline duct and vitelline reservoir. Globules within the clusters become confluent, and, when the vitellocytes reach the lumen of the oviduct and proximal ootype, these consolidated clusters contain a shapeless, loosely packed, dense material which is released from the vitellocytes by exocytosis. This investigation has provided morphological evidence for shell formation from modified vitelline globules in the form of a discontinuous, thin layer (~ 0.07 μm in thickness) of electron-dense shell material around the fertilized ovum and associated vitellocytes in the proximal ootype. The eggshell of intra-uterine eggs acquires an additional thin, heterogeneous outer layer, increasing its thickness to ~ 0.1 μm. The cytoarchitecture of the vitellarium, modifications of the vitelline globules within the clusters and the structure of the eggshell of A. simplex may prove to be of value in studies examining relationships between the three distinct lineages of aporocotylid digeneans.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bullard SA, Overstreet RM (2008) Digeneans as enemies of fishes. In: Eiras JC, Segner H, Wahli T, Kapoor BG (eds) Fish diseases, Volume 2. Chapter 14. Science Publishers, Enfield, pp 817–976
Burton PR (1967) Fine structure of the reproductive system of a frog lung fluke. I Mehlis’ gland and associated ducts. J Parasitol 53:540–555. https://doi.org/10.2307/3276713
Colhoun LM, Fairweather I, Brennan GP (1998) Observations on the mechanism of eggshell formation in the liver fluke, Fasciola hepatica. Parasitology 116:555–567. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182098002662
Conn DB (1993) The biology of flatworms (Platyhelminthes): parenchyma cells and extracellular matrices. Trans Am Microsc Soc 112:241–261. https://doi.org/10.2307/3226561
Cribb TH, Chick RC, O’Connor W, O’Connor S, Johnson D, Sewell KB, Cutmore SC (2017) Evidence that blood flukes (Trematoda: Aporocotylidae) of chondrichthyans infect bivalves as intermediate hosts: indications of an ancient diversification of the Schistosomatoidea. Int J Parasitol 47:885–891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2017.05.008
Ehlers U (1995) The basic organization of the Plathelminthes. Hydrobiologia 305:321–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00036358
Erasmus DA, Popiel I, Shaw JR (1982) A comparative study of the vitelline cell in Schistosoma mansoni, S. haematobium, S. japonicum and S. mattheei. Parasitology 84:283–287. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182000044838
Grant WC, Harkema R, Muse KE (1977) Ultrastructure of Pharyngostomoides procyonis Harkema 1942 (Diplostomatidae) II The female reproductive system. J Parasitol 63:1019–1030. https://doi.org/10.2307/3279038
Greani S, Quilichini Y, Foata J, Marchand B (2012) Ultrastructural study of vitellogenesis of Aphallus tubarium (Rudolphi, 1819) Poche, 1926 (Digenea: Cryptogonimidae), an intestinal parasite of Dentex dentex (Pisces: Teleostei). J Parasitol 98:938–943. https://doi.org/10.1645/GE-3123.1
Greani S, Quilichini Y, Foata J, Greiman SE, Ndiaye PI, Tkach VV, Marchand B (2014) Vitellogenesis in the digenean Plagiorchis elegans (Rudolphi, 1802) (Plagiorchioidea, Plagiorchiidae). Parasitol Int 63:537–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2013.12.010
Halton DW (1967) Studies on glycogen deposition in Trematoda. Comp Biochem Physiol 23:113–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-406X(67)90478-1
Hendow HT, James BI (1989) Ultrastructure of vitellarium, vitellogenesis and associated ducts in Maritrema linguilla (Digenea: Microphallidae). Int J Parasitol 19:489–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-7519(89)90078-7
Holy JM, Wittrock DD (1986) Ultrastructure of the female reproductive organs (ovary, vitellaria and Mehlis’ gland) of Halipegus eccentricus (Trematoda: Derogenidae). Can J Zool 64:2203–2212. https://doi.org/10.1139/z86-334
Irwin SWB, Threadgold LT (1972) Electron microscope studies of Fasciola hepatica. X. Egg formation. Exp Parasitol 31:321–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-4894(72)90093-8
Køie M (1982) The redia, cercaria and early stages of Aporocotyle simplex Odhner, 1900 (Sanguinicolidae) – a digenetic trematode which has a polychaete annelid as the only intermediate host. Ophelia 21:115–145. https://doi.org/10.1080/00785326.1982.10426582
Køie M, Petersen ME (1988) A new annelid intermediate host (Lanassa nordenskioeldi Malmgren, 1866) (Polychaeta: Terebellidae) for Aporocotyle sp. and a new final host family (Pisces: Bothidae) for Aporocotyle simplex Odhner, 1900 (Digenea: Sanguinicolidae). J Parasitol 74:499–502. https://doi.org/10.2307/3282065
Levron C, Poddubnaya L, Oros M, Scholz T (2010) Vitellogenesis of basal trematode Aspidogaster limacoides (Aspidogastrea: Aspidogastridae). Parasitol Int 59:532–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2010.06.011
McMichael-Phillips DF, Lewis JW, Thorndyke MC (1992) Ultrastructure of the egg of Sanguinicola inermis Plehn, 1905 (Digenea: Sanguinicolidae). J Nat Hist 26:895–904. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222939200177054
Meepool A, Sobhon P (2009) Oogenesis of the liver fluke Fasciola gigantica. Microsc Microanal Res 23:15–19
Neill PJG, Smith JH, Doughty BL, Kemp M (1988) The ultrastructure of the Schistosoma mansoni egg. Am J Trop Med Hyg 39:52–65. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.1988.39.52
Olson PD, Cribb TH, Tkach VV, Bray RA, Littlewood DTJ (2003) Phylogeny and classification of the Digenea (Platyhelminthes: Trematoda). Int J Parasitol 33:733–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0020-7519(03)00049-3
Pérez-Ponce de León G, Hernández-Mena DI (2019) Testing the higher-level phylogenetic classification of Digenea (Platyhelminthes, Trematoda) based on nuclear rDNA sequences before entering the age of the ‘next-generation’ tree of life. J Helminthol 93:260–276. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X19000191
Poddubnaya LG, Gibson DI (2020) Are glial cells of the Digenea (Platyhelminthes) muscle cells? Parasitol Res 119:317–319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-019-06490-9
Poddubnaya LG, Bruňanská M, Świderski Z, Gibson DI (2012) Ultrastructure of the vitellarium in the digeneans Phyllodistomum angulatum (Plagiorchiida, Gorgoderidae) and Azygia lucii (Strigeida, Azygiidae). Acta Parasitol 57:235–246. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11686-012-0030-9
Poddubnaya LG, Bruňanská M, Brázová T, Zhokhov AE, Gibson DI (2013a) Ultrastructural characteristics of the vitellarium of Brandesia turgida (Brandes, 1888) (Digenea: Pleurogenidae) and an examination of the potential usefulness of such vitelline traits in digenean systematics. Helminthologia 50:119–126. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11687-013-0119-1
Poddubnaya LG, Bruňanská M, Świderski Z, Gibson DI (2013b) Ultrastructure of the vitellarium of Ancyrocephalus paradoxus (Monogenea: Monopisthocotylidea), with comments on the nature of the vitellarium in the Monogenea and related platyhelminth groups. Parasitol Res 113:1169–1177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-3248-4
Poddubnaya LG, Hemmingsen W, Poddubny SA, Gibson DI (2019) Unique ultrastructural characteristics of the tegument of the digenean blood fluke Aporocotyle simplex Odhner, 1900 (Digenea: Aporocotylidae), a parasite of flatfishes. Parasitol Res 118:2801–2810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-019-06436-1
Podvyaznaya IM (1990) The morphology and ultrastructure of the female reproductive system of Prosthodendrium ascidia (Trematoda: Lecithodendriidae). In: Mamkaev YUV, Ioffe BI (eds) Parasitic and free-living Plathelminthes: faunistics and morphology. Trudy Zool Inst, Leningrad 221:61–78 (In Russian)
Rohde K (1972) The Aspidogastrea, especially Multicotyle purvisi Dawes 1941. Adv Parasitol 10:77–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0065-308x(08)60173-6
Smyth JD, Halton DW (1983) The physiology of trematodes, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 446 pp
Świderski Z (1994) Origin, differentiation and ultrastructure of egg envelopes surrounding the miracidia of Schistosoma mansoni. Acta Parasitol 39:64–72
Świderski Z, Xylander WER (2000) Vitellocytes and vitellogenesis in cestodes in relation to embryonic development, egg production and life cycle. Int J Parasitol 30:805–817. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7519(00)00066-7
Świderski Z, Bakhoum AJS, Montoliu I, Felui C, Miquel J (2011) Ultrastructural study of vitellogenesis in Maritrema feliui (Digenea, Microphallidae). Parasitol Res 109:1707–1714. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2444-y
Świderski Z, Kacem H, Mackiewicz JS, Miquel J (2019) Functional ultrastructure and cytochemistry of vitellogenesis and mature vitellocytes of the digenean Cainocreadium labracis (Dujardin, 1845), parasite of Dicentrarchus labrax (L., 1758). Parasitol Res 118:493–504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-018-6180-4
Threadgold LT (1982) Fasciola hepatica: stereological analysis of vitelline cell development. Exp Parasitol 54:352–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-4894(82)90044-3
Thulin J (1980) A redescription of the fish blood-fluke Aporocotyle simplex Odhner, 1900 (Digenea, Sanguinicolidae) with comments on is biology. Sarsia 65:35–48. https://doi.org/10.1080/00364827.1980.10431470
Thulin J (1982) Structure and function of the female reproductive ducts of the fish blood-fluke Aporocotyle simplex, 1900 (Digenea: Sanguinicolidae). Sarsia 67:227–248. https://doi.org/10.1080/00364827.1982.10421338
Wells KE, Cordingley JS (1991) Schistosoma mansoni: eggshell formation is regulated by pH and calcium. Exp Parasitol 73:295–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-4894(91)90101-2
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the staff of the RV ‘Johan Ruud’, belonging to Tromsø University (Norway), for their help with the fishing. We are also grateful to the staff of the Centre of Electron Microscopy, I.D. Papanin Institute for the Biology of Inland Waters (Borok, Russia), for technical assistance.
Funding information
The study was funded by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (RFBR) for Research Project No. 20-04-00086A (to LGP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Section Editor: David Bruce Conn
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poddubnaya, L.G., Hemmingsen, W., Bruňanská, M. et al. Interrelationships of vitelline and muscle cells within the vitelline follicles of the blood fluke Aporocotyle simplex (Digenea, Aporocotylidae) and morphological evidence for the modification of vitelline material for eggshell formation. Parasitol Res 119, 3967–3976 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-06849-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-06849-3