Abstract
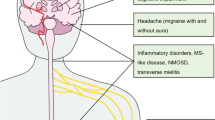
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune disorder characterized by arterial, venous, and/or small vessel thrombosis, pregnancy morbidity, and persistently elevated levels of antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL). Cardiovascular disease (CVD) in APS can present as heart valvular disease (HVD), macro-micro-coronary artery disease (CAD), myocardial dysfunction, cardiac thrombi, or pulmonary hypertension. Brain disease presents as stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) and less frequently as cerebral venous thrombosis, seizures, cognitive dysfunction, multiple sclerosis (MS)−like syndrome, or chorea. Infarcts and focal white matter hyperenhancement are the commonest brain (MRI) abnormalities, while myocardial ischemia/fibrosis, valvular stenosis/regurgitation, or cardiac thrombi are the main abnormalities detected by cardiovascular magnetic resonance. This review aims to present the existing evidence on brain/heart involvement and their interrelationship in APS and the role of brain/heart MRI in their evaluation. Embolic brain disease, due to HVD, CAD, and/or cardiac thrombus, or brain hypo-perfusion, due to myocardial dysfunction, are among the main brain/heart interactions in APS and they are considered determinants of morbidity and mortality. Currently, there is no evidence to support the use of combined brain/heart MRI in asymptomatic APS patients. Until more data will be available, this approach may be considered in APS patients at high risk for CVD/stroke, such as systemic lupus erythematosus with high-risk aPL profile or high scores in CVD risk prediction models; APS patients with HVD/thrombus, CAD, or heart failure; those with classic and non-criteria neurologic APS manifestations (seizures, cognitive dysfunction, MS-like syndrome); or with aggressive multi-organ disease.
Key Points • Cardiovascular disease (CVD) in antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) can present as heart valvular disease (HVD), macro-micro-coronary artery disease (CAD), myocardial dysfunction, cardiac thrombi, or pulmonary hypertension. • Brain disease presents as stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA), and less frequently as cerebral venous thrombosis, seizures, cognitive dysfunction, and multiple sclerosis (MS). • A combined brain/heart MRI may be considered in APS patients at high risk for CVD/stroke, such as systemic lupus erythematosus with high-risk aPL profile or high scores in CVD risks; APS patients with HVD/thrombus, CAD, or heart failure; those with classic and non-criteria neurologic APS manifestations (seizures, cognitive dysfunction, MS-like syndrome); or with aggressive multi-organ disease. |


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APS:
-
Am antiphospholipid antibodies
- Apl:
-
Antiphospholipid antibodies
- CAD:
-
Coronary artery disease
- HVD:
-
Heart valvular disease
- TIA:
-
Transient ischemic attack
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- MS:
-
Multiple sclerosis
- SLE:
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus
- CV:
-
Cardiovascular
- CVD:
-
Cardiovascular disease
- TTE:
-
Transthoracic echocardiography
- CMR:
-
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance
- HF:
-
Heart failure
- PAPS:
-
Primary antiphospholipid syndrome
- CAPS:
-
Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome
- LV-RV:
-
Left-right ventricle
- PHT:
-
Pulmonary hypertension
- CTEPH:
-
Thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension
- LAC:
-
Lupus anticoagulant
- aCL:
-
Anticardiolipin antibodies
- anti-b2GPI:
-
Anti–beta2-glycoprotein I antibodies
- WMH:
-
White matter hyperenhancement
- HELLP:
-
Hemolysis-elevated liver enzyme-low platelet syndrome
- aGAPSS:
-
Global AntiphosPholipid Syndrome Score
- aGAPSScvd score:
-
Global AntiphosPholipid Syndrome Score for CVD
- FLAIR:
-
T2/fluid-attenuated inversion recovery
- DW:
-
Diffusion-weighted images
References
Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T, Branch DW, Brey RL, Cervera R et al (2006) International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). J Thromb Haemost J Thromb Haemost 4:295–306
Shoenfeld Y, Blank M, Cervera R, Font J, Raschi E, Meroni PL (2006) Infectious origin of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. BMJ Publishing Group Ltd, 2–6
Tripodi A, de Groot PG, Pengo V (2011) Antiphospholipid syndrome: Laboratory detection, mechanisms of action and treatment. J Intern Med. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 110–122
Jara LJ, Medina G, Vera-Lastra O, Amigo MC (2006) Accelerated atherosclerosis, immune response and autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Autoimmun Rev. Elsevier, 195–201
Djokovic A, Stojanovich L, Kontic M, Stanisavljevic N, Radovanovic S, Marisavljevic D (2014) Association between cardiac manifestations and antiphospholipid antibody type and level in a cohort of Serbian patients with primary and secondary antiphospholipid syndrome. Isr Med Assoc J 16:162–167
Tektonidou MG, Andreoli L, Limper M, Amoura Z, Cervera R, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, et al (2019). EULAR recommendations for the management of antiphospholipid syndrome in adults. Ann Rheum Dis. BMJ Publishing Group; 78:1296–12304.
Tektonidou MG, Andreoli L, Limper M, Tincani A, Ward MM (2019). Management of thrombotic and obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome: A systematic literature review informing the EULAR recommendations for the management of antiphospholipid syndrome in adults. RMD Open. BMJ Publishing Group
Andrade D, Tektonidou M (2016) Emerging therapies in antiphospholipid syndrome. Curr Rheumatol Rep. Current Medicine Group LLC 1
Chatzidionysiou K, Samoli E, Sfikakis PP, Tektonidou MG (2019) Effect of belimumab treatment on antiphospholipid antibodies levels: Post-hoc analysis based on two randomised placebo-controlled trials in systemic lupus erythematosus (2019). Ann Rheum Dis. BMJ Publishing Group
Dobrowolski C, Erkan D (2019) Treatment of antiphospholipid syndrome beyond anticoagulation. Clin Immunol. Academic Press Inc 206:53–62
Gasparyan AY, Ayvazyan L, Blackmore H, Kitas GD (2011) Writing a narrative biomedical review: considerations for authors, peer reviewers, and editors. Rheumatol Int Rheumatol Int:1409–1417
Kaplan SD, Chartash EK, Pizzarello RA, Furie RA (1992) Cardiac manifestations of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Am Heart J Am Heart J124:1331–1338
Cervera R, Tektonidou MG, Espinosa G, Cabral AR, González EB, Erkan D et al (2011) Task Force on Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) and non-criteria APS manifestations (I): catastrophic APS, APS nephropathy and heart valve lesions. Lupus 20:165–173
Tenedios F, Erkan D, Lockshin MD (2006) Cardiac Manifestations in the Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Rheum. Dis Clin North Am:491–507
Roldan CA (2008) Valvular and coronary heart disease in systemic inflammatory diseases. Heart:1089–1101
Silbiger JJ (2009) The cardiac manifestations of antiphospholipid syndrome and their echocardiographic recognition. J Am Soc Echocardiogr:1100–1108
Long BR, Leya F (2008) The role of antiphospholipid syndrome in cardiovascular disease. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am:79–94
Nesher G, Ilany J, Rosenmann D, Abraham AS (1997) Valvular dysfunction in antiphospholipid syndrome: prevalence, clinical features, and treatment. Semin Arthritis Rheum. W.B. Saunders, 27:27–35
Galve E, Ordi J, Barquinero J, Evangelista A, Vilardell M, Soler-Soler J (1992) Valvular heart disease in the primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann Intern Med. American College of Physicians 116:293–298
Brenner B, Blumenfeld Z, Markiewicz W, Reisner SA (1991) Cardiac involvement in patients with primary antiphospholipid syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. J Am Coll Cardiol 18:931–936
Hojnik M, George J, Ziporen L, Shoenfeld Y (1996) Heart valve involvement (Libman-Sacks endocarditis) in the antiphospholipid syndrome. Circulation. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 1579–87
Zuily S, Regnault V, Selton-Suty C, Eschwège V, Bruntz JF, Bode-Dotto E et al (2011) Increased risk for heart valve disease associated with antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: meta-analysis of echocardiographic studies. Circulation 124:215–224
Erdogan D, Goren MT, Diz-Kucukkaya R, Inanc M (2005). Assessment of cardiac structure and left atrial appendage functions in primary antiphospholipid syndrome: a transesophageal echocardiographic study. Stroke. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 36:592–596
Krause I, Lev S, Fraser A, Blank M, Chapman J, Shoenfeld Y (2005) Close association between valvular heart disease and central nervous system manifestations in antiphospholipid syndrome. Arthritis Res Ther. BioMed Central 7:12
Pardos-Gea J, Ordi-Ros J, Avegliano G, Cortés-Hernández J, Balada E, Evangelista A et al (2010) Echocardiography at diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome provides prognostic information on valvular disease evolution and identifies two subtypes of patients. Lupus 19:575–582
Vlachoyiannopoulos PG, Kanellopoulos PG, Ioannidis JPA, Tektonidou MG, Mastorakou I, Moutsopoulos HM (2003) Atherosclerosis in premenopausal women with antiphospholipid syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus: a controlled study. Rheumatology 42:645–651
Ambrosino P, Lupoli R, Di Minno A, Iervolino S, Peluso R, Di Minno MND (2014) Markers of cardiovascular risk in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome: a meta-analysis of literature studies. Ann Med. Informa Healthcare 46:693–702
Nazir S, Tachamo N, Lohani S, Hingorani R, Poudel DR, Donato A (2017) Acute myocardial infarction and antiphospholipid antibody syndrome: a systematic review. Coron Artery Dis. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins 28:332–335
Denas G, Jose SP, Bracco A, Zoppellaro G, Pengo V (2015) Antiphospholipid syndrome and the heart: a case series and literature review. Autoimmun Rev. Elsevier, 214–222
Boekholdt SM, Kramer MHH (2007) Arterial thrombosis and the role of thrombophilia. Semin Thromb Hemost 588–596
Urbanus RT, Siegerink B, Roest M, Rosendaal FR, de Groot PG, Algra A (2009) Antiphospholipid antibodies and risk of myocardial infarction and ischaemic stroke in young women in the RATIO study: a case-control study. Lancet Neurol 8:998–1005
Lauwerys BR, Lambert M, Vanoverschelde JL, Cosyns JP, Houssiau FA (2001) Myocardial microangiopathy associated with antiphospholipid antibodies. Lupus 10:123–125
Azeem T, Vassallo M, Samani NJ (2000) Endomyocardial fibrosis associated with antiphospholipid syndrome. Heart 84:156
Paran D, Caspi D, Levartovsky D, Elkayam O, Kaufman I, Litinsky I et al (2007) Cardiac dysfunction in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 66:506–510
Tektonidou MG, Ioannidis JPA, Moyssakis I, Boki KA, Vassiliou V, Vlachoyiannopoulos PG et al (2001) Right ventricular diastolic dysfunction in patients with anticardiolipin antibodies and antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 60:43–48
Kampolis C, Tektonidou M, Moyssakis I, Tzelepis GE, Moutsopoulos H, Vlachoyiannopoulos PG (2014) Evolution of cardiac dysfunction in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies and/or antiphospholipid syndrome: a 10-year follow-up study. Semin Arthritis Rheum 43:558–565
Cervera R, Serrano R, Pons-Estel GJ, Ceberio-Hualde L, Shoenfeld Y, De Ramón E, et al (2015) Morbidity and mortality in the antiphospholipid syndrome during a 10-year period: a multicentre prospective study of 1000 patients. Ann Rheum Dis. BMJ Publishing Group 74:1011–1018
Atsumi T, Khamashta MA, Haworth RS, Brooks G, Amengual O, Ichikawa K et al (1998) Arterial disease and thrombosis in the antiphospholipid syndrome: a pathogenic role for endothelin 1. Arthritis Rheum 41:800–807
Vaccaro F, Caccavo D, Roumpedaki E, De Vincentis G, Di Gioia CRT, Gallo P, et al (2008) Dilated cardiomyopathy due to thrombotic microangiopathy as the only manifestation of antiphospholipid syndrome: a case report. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. Biomedical Research Press s.a.s. 21:237–241
Lang IM (2004) Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension - not so rare after all. N Engl J Med 2236–2238
Chen Y, Chen GL, Zhu CQ, Lu X, Ye S, De YC (2011) Severe systemic lupus erythematosus in emergency department: a retrospective single-center study from China. Clin Rheumatol 30:1463–1469
Brucato A, Baudo F, Barberis M, Redaelli R, Casadei G, Allegri F et al (1994) Pulmonary hypertension secondary to thrombosis of the pulmonary vessels in a patient with the primary antiphospholipid syndrome. J Rheumatol 21:942–944
Chaouat A, Weitzenblum E, Higenbottam T (1996) The role of thrombosis in severe pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J 356–363
Zuily S, Wahl D (2015) Pulmonary hypertension in antiphospholipid syndrome. Curr Rheumatol Rep. Current Medicine Group LLC 1
Wolf M, Boyer-Neumann C, Parent F, Eschwege V, Jaillet H, Meyer D et al (2000) Thrombotic risk factors in pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J 15:395–399
Waisayarat J, Plumworasawat S, Vilaiyuk S, Sirachainan N (2019) Intracardiac thrombus in a patient with catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome: an autopsy case report and review of the literature. Vasc Health Risk Manag. Dove Medical Press Ltd, 15:253–258
Dhibar DP, Sahu KK, Varma SC, Kumari S, Malhotra P, Mishra AK, et al (2016) Intra-cardiac thrombus in antiphospholipid antibody syndrome: an unusual cause of fever of unknown origin with review of literature. J Cardiol Cases. Elsevier Ltd, 14:153–156
Cianciulli TF, Saccheri MC, Lax JA, Neme RO, Sevillano JFA, Maiori ME et al (2009) Left ventricular thrombus mimicking primary cardiac tumor in a patient with primary antiphospholipid syndrome and recurrent systemic embolism. Cardiol J 16:560–563
Marie I, Derumeaux G, Delahaye F, Mouton-Schleifer D, Reumont G, Levesque H, et al (2003) Intracardiac thrombi in primary antiphospholipid syndrome: two case reports. Eur J Intern Med. Elsevier 14:504–508
Harel L, Sandborg C, Lee T, Von Scheven E (2006) Neuropsychiatric manifestations in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus and association with antiphospholipid antibodies [Internet]. J. Rheumatol. 1873–7
Montalban J, Rio J, Khamastha M, Davalos A, Codina M, Swana GT et al (1994) Value of immunologic testing in stroke patients a prospective multicenter study. Stroke 25:2412–2415
Sciascia S, Sanna G, Khamashta MA, Cuadrado MJ, Erkan D, Andreoli L, et al (2015) The estimated frequency of Antiphospholipid antibodies in young adults with cerebrovascular events: a systematic review. Ann Rheum Dis. BMJ Publishing Group 74:2028–2033
Schellong SM, Weissenborn K, Niedermeyer J, Wollenhaupt J, Sosada M, Ehrenheim C et al (1997) Classification of Sneddon’s syndrome. Vasa - J Vasc Dis 26:215–221
Hilton DA, Footitt D (2003) Neuropathological findings in Sneddon’s syndrome. Neurology. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 60:1181–1182
Francès C, Piette JC (2000) The mystery of Sneddon syndrome: relationship with antiphospholipid syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun. Academic Press 139–143
Sanna G, Bertolaccini ML, Hughes GRV (2005) Hughes syndrome, the antiphospholipid syndrome: a new chapter in neurology. Ann N Y Acad Sci:465–486
Krnic-Barrie S (1997) A retrospective review of 61 patients with antiphospholipid syndrome. Arch Intern Med. American Medical Association (AMA) 157:2101
Shah NM, Khamashta MA, Atsumi T, Hughes GRV (1998) Outcome of patients with anticardiolipin antibodies: A 10 year follow-up of 52 patients. Lupus. Sage PublicationsSage CA: Thousand Oaks, CA 7:3–6
Sastre-Garriga J, Montalban X (2003) APS and the brain [Internet]. Lupus. Sage PublicationsSage CA: Thousand Oaks, CA, 877–882
Cervera R, Piette JC, Font J, Khamashta MA, Shoenfeld Y, Camps MT, et al. (2002) Antiphospholipid syndrome: clinical and immunologic manifestations and patterns of disease expression in a cohort of 1,000 patients. Arthritis Rheum. John Wiley and Sons Inc, 46:1019–1027.
Djokovic A, Stojanovich L, Stanisavljevic N, Banicevic S, Smiljanic D, Milovanovic B (2018) Relationship between cerebrovascular and valvular manifestations in a Serbian cohort of patients with antiphospholipid syndrome. Clin Exp Rheumatol 36:850–855
Cuadrado MJ, Khamashta MA, Ballesteros A, Godfrey T, Simon MJ, Hughes GRV (2000) Can neurologic manifestations of Hughes (antiphospholipid) syndrome be distinguished from multiple sclerosis? Analysis of 27 patients and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 79:57–68
D’Angelo C, Franch O, Fernández-Paredes L, Oreja-Guevara C, Núñez-Beltrán M, Comins-Boo A, et al (2019) Antiphospholipid antibodies overlapping in isolated neurological syndrome and multiple sclerosis: neurobiological insights and diagnostic challenges. Front Cell Neurosci. Frontiers Media S.A 13:107
Ricarte IF, Dutra LA, Abrantes FF, Toso FF, Barsottini OGP, Silva GS, et al (2018) Neurologic manifestations of antiphospholipid syndrome [Internet]. Lupus. SAGE Publications Ltd 1404–1414
Katzav A, Menachem A, Maggio N, Pollak L, Pick CG, Chapman J (2014) IgG accumulates in inhibitory hippocampal neurons of experimental antiphospholipid syndrome. J Autoimmun. Academic Press 55:86–93
Islam MA, Alam F, Cavestro C, Calcii C, Sasongko TH, Levy RA, et al (2018) Antiphospholipid antibodies in epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Autoimmun. Rev. Elsevier B.V, 755–767
Noureldine MHA, Haydar AA, Berjawi A, Elnawar R, Sweid A, Khamashta MA, et al (2017) Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) revisited: would migraine headaches be included in future classification criteria? Immunol Res. Humana Press Inc 65:230–241
Peluso S, Antenora A, De Rosa A, Roca A, Maddaluno G, Morra VB et al (2012) Antiphospholipid-related chorea. Front Neurol 3:150
Cervera R, Asherson RA, Font J, Tikly M, Pallarés L, Chamorro A et al (1997) Chorea in the antiphospholipid syndrome: clinical, radiologic, and immunologic characteristics of 50 patients from our clinics and the recent literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 76:203–212
Orzechowski NM, Wolanskyj AP, Ahlskog JE, Kumar N, Moder KG (2008) Antiphospholipid antibody-associated chorea. J Rheumatol 35:2165–2170
Arvanitakis Z, Capuano AW, Brey R, Fleischman DA, Arfanakis K, Buchman AS, et al (2019) Antiphospholipid antibodies: cognitive and motor decline, neuroimaging and neuropathology. Neuroepidemiology. S. Karger AG 53:100–7
Homayoon N, Schwingenschuh P, Hofer E, Katschnig-Winter P, Schmidt R. (2014) Anticardiolipin antibodies are associated with cognitive dysfunction in stroke-free individuals. Eur J Neurol 21
Mosek A, Yust I, Treves TA, Vardinon N, Korczyn AD, Chapman J (2000) Dementia and antiphospholipid antibodies. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. S. Karger AG 11:36–8
Islam MA, Alam F, Kamal MA, Gan SH, Sasongko TH, Wong KK (2017) Presence of anticardiolipin antibodies in patients with dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Aging Neurosci. Frontiers Media S.A 9:250
Denburg SD, Carbotte RM, Ginsberg JS, Denburg JA (1997) The relationship of antiphospholipid antibodies to cognitive function in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 3:377–386
Menon S, Jameson-Shortall E, Newman SP, Hall-Craggs MR, Chinn R, Isenberg DA (1999) A longitudinal study of anticardiolipin antibody levels and cognitive functioning in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 42:735–741
Katzav A, Pick CG, Korczyn AD, Oest E, Blank M, Shoenfeld Y, et al (2001) Hyperactivity in a mouse model of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus. Sage PublicationsSage CA: Thousand Oaks, CA 10:496–9
Tektonidou MG, Varsou N, Kotoulas G, Antoniou A, Moutsopoulos HM (2006) Cognitive deficits in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome: association with clinical, laboratory, and brain magnetic resonance imaging findings. Arch Intern Med. American Medical Association 166:2278–2284
Erkan D, Vega J, Ramón G, Kozora E, Lockshin MD (2013) A pilot open-label phase II trial of rituximab for non-criteria manifestations of antiphospholipid syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 65:464–471
Garcia D, Erkan D (2018) Diagnosis and management of the antiphospholipid syndrome [Internet]. Longo DL, editor. N. Engl. J. Med. Massachussetts Medical Society 2010–110
Shoenfeld Y, Cervera R (2008) Asherson’s syndrome of the catastrophic antiphospholipid antibodies. J Rheumatol 35:2066–2068
Cervera R, Rodríguez-Pintó I, Espinosa G (2018). The diagnosis and clinical management of the catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome: a comprehensive review. J. Autoimmun. Academic Press 1–11
George JN, Nester CM (2014) Syndromes of thrombotic microangiopathy. N Engl J Med. Massachussetts Medical Society 654–66
Provenzale JM, Barboriak DP, Allen NB, Ortel TL (1996) Patients with antiphospholipid antibodies: CT and MR findings of the brain. Am J Roentgenol. American Roentgen Ray Society167:1573–1578
Provenzale JM, Ortel TL, Allen NB (1998) Systemic thrombosis in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies: lesion distribution and imaging findings. Am J Roentgenol. American Roentgen Ray Society 170:285–290
Theodoridou A, Settas L (2006) Demyelination in rheumatic diseases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. BMJ Publishing Group 290–295
Bot JCJ, Barkhof F, Lycklama À Nijeholt GL, Van Schaardenburg D, Voskuyl AE, Ader HJ, et al (2002) Differentiation of multiple sclerosis from other inflammatory disorders and cerebrovascular disease: value of spinal MR imaging. Radiology. Radiological Society of North America Inc 223:46–56
Zhu DS, Fu J, Zhang Y, Li SX, Zhang GX, Guan YT, et al (2014) Neurological antiphospholipid syndrome: clinical, neuroimaging, and pathological characteristics. J Neurol Sci. Elsevier B.V 346:138–144
Arnold DL, Matthews PM (2002) MRI in the diagnosis and management of multiple sclerosis. Neurology. Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology 58:S23–S31
Cikes N, Bosnic D, Sentic M (2008) Non-MS autoimmune demyelination. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. Elsevier 905–912
Rovaris M, Viti B, Ciboddo G, Gerevini S, Capra R, Iannucci G, et al (2000) Brain involvement in systemic immune mediated diseases: magnetic resonance and magnetisation transfer imaging study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. BMJ Publishing Group 68:170–177
Mavrogeni SI, Sfikakis PP, Kitas GD, Kolovou G, Tektonidou MG (2016) Cardiac involvement in antiphospholipid syndrome: the diagnostic role of noninvasive cardiac imaging. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. W.B. Saunders, 611–6
Mavrogeni SI, Markousis-Mavrogenis G, Karapanagiotou O, Toutouzas K, Argyriou P, Velitsista S, et al (2019) Silent myocardial perfusion abnormalities detected by stress cardiovascular magnetic resonance in antiphospholipid syndrome: a case-control study. J Clin Med. MDPI AG 8:1084
Mavrogeni S, Markousis-Mavrogenis G, Kolovou G (2014) Clinical use of cardiac magnetic resonance in systemic heart disease. Eur Cardiol Rev. Touch Briefings, 9:21–27
Mavrogeni SI, Sfikakis PP, Koutsogeorgopoulou L, Markousis-Mavrogenis G, Dimitroulas T, Kolovou G, et al (2017) Cardiac tissue characterization and imaging in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging. Elsevier Inc 1387–1396
Mavrogeni S, Markousis-Mavrogenis G, Koutsogeorgopoulou L, Kolovou G (2017) Cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging: clinical implications in the evaluation of connective tissue diseases. J Inflamm Res. Dove Medical Press Ltd, 55–61.
Barkhausen J, Hunold P, Eggebrecht H, Schüler WO, Sabin GV, Erbel R, et al. (2002) Detection and characterization of intracardiac thrombi on MR imaging. Am J Roentgenol. American Roentgen Ray Society179:1539–1544
Mavrogeni SI, Sfikakis PP (2017) Systemic lupus erythematosus with antiphospholipid syndrome: cardiovascular magnetic resonance for evaluation of cardiac hypertrophy. Mediterr J Rheumatol 28:221–222
Zuily S, Huttin O, Mohamed S, Marie PY, Selton-Suty C, Wahl D (2013) Valvular heart disease in antiphospholipid syndrome. Curr Rheumatol Rep. Current Medicine Group LLC 1, 15:1–7
Patrignani A, Nannicosta MP, Antonini L, D’Aroma A, De Berardinis G, Cicogna S (2009) Myocardial and cerebral infarction as initial presentation of antiphospholipid syndrome. G Ital Cardiol (Rome) 10:259–62
Jung F, Miesbach W, Scharrer I (2002) Cardiac and cerebral manifestations of antiphospholipid syndrome. Z Kardiol 91:650–8
Markousis-Mavrogenis G, Mitsikostas DD, Koutsogeorgopoulou L, Dimitroulas T, Katsifis G, Argyriou P, et al (2020) Combined brain-heart magnetic resonance imaging in autoimmune rheumatic disease patients with cardiac symptoms: hypothesis generating insights from a cross-sectional study. J Clin Med. MDPI AG 9:447
Sciascia S, Radin M, Sanna G, Cecchi I, Roccatello D, Bertolaccini ML (2018) Clinical utility of the global anti-phospholipid syndrome score for risk stratification: a pooled analysis. Rheumatol (United Kingdom) 57:661–665
Di Minno MND, Scalera A, Tufano A, Ambrosino P, Bettiol A, Silvestri E, et al. (2018) The association of adjusted Global AntiphosPholipid Syndrome Score (aGAPSS) with cardiovascular disease in subjects with antiphospholipid antibodies. Atherosclerosis. Elsevier Ireland Ltd, 278:60–65
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Markousis-Mavrogenis, G., Sfikakis, P.P., Mavrogeni, S.I. et al. Combined brain/heart magnetic resonance imaging in antiphospholipid syndrome-two sides of the same coin. Clin Rheumatol 40, 2559–2568 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05498-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05498-2