Abstract
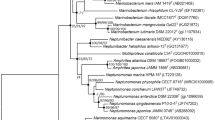
Here, we describe a novel bacterial strain, designated T37T, which was isolated from the marine sediment of Xiaoshi Island, PR China. Growth of strain T37T occurs at 15–40 °C (optimum 37 °C), pH 6.0–9.0 (optimum 7.5), and in the presence of 0.5–5.5% (w/v) NaCl (optimum 1.5%). Characteristic biochemical traits of the novel strain include MK-9 as the major menaquinone. The major fatty acids identified were iso-C14:0 and C16:1 ω9c (oleic acid). Phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylglycerol, diphosphatidylglycerol, and phosphoglycolipids were the major cellular polar lipids. The G + C content of genomic DNA was 58.4 mol%. Unusual outer membrane features deduced from the analysis of cell morphology point towards the formation of an enlarged periplasmic space putatively used for the digestion of macromolecules. Phylogenetic analyses based on 16S rRNA genes and the genome indicated that strain T37T represents a novel species and genus affiliated with a distinct family level lineage of the verrucomicrobial subdivision 1. Our polyphasic taxonomy approach places the novel strain in a new genus within the current family Verrucomicrobiaceae, order Verrucomicrobiales, class Verrucomicrobiae. Strain T37T (= KCTC 72799 T = MCCC 1H00391T) is the type strain of a novel species, for which the name Sulfuriroseicoccus oceanibius gen. nov., sp. nov. is proposed.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The 16S rRNA gene sequence and the complete genome sequence of strain T37T, are deposited in GenBank under accession numbers MN412654 and CP066776.1, respectively. The type strain T37T can be obtained from the Korean Collection for Type Cultures (KCTC 72799 T) and the Marine Culture Collection of China (MCCC 1H00391T).
Abbreviations
- PR:
-
People’s republic
- KCTC:
-
Korean collection for type cultures
- DSMZ:
-
Leibniz institute german collection of microorganisms and cell cultures
- MCCC:
-
Marine culture collection of china
- NBRC:
-
NITE biological resource center
- BD:
-
Becton dickinson
- MEGA:
-
Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis
- MA:
-
Marine agar 2216
- MB:
-
Marine broth 2216
- OD:
-
Optical density
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- TLC:
-
Thin-layer chromatography
References
Addinall SG, Holland B (2002) The tubulin ancester, FtsZ, draughtsman, designer and driving force for bacterial cytokinesis. J Mol Biol 318:219–236
Albrecht W, Fischer A, Smida J, Stackebrandt E (1987) Verrucomicrobium spinosum, a eubacterium representing an ancient line of descent. Syst Appl Microbiol 10:57–62
Alcock BP, Raphenya AR, Lau T, Kara KT, Mégane B et al (2019) CARD 2020: antibiotic resistome surveillance with the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res 48:D517–D525
Alexandros S (2014) RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 1312–1313
Amerik A, Hochstrasser SM (2006) A conserved late endosome-targeting signal required for Doa4 deubiquitylating enzyme function. J Cell Biol 175:825–835
Athalye M, Noble WC, Minnikin DE (2010) Analysis of cellular fatty acids by gas chromatography as a tool in the identification of medically important coryneform bacteria. J Appl Bacteriol 58:507–512
Bergmann GT, Bates ST, Eilers KG, Lauber CL, Caporaso JG, Walters WA et al (2011) The under-recognized dominance of Verrucomicrobia in soil bacterial communities. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1450–1455
Boedeker C, Schüler M, Reintjes G, Jeske O, van Teeseling MCF et al (2017) Determining the bacterial cell biology of Planctomycetes. Nat Commun 8:14853
Cantarel BL, Coutinho PM, Corinne R et al (2009) The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes database (CAZy): an expert resource for Glycogenomics. Nuclc Acids Res 37:D233–D238
Capella-Gutierrez S, Silla-Martinez JM, Gabaldon T (2009) trimAl: a tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 25:1972–1973
Cayrou C, Raoult D, Drancourt M (2010) Broad-spectrum antibiotic resistance of Planctomycetes organisms determined by Etest. J Antimicrob Chemother 65:2119–2122
Chiang E, Schmidt ML, Berry MA, Biddanda BA, Burtner A, Johengen TH et al (2018) Verrucomicrobia are prevalent in north-temperate freshwater lakes and display class-level preferences between lake habitats. Plos One 13(3):e0195112
Cho J, Vergin KL, Morris RM, Giovannoni SJ (2004) Lentisphaera araneosa gen. nov., sp. nov, a transparent exopolymer producing marine bacterium, and the description of a novel bacterial phylum. Lentisphaerae Environ Microbiol 6:611–621
Cockerill F, Wikler M, Bush K, Cockerill FR (2011) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; twenty-first informational supplement: CLSI document M100-S21
Depommier C, Everard A, Druart C, Plovier H, Hul MV et al (2019) Supplementation with Akkermansia muciniphila in overweight and obese human volunteers: a proof-of-concept exploratory study. Nat Med 25:1096
Derrien M, Vaughan EE, Plugge CM, de Vos WM (2004) Akkermansia muciniphila gen. nov., sp. nov., a human intestinal mucin-degrading bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1469–1476
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: a multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinformatics 5:113
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Feng X, Zou QH, Zhang XY, Ye MQ, Du ZJ (2020) Oceanipulchritudo coccoides gen. nov., sp. Nov., isolated from marine sediment within the family Puniceicoccaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70(11):5654–5664
García-López M, Meier-Kolthoff JP, Tindall BJ, Gronow S, Woyke T et al (2019) Analysis of 1,000 type-strain genomes improves taxonomic classification of Bacteroidetes. Front Microbiol 10:2083
Glaeser SP, Galatis H, Martin K, Kämpfer P (2012) Luteolibacter cuticulihirudinis sp. nov., isolated from Hirudo medicinalis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 102:319–324
Godinho O, Calisto R, Øvreås L, Quinteira S, Lage OM (2019) Antibiotic susceptibility of marine Planctomycetes. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 112:1273–1280
Goris J, Konstantinidis KT, Klappenbach JA, Coenye T, Vandamme P et al (2007) DNA-DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:81–91
Hedlund BP, Gosink JJ, Staley JT (1997) Verrucomicrobia div. nov., a new division of the bacteria containing three new species of Prosthecobacter. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 72:29–38
Hou S, Makarova KS, Saw JH, Senin P, Ly V, BV, et al (2008) Complete genome sequence of the extremely acidophilic methanotroph isolate V4, Methylacidiphilum infernorum, a representative of the bacterial phylum Verrucomicrobia. Biol Direct 3:26
Jana T, Lam-Tung N, Arndt von H, Quang MB (2016) W-IQ-TREE: a fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res W232–W235
Jenkins C, Samudrala R, Anderson I, Hedlund BP, Petroni G et al (2003) Genes for the cytoskeletal protein tubulin in the bacterial genus Prosthecobacter. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99:17049–17054
Jones LJ, Carballido-López R, Errington J (2001) Control of cell shape in bacteria: helical, actin-like filaments in Bacillus subtilis. Cell 104:913–922
Kai B, Simon S, Alexander MK, Zach CP, Gilles PW et al (2021) antiSMASH 6.0: improving cluster detection and comparison capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res 49:W29–W35
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Kawashima M, Furumichi M, Tanabe M (2016) KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D457–D462
Karin L, Peter H, Andreas RE, Staerfeldt HH, Rognes T et al (2007) RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 35:3100–3108
Kroppenstedt RM (1982) Separation of bacterial menaquinones by HPLC using reverse phase (rp18) and a silver loaded ion exchanger as stationary phases. J Liq Chromatogr 5:2359–2367
Kumars S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic Acid Tech Bact Syst. Wiley, New York, pp 115–175
Lee I, Chalita M, Ha SM, Na SI, Yoon SH et al (2017) ContEst16S: an algorithm that identifies contaminated prokaryotic genomes using 16S RNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:2053–2057
Lonhienne T, Sagulenko E, Webb RI, Lee KC, Franke J et al (2010) Endocytosis-like protein uptake in the bacterium Gemmata obscuriglobus. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:12883–12888
Manuel MG, Brazel DM, Swan BK, Arnosti C, Chain PSG et al (2012) Capturing single cell genomes of active polysaccharide degraders: an unexpected contribution of Verrucomicrobia. Plos One 7:e35314
Meuric V, Gracieux P, Tamanai-Shacoori Z, Perez-Chaparro J, Bonnaure-Mallet M et al (2010) Expression patterns of genes induced by oxidative stress in Porphyromonas gingivalis. Oral Microbiol Immunol 23:308–314
Minnikin DE, Minnikin SM, Goodfellow M, Stanford JL (1982) The mycolic acids of Mycobacterium chelonei. J Gen Microbiol 128:817–822
Na SI, Kim YO, Yoon SH, Ha SM, Baek I et al (2018) UBCG: Up-to-date bacterial core gene set and pipeline for phylogenomic tree reconstruction. J Microbiol 56:280–285
Ogura T, Bouloc P, Niki H, D’Ari R, Hiraga S, Jaffé A (1989) Penicillin-binding protein 2 is essential in wild-type Escherichia coli but not in lov or cya mutants. J Bacteriol 171:3025–30
Parte AC, Carbasse JS, Meier-Kolthoff JP, Reimer LC, Göker M (2020) List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) moves to the DSMZ. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:5607–5612
Pimentel-Elardo S, Wehrl M, Friedrich AB, Schlesner H, Jensen PR et al (2003) Isolation of Planctomycetes from Aplysina sponges. Aquat Microb Ecol 33:239–245
Piotr S, Elzbieta DZ (2001) “Liquidless” cell staining by dye diffusion from gels and analysis by laser scanning cytometry: Potential application at microgravity conditions in space. Cytometry 44:355–360
Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP (2010) FastTree 2-Approximately Maximum-Likelihood Trees for Large Alignments. PloS One 5:e9490
Qin QL, Xie BB, Zhang XY, Chen XL, Zhou BC (2014) A proposed genus boundary for the prokaryotes based on genomic insights. J Bacteriol 196:2210–2215
Rodriguez-R LM, Konstantinidis KT (2014) Bypassing cultivation to identify bacterial species. Microbe 9:111–118
Saier MH, Tran CV, Barabote RD (2006) TCDB: the Transporter Classification Database for membrane transport protein analyses and information. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D181
Sait M, Kamneva OK, Fay DS, Kirienko NV, Polek J et al (2011) Genomic and experimental evidence suggests that Verrucomicrobium spinosum interacts with eukaryotes. Front Microbiol 18(2):211
Scheuermayer M, Gulder T, Bringmann G (2006) Rubritalea marina gen. nov., sp. nov., a marine representative of the phylum “Verrucomicrobia”, isolated from a sponge (Porifera). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2119–2124
Simon A, Adam A, Vermeesch JR, Hestand MS (2018) Single molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing comes of age: applications and utilities for medical diagnostics. Nucleic Acids Res 46:2159–2168
Spring S, Bunk B, Spröer C, Schumann P, Rohde M et al (2016) Characterization of the first cultured representative of Verrucomicrobia subdivision 5 indicates the proposal of a novel phylum. ISME J 10:2801–2816
Tatusov RL, Fedorova ND, Jackson JD, Jacobs AR, Kiryutin B et al (2003) The COG database: an updated version includes eukaryotes. BMC Bioinformatics 4:41–41
Vaughan S, Wickstead B, Gull K, Addinall SG (2004) Molecular evolution of FtsZ protein sequences encoded within the genomes of Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukaryota. J Mol Evol 58:19–29
Wagner M, Horn M (2006) The Planctomycetes, Verrucomicrobia, Chlamydiae and sister phyla comprise a superphylum with biotechnological and medical relevance. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:241–249
Wiegand S, Jogler M, Boedeker C, Pinto D, Vollmers J et al (2020) Cultivation and functional characterization of 79 planctomycetes uncovers their unique biology. Nat Microbiol 5:126–140
Yarza P, Yilmaz P, Pruesse E, Glöckner FO, Ludwig W et al (2014) Uniting the classification of cultured and uncultured bacteria and archaea using 16S rRNA gene sequences. Nat Rev Microbiol 12:635–645
Yoon J, Matsuo Y, Matsuda S, Adachi K, Kasai H et al (2007) Rubritalea spongiae sp. nov. and Rubritalea tangerina sp. nov., two carotenoid- and squalene-producing marine bacteria of the family Verrucomicrobiaceae within the phylum “Verrucomicrobia”, isolated from marine animals. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2337–2343
Yoon J, Matsuo Y, Katsuta A, Jang JH, Matsuda S et al (2008a) Haloferula rosea gen. nov., sp. nov., Haloferula harenae sp. nov., Haloferula phyci sp. nov., Haloferula helveola sp. nov. and Haloferula sargassicola sp. nov., five marine representatives of the family Verrucomicrobiaceae within the phylum 'Verrucomicrobia’. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2491–2500
Yoon J, Matsuo Y, Adachi K, Nozawa M, Matsuda SH et al (2008b) Description of Persicirhabdus sediminis gen. nov., sp. nov., Roseibacillus ishigakijimensis gen. nov., sp. nov., Roseibacillus ponti sp. nov., Roseibacillus persicicus sp. nov., Luteolibacter pohnpeiensis gen. nov., sp. nov. and Luteolibacter algae sp. nov., six marine members of the phylum “Verrucomicrobia”, and emended descriptions of the class Verrucomicrobiae, the order Verrucomicrobiales and the family Verrucomicrobiaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:998–1007
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Lim J, Kwon S, Chun J (2017) A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 110:1281–1286
Acknowledgements
Scanning electron microscopy was supported by the Physical-Chemical Materials Analytical & Testing Centre of Shandong University at Weihai. We would also like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for English language editing.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32070002, 31770002) and National Science and Technology Fundamental Resources Investigation Program of China (2019FY100700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XF performed most of the experiments, wrote the main part of the manuscript, and functions as the first author. QHZ helped with the isolation of the novel strain and with cultivation measurements. MQY contributed to the literature search and analysed the sequencing data. XF and ZJD designed the study and helped with experimental setups and design.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, X., Liang, QY., Zou, QH. et al. Sulfuriroseicoccus oceanibius gen. nov., sp. nov., a representative of the phylum Verrucomicrobia with a special cytoplasmic membrane. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 115, 337–352 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-021-01689-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-021-01689-2