Abstract
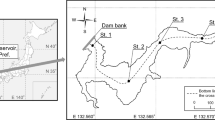
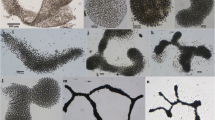
The previous studies indicated that Tychonema-like strains from Lake Erhai could release geosmin so that the species was listed as the potential harmful cyanobacteria influencing the drinking water safety around Lake Erhai. But, the dynamics and biological information of this species were too limited. In this study, the polyphasic approach was used to reveal its biological characterization and the dynamics in Lake Erhai. The characters of trichomes, including filaments with solitary or bundle state, reddish-brown or blue-green color, planktonic habitat, and presence of keritomized content, were examined by the microscopic method. The 16S rDNA sequences of these strains were used for phylogenetic analysis and molecular identification. The strains were morphologically classified as Tychonema bourrellyi, and geosmin and β-ionone were identified as the major volatile substances using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis. No strains of T. bourrellyi were found to produce microcystin by the HPLC and mcy gene approaches. Cell numbers at 12 sampling sites in Lake Erhai were shown as an average of 3 × 104 cells L−1 in 2009 and 2010. The obvious peaks occurred in July and August each year. This was the first report on occurrence of T. bourrellyi from outside of Europe, and T. bourrellyi was also a newly recorded species in China. Such a result demonstrated that T. bourrellyi could distribute extending from cold waters in North Europe to the warm waters in subtropical regions. It was interesting to observe the coincidence of the occurrence of T. bourrellyi with slightly eutrophicated waters since Lake Erhai had been regarded as an early phase of eutrophicated lake.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen MM (1984) Cyanobacterial cell inclusions. Annu Rev Microbiol 38:1–25
Anagnostidis K, Komárek J (1988) Modern approach to the classification system of cyanophytes 3 – Oscillatoriales. Algol Stud 50–53:327–472
Berglind L, Holtan H, Skulberg OM (1983) Case studies on off-flavours in some Norwegian lakes. Water Sci Technol 15:199–209
Brookes JD, Ganf GG (2001) Variations in the buoyancy response of Microcystis aeruginosa to nitrogen, phosphorus and light. J Plankton Res 23:1399–1411
Camacho A, Garcia-Pichel F, Vicente E, Castenholz RW (1996) Adaptation to sulfide and to the underwater light field in three cyanobacterial isolates from Lake Arcas (Spain). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 21(4):293–301
Carmichael WW (2001) Health effects of toxin-producing cyanobacteria: “The CyanoHABs”. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 7(5):1393–1407
Cook D, Newcombe G, Sztajnbok P (2001) The application of powdered activated carbon for MIB and geosmin removal: predicting PAC doses in four raw waters. Water Res 35:1325–1333
Dionigi CP, Lawlor TE, McFarland JE, Johnsen PB (1993) Evaluation of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol on the histidine dependence of TA98 and TA100 Salmonella typhimurium tester strains. Water Res 27:1615–1618
Ganf GG, Heaney SI, Corry J (1991) Light absorption and pigment content in natural populations and cultures of a non-gas vacuolate cyanobacterium Oscillatoria bourrellyi (= Tychomema bourrellyi). J Plankton Res 13(5):1101–1121
Geitler L (1932) Cyanophyceae. In: Rabenhorst L (ed) Kryptogamen Flora von Deutschland, Osterreich und der Schweiz 14. Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft, Leipzig, pp 130–159 (in German)
Guindon S, Gascuel O (2003) A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol 52:696–704
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hu HJ, Wei YX (2006) The freshwater algae of China: systematics, taxonomy, and ecology. Science Press, Beijing, pp 125–126 (in Chinese)
Izaguirre G, Taylor WD (2004) A guide to geosmin- and MIB-producing cyanobacteria in the United States. Water Sci Technol 49:19–24
Jacobson L, Halmann M (1982) Polyphosphate metabolism in the blue-green alga Microcystis aeruginosa. J Plankton Res 4:481–488
Jochimsen EM, Carmichael WW, An J, Cardo DM, Cookson ST, Holmes CEM, Antunes CMB, Melo FDA, Lyra TM, Barreto VST, Azevedo SMFO, Jarvis WR (1998) Liver failure and death after exposure to microcystins at a hemodialysis center in Brazil. N Engl J Med 338(13):873–878
Jüttner F, Watson SB (2007) Biochemical and ecological control of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in source waters. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(14):4395–4406
Kameyama K, Sugiura N, Isoda H, Maekawa T (2002) Effects of nitrate and phosphate concentration on production of microcystins by Microcystis viridis NIES-102. Aquat Ecosyst Health Manage 5(4):443–449
Kasai F, Kawachi M, Erata M, Mori F, Yumoto K, Sato M, Ishimoto M (2009) NIES-Collection, List of Strains, 8th edn. Jap J Phycol 57(1):216–217
Komárek J, Albertano P (1994) Cell structure of a planktic cyanoprokaryote, Tychonema bourrellyi. Algol Stud 75:157–166
Komárek J, Anagnostidis K (2005) Cyanoprokaryota–2. Teil: Oscillatoriales. Elsevier GmbH, Heifelberg, p 70
Komárek J, Kaštovsky J, Mareš J, Johansen JR (2014) Taxonomic classification of cyanoprokaryotes (cyanobacterial genera) 2014, using a polyphasic approach. Preslia 86:295–335
Lin S, Wu ZX, Yu GL, Zhu ML, Yu BS, Li RH (2010) Genetic diversity and molecular phylogeny of Planktothrix (Oscillatoriales, cyanobacteria) strains from China. Harmful Algae 9:87–97
Lin S, Shen JZ, Liu Y, Liu Q, Li RH (2011) Molecular evaluation on the distribution, diversity and toxicity of Microcystis (Cyanobacteria) species from Lake Ulungur: a mesotrophic and brackish desert lake in Xinjiang, China. Environ Monit Assess 175:139–150
Lund JWG (1955) Contribution to our knowledge of British algae, VIV. Three new species from the English Lake District. Hydrobiologia 7:219–229
Neilan BA, Jacobs D, Del Dot T, Blackall LL, Hawkins PR, Cox PT, Goodman AE (1997) rRNA sequences and evolutionary relationships among toxic and non-toxic cyanobacteria of the genus Microcystis. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47(3):693–697
Nübel U, Garcia-Pichel F, Muyzer G (1997) PCR Primers to amplify 16S rRNA genes from cyanobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3327–3332
Ojala A (1993) The influence of light quality on growth and phycobiliprotein/chlorophyll a fluorescence quotients of some species of freshwater algae in culture. Phycologia 32(1):22–28
Otten TG, Xu H, Qin BQ, Zhu G, Paerl HW (2012) Spatiotemporal patterns and ecophysiology of toxigenic Microcystis blooms in Lake Taihu, China: implications for water quality management. Environ Sci Technol 46(6):3480–3488
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) Modeltest: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14(9):817–818
Revaclier R. (1978) Examens biologiques des eaux du Léman, étude du phytoplancton. Rapports de la commission internationale pour la protection des eaux du Léman contre la pollution, 99–166
Rippka R (1988) Isolation and purification of cyanobacteria. Methods Enzymol 167:3–27
Shao JH, Xu Y, Wang ZJ, Jiang YG, Yu GL, Peng X, Li RH (2011) Elucidating the toxicity targets of β-ionone on photosynthetic system of Microcystis aeruginosa NIES-843 (Cyanobacteria). Aquat Toxicol 104:48–55
Shao JH, Peng L, Luo S, Yu GL, Gu JD, Lin S, Li RH (2013) First report on the allelopathic effect of Tychonema bourrellyi (Cyanobacteria) against Microcystis aeruginosa (Cyanobacteria). J Appl Phycol 25:1567–1573
Skulberg OM, Skulgerg R (1991) A comparative investigation and taxonomic relationship of Tychonema tenuis and Tychonema bourrellyi. Algol Stud 64:271–279
Sommer U (1985) Comparison between steady-state and non-steady state competition: experiments with natural phytoplankton. Limnol Oceanogr 30(2):335–346
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Wang SM, Dou HS (1998) A directory of lakes in China. Science Press, Beijing, p 580 (in Chinese)
Wang Z, Wang YC, Hu MM, Li YH, Liu YD, Shen YW, Li GB, Wang GH (2011) Succession of the phytoplankton community in response to environmental factors in north Lake Erhai during 2009–2010. Fresenius Environ Bull 20(9):2221–2231
Wei ZH, Zhu ML, Yu GL, Li RH (2012) Occurrence of planktonic cyanobaterium Tychonema bourrellyi in Erhai Lake and its taxonomic studies. Acta Hydrobiol Sin 36(6):1171–1175 (in Chinese)
WHO (World Health Organization) (2006) Guidelines for drinking water quality, first adendum to third ed. recommendations. 1 Geneva 195
Wu SK, Xie P, Liang GD, Wang SB, Liang XM (2006) Relationships between microcystins and environmental parameters in 30 subtropical shallow lakes along the Yangtze River, China. Freshw Biol 51:2309–2319
Yu GL, Jiang YG, Song GF, Tan WH, Zhu ML, Li RH (2014) Variation of Microcystis and microcystins coupling nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients in Lake Erhai, a drinking-water source in southwest plateau. China Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:9887–9898
Yu GL, Zhu ML, Chen YX, Pan QQ, Chai WB, Li RH (2015) Polyphasic characterization of four species of Pseudanabaena (Oscillatoriales, Cyanobacteria) from China and insights into polyphyletic divergence within the Pseudanabaena genus. Phytotaxa 192(1):1–12
Yuan L, Zhu W, Xiao L, Yang LY (2009) Phosphorus cycling between the colonial cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa and attached bacteria, Pseudomonas. Aquat Ecol 43(4):859–866
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (No. 2012ZX07105-004), also by JSPS RONPAKU (Dissertation PhD) Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Song, G., Shao, J. et al. Dynamics and polyphasic characterization of odor-producing cyanobacterium Tychonema bourrellyi from Lake Erhai, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 5420–5430 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5749-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5749-z