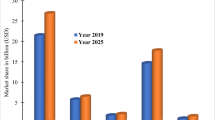
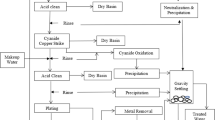
Abstract
Produced water is the largest liquid effluent in volume generated in petroleum production. It originates from natural wells or from water that was previously injected during the exploration process. The composition of produced water is complex, containing high salt concentration, emulsified oil, suspended solids, chemical additives used in the various stages of oil production, heavy metals, and other contaminants. Several technologies can be used in the treatment of produced water in order to meet the conditions specified in local legislations and the most used are phase separators, decanters, cyclones, and filters. The separation process mechanism of oil emulsions by coalescence in fibrous media has excellent results, though it is not fully understood and is frequently based on empirical, as well as on experimental, observations. This article presents a general overview on produced water, including origin, production, composition, environmental impact, treatment techniques, disposal, and legislation, as well as an updated discussion utilizing recent literature regarding the unit operation of coalescence: general aspects, kinetics, mechanisms, and factors that influence the coalescence process.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
ACS Industries (2006) Liquid-liquid coalescer design manual. Separations Technology Division 18:20
Adamson AW (1990) Physical chemical of surfaces – 5a EDITION. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken
Agarwal S, Von Arnim V, Stegmaier T, Planck H, Agarwal A (2013) Effect of fibrous coalescer geometry and operating conditions on emulsion separation. Ind Eng Chem Res 52(36):13164–13170
Agency, International Energy (2018) World energy balances: an overview.
Almeida FBPS, Meili L, Esquerre KPSOR, Ribeiro LMO, Silva C, E F (2019) Oil producedwater treatment using sugarcane solid residue as biosorbent. Rev Mex Ing Quím 18(1):27–38
Amini S, Mowla D, Golkar M, Esmaeilzadeh F (2012) Mathematical modelling of a hydrocyclone for the down-hole oil-water separation (DOWS). Chem Eng Res Des 90(12):2186–2195
Arthur JD, Dillon LW, Drazan DJ (2011) Management of produced water from oil and gas wells. Management of Produced Water:1–32
Austin DG (1979) Coalescence of secundary dispersions. University of Aston, Birmingham
Bufo MJ (2006) Coalescência de Imiscíveis em Filme de Água Residuária, Universidade Estadual de Campinas. BusinessDictionary.http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/environmental-impact.html.Accessed 14 December 2018
Cerqueira AA, Regina M, Russo AC (2009) Gestão das Águas de Produção: Histórico, Políticas Ambientais e Alternativa Tecnológica. Revista Uniara 12(December):21–36
Clayfield, Eric J., A. Graham Dixon, Andrew W. Foulds, and R. J Lionel Miller (1985). The coalescence of secondary dispersions: II. The role of electrokinetic properties in determining coalescence performance. Journal of Colloid And Interface Science 104(2):500–511.
Conama 393 (2007). Resolução CONAMA 393/2007. Diário Oficial Da União, Brazil
CONAMA 430 (2011). Resolução CONAMA 430/2011. Diário Oficial Da União, Brazil.
Crittenden JC, Suri RPS, Perram DL, Hand DW (1997) Decontamination of water using adsorption and photocatalysis. Pergamon 31(3):411–418
da Motta ARP (2014) Tratamento de Água Produzida de Petróleo para Remoção de Óleo através da Integração dos Processos com Coalescedor em Leito e Microfiltração. Universidade Federal da Bahia, Salvador
Dacal (2017) Remoção do Óleo da Água Produzida de Petróleo Utilizando Leitos Coalescedores de Fibra de Coco e Fibra Sintética. Universidade Federal de Alagoas
Daigle TP (2012) Ultra deep water discharge of produced water and/or solids at the seabed. Research Partnership to Secure Energy for America (RPSEA)
Danov KD, Stoyanov SD, Vitanov NK, Ivanov IB (2012) Role of surfactants on the approaching velocity of two small emulsion drops. J Colloid Interface Sci 368:342–355
Dezhi S, Shik Chung J, Xiaodong D, Ding Z (1999) Demulsification of water-in-oil emulsion by wetting coalescence materials in stirred- and packed-columns. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 150(1–3):69–75
Do Carmo S, Alves Neto TL, Oliveira GN, de Castro VD, Figueiredo KC d S (2017) Tratamento de Água Produzida de Petróleo Utilizando Microfiltração. E-Xacta 10(2):95
Dores R, Hussain A, Katebah M, Adham S, Conocophillips Global, Water Sustainability (2012) Using advanced water treatment technologies to treat produced water from the petroleum industry. SPE International no. 157108
Duraisamy RT, Beni AH, Henni A (2013) Chapter 9: state of the art treatment of produced water. In: Water Treatment. Elshorbagy, W and Chowdhury, R. https://doi.org/10.5772/53478
Fakhru’l-Razi A, Pendashteh A, Abdullah LC, Biak DRA, Madaeni SS, Abidin ZZ (2009) Review of technologies for oil and gas produced water treatment. J Hazard Mater 170(2–3):530–551
Fonte SSD, Simonelli G, Santos LCL (2018) A review of the main techniques to avoid the formation of hydrates. Braz J Pet Gas 12:61–73
Gabardo IT (2007) Caracterização Química e Toxicológica da Água Produzida Descartada em Plataformas de Óleo e Gás na Costa Brasileira e seu Comportamento Dispersivo no Mar. Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte, Tese de doutorado.
Govedarica DD, Sokolovic RMS, Sokolović DS, Sokolović SM (2013) A novel approach for the estimation of the efficiency of steady-state fiber bed coalescence. Sep Purif Technol 104:268–275
Govedarica DD, Radmila M, Sokolovic S, Kiralj AI, Govedarica OM, Sokolovic DS, Hadnadjev-Kostic MS (2015) Separation of mineral oil droplets using polypropylene fibre bed coalescence. Hemijska Industrija 69(4):339–345
Guerra K, Dahm K, Dundorf S (2011) Oil and gas produced water management and beneficial use in the Western United States. U.S. Department of the Interior Bureau of Reclamation, Managing Water in the West, no. 157, p 129
Haarhoff J, Edzwald JK (2013) Adapting dissolved air Fl Otation for the Clari Fi Cation of Seawater. Desalination 311:90–94
Hazlett RN (1969) Fibrous bed coalescence of water: role of a sulfonate surfactant in the coalescence process. Ind Eng Chem Fundam 8(4):633–640
Igunnu ET, Chen GZ (2014) Produced water treatment technologies. Int J Low-Carbon Technol 9(3):157–177
Jeffreys, G.V. and Hawksley, J.L. (1965). Coalescence of liquid droplets in two-component two-phase systems. – A.I.Ch.E Journal vol 11, n° 3.
Ji F, Li C, Dong X, Li Y, Wang D (2009) Separation of oil from oily wastewater by sorption and coalescence technique using ethanol grafted polyacrylonitrile. J Hazard Mater 164(2–3):1346–1351
Jiménez S, Micó MM, Arnaldos M, Medina F, Contreras S (2018) State of the art of produced water treatment. Chemosphere 192:186–208
Kolmetz K (2012) KLM technology group practical engineering guidelines for processing plant solutions coalescer (Engineering Design Guideline).
Kunert R, Luis Figueira da Silva A, Erasmo de Souza Filho J, Ramalho JBV d S, Melo M d V, Leite M d M, do Brasil NÍ (2007) Processamento Primário de Petróleo. Universidade Petrobras - Escola de Ciências e Tecnologia E&P, p 53
Langdon WM, Naik PP, Wasan DT (1972) Separation of oil dispersions from water by fibrous bed coalescence. Environ Sci Technol 6(10):905–910
Langmuir I. (1942) OSRD report 865, Office of the Scientific Research and Development, Government Report
Leva M (1953) Tower packings and packed tower design – 2a edition. Stoneware Company, USA
Li J, Gu Y (2005) Coalescence of oil-in-water emulsions in fibrous and granular beds. Sep Purif Technol 42(1):1–13
Lu H, Yang Q, Liu S, Xie LS, Wang HL (2016a) Effect of fibrous coalescer redispersion on W/O emulsion separation. In: Separation and Purification Technology, vol 159. Elsevier B.V, Amsterdam, pp 50–56
Lu H, Yang Q, Xu X, Wang HL (2016b) Effect of the mixed oleophilic fibrous coalescer geometry and the operating conditions on oily wastewater separation. Chem Eng Technol 39(2):255–262
Lucchesi CF (1998) Petróleo. Estudos Avançados 12(33):17–40
Ma S, Kang Y, Cui S (2014) Oil and water separation using a glass microfiber coalescing bed. J Dispers Sci Technol 35(1):103–110
Madia JR, Fruh SM, Miller CA, Beerbower A (1976) Granular packed bed coalescer: influence of packing wettability on coalescence. Environ Sci Technol 10(10):1044–1046
Motta A, Borges C, Esquerre K, Kiperstok A (2014) Oil produced water treatment for oil removal by an integration of coalescer bed and microfiltration membrane processes. Journal of Membrane Science 469. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 371–378
Mouchet P, Berne F. e Puill A (1984). La coalescence sur sable: Principe du procédé et son application à la récupération des solvants en hydrométallurgie – Industrie Minérale – Les Techiques
Neff JM, Lee K, Deblois EM (2011) Produced water: overview of composition, fates, and effect. In: Lee K, Neff J (eds) Produced Water. Springer, New York, NY
Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (2018). World Oil Outlook 2040.
Ospar Commission (2007). Background document to support the assessment of whether the OSPAR network of marine protected areas is ecologically coherent ospar commission.
Patel NM (1975) Wastewater treatment using combined techniques of sand filtration an coalescence in fibrous media. University of Texas
Reynolds RR, Kiker RD (2003) Produced water and associated issues — a manual for the independent operator. In: Oklahoma Geological Survey Open File Report, vol 21
Sareen, S. S.; Rose, P. M.; Gudsen, R. C. e Kintner, R. C. (1966). Coalescence in fibrous beds. – A.I.Ch. E Journal – vol 12, n° 6, 1966
Sharifi H, Shaw JM (1996). Secondary Drop Production in Packed-Bed Coalescers. Chem Eng Sci 51(21):4817–26
Shokrollahzadeh S, Golmohammad F, Naseri N, Shokouhi H (2012) Chemical oxidation for removal of hydrocarbons from gas- field produced water. Procedia Eng 42(August):942–947
Sokolovic S, Radmila M, Sokolović SM, Cross BD, Signoković D (1997) Effect of working conditions on bed coalescence of an oil-in-water emulsion using a polyurethane foam bed. Ind Eng Chem Res 36(11):4949–4953
Sokolovic S, Radmila M, Vulić TJ, Sokolović SM, Nedučin RPM (2003) Effect of fibrous bed permeability on steady-state coalescence. Ind Eng Chem Res 42(13):3098–3102
Sokolovic S, Radmila M, Vulić TJ, Sokolović SM (2006) Effect of fluid flow orientation on the coalescence of oil droplets in steady-state bed coalescers. Ind Eng Chem Res 45(11):3891–3895
Sokolović S, Radmila SS, Šević S (2009) Oily water treatment using a new steady-state fiber-bed coalescer. J Hazard Mater 162(1):410–415
Sokolovic RM, Govedarica DD, Sokolovic DS (2010) Separation of oil-in-water emulsion using two coalescers of different geometry. J Hazard Mater 175(1–3):1001–1006
Sokolovic S, Radmila M, Govedarica DD (2014) Selection of filter media for steady-state bed coalescers. Ind Eng Chem Res 53(6):2484–2490
Sokolović S, Radmila M, Sokolović DS, Govedarica DD (2016) Liquid–liquid separation using steady-state bed coalescer. Hemijska Industrija 70(4):367–381
Spielman LA (1968) Separation of finely dispersed liquid–liquid suspensions by flow through fibrous media. University of California, Berkeley
Spielman LA, Fitzpatrick JA (1974) (1974). Role of the electrical double layer in particle deposition by convective diffusion. J Colloid Interface Sci [Sl] 46(1):22–31
Tadros TF (2013) Emulsion formation,stability, and rheology. In: Emulsion Formation and Stability, pp 1–76
Technology, Pgt - Petroleum Geoscience (2012). Geologia do Petróleo 24. https://albertowj.files.wordpress.com/2010/03/geologia_do_petroleo.pdf.
Tellez GT, Nirmalakhandan N, Gardea-torresdey JL (2002) Performance evaluation of an activated sludge system for removing petroleum hydrocarbons from oilfield produced water. Adv Environ Res 6:455–470
Thomas, E. J. (2004). Fundamentos de Engenharia de Petróleo. 2a. Interciência.
Veil J (2012) U . S . Produced water volumes and management practices in 2012. Ground Water Protection Council, no. April, p 2015
Veil JA, Puder MG, Elcock D, Redweik RJ Jr (2004) A white paper describing produced water from production of crude oil, natural gas, and coal bed methane. U.S. Department of Energy, Energy Technology Laboratory no. January: 87
Xia Y, Boufadel MC (2010) Lessons from the Exxon Valdez oil spill disaster in Alaska. In: Disaster Advances n°3 (December)
Acknowledgments
F.B.P.S. Almeida acknowledges the financial support from the Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology of Alagoas and Separation Systems and Process Optimization Laboratory for the determinations and facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Silva Almeida, F.B.P., Esquerre, K.P.S.O.R., Soletti, J.I. et al. Coalescence process to treat produced water: an updated overview and environmental outlook. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 28668–28688 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06016-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06016-x