Abstract
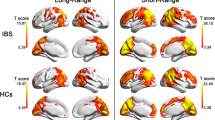
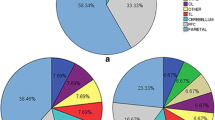
The postcentral cortex (poCC) is commonly found to respond to visceral stimulation, but researchers usually pay less attention to this role of the poCC in the patients with functional gastrointestinal disorders, because it is a primary receptor for general bodily feeling of touch, such as temperature and pain. The current study focuses on the changes around the poCC in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) patients based on the resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging, aiming to investigate whether the poCC-centric brain metrics may be directly related to visceral perception. In the study, we calculated the regional homogeneity, seed-based correlation (SBC) and nodal centralities of the poCC to explore the changes in the regional activity and information flow around the poCC in IBS patients. Moreover, we examined the performance of the poCC-centric features in classifying the IBS group and healthy group in comparison to those features unrelated to the poCC. The results found that central alterations around the poCC in IBS patients were associated with the level of visceral pain, and exhibited a better discriminative power than those around the whole brain and the insula when classifying the IBS group and healthy group. In conclusion, the preliminary investigation provided fundamental advances in understanding the roles of the poCC in the pathphysiology of the IBS.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aziz, Q., Thompson, D. G., Ng, V. W. K., Hamdy, S., Sarkar, S., Brammer, M. J., et al. (2000). Cortical processing of human somatic and visceral sensation. Journal of Neuroscience, 20(7), 2657–2663.
Bullmore, E. T., & Bassett, D. S. (2011). Brain graphs: Graphical models of the human brain connectome. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 7, 113–140.
Bullmore, E., & Sporns, O. (2009). Complex brain networks: Graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 10(3), 186–198.
Chassany, O., Bonaz, B., Bruley Des Varannes, S., Bueno, L., Cargill, G., Coffin, B., et al. (2007). Acute exacerbation of pain in irritable bowel syndrome: Efficacy of phloroglucinol/trimethylphloroglucinol–a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 25(9), 1115–1123.
Chen, J. Y.-W., Blankstein, U., Diamant, N. E., & Davis, K. D. (2011). White matter abnormalities in irritable bowel syndrome and relation to individual factors. Brain Research, 1392, 121–131.
Chudler, E. H., Anton, F., Dubner, R., & Kenshalo, D. R. (1990). Responses of nociceptive SI neurons in monkeys and pain sensation in humans elicited by noxious thermal stimulation: Effect of interstimulus interval. Journal of Neurophysiology, 63(3), 559–569.
Coen, S. J., Aziz, Q., Yágüez, L., Brammer, M., Williams, S. C., & Gregory, L. J. (2008). Effects of attention on visceral stimulus intensity encoding in the male human brain. Gastroenterology, 135(6), 2065–2074.
Craig, A. (2003). Interoception: The sense of the physiological condition of the body. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 13(4), 500–505.
Critchley, H. D., & Harrison, N. A. (2013). Visceral influences on brain and behavior. Neuron, 77(4), 624–638.
Drossman, D. A., & Dumitrascu, D. L. (2006). Rome III: New standard for functional gastrointestinal disorders. Journal of Gastrointestinal and Liver Diseases, 15(3), 237.
Ellingson, B. M., Mayer, E., Harris, R. J., Ashe-McNally, C., Naliboff, B. D., Labus, J. S., et al. (2013). Diffusion tensor imaging detects microstructural reorganization in the brain associated with chronic irritable bowel syndrome. PAIN, 154(9), 1528–1541.
Frøkjær, J. B., Olesen, S. S., Gram, M., Yavarian, Y., Bouwense, S. A., Wilder-Smith, O. H., et al. (2011). Altered brain microstructure assessed by diffusion tensor imaging in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Gut, 60(11), 1554–1562.
Hong, J. Y., Labus, J. S., Jiang, Z., Ashe-McNalley, C., Dinov, I., Gupta, A., et al. (2014). Regional neuroplastic brain changes in patients with chronic inflammatory and non-inflammatory visceral pain. PLoS One, 9(1), e84564.
Ito, S. I. (2002). Visceral region in the rat primary somatosensory cortex identified by vagal evoked potential. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 444(1), 10–24.
Jiang, Z., Dinov, I. D., Labus, J., Shi, Y., Zamanyan, A., Gupta, A., et al. (2013). Sex-related differences of cortical thickness in patients with chronic abdominal pain. PLoS One, 8(9), e73932.
Kairys, A. E., Schmidt-Wilcke, T., Puiu, T., Ichesco, E., Labus, J. S., Martucci, K., et al. (2015). Increased brain gray matter in the primary somatosensory cortex is associated with increased pain and mood disturbance in patients with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. The Journal of Urology, 193(1), 131–137.
Kilpatrick, L. A., Kutch, J. J., Tillisch, K., Naliboff, B. D., Labus, J. S., Jiang, Z., et al. (2014). Alterations in resting state oscillations and connectivity in sensory and motor networks in women with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. The Journal of Urology, 192(3), 947–955.
Leung, C., & Chau, H. (2007). Weighted assortative and disassortative networks model. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 378(2), 591–602.
Li, L., Wang, H., & Shen, Y. (2003). Chinese SF-36 health survey: Translation, cultural adaptation, validation, and normalisation. Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health, 57(4), 259–263.
Liu, P., Qin, W., Wang, J., Zeng, F., Zhou, G., Wen, H., et al. (2013). Identifying neural patterns of functional dyspepsia using multivariate pattern analysis: A resting-state fMRI study. PLoS One, 8(7), e68205.
Mayer, E. A., Aziz, Q., Coen, S., Kern, M., Labus, J. S., Lane, R., et al. (2009). Brain imaging approaches to the study of functional GI disorders: A Rome working team report. Neurogastroent Motil, 21(6), 579–596.
Mayer, E. A., Gupta, A., Kilpatrick, L. A., & Hong, J. Y. (2015). Imaging brain mechanisms in chronic visceral pain. Pain, 156(Suppl 1), S50–S63. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000106.
Newman, M. E. (2002). Assortative mixing in networks. Physical Review Letters, 89(20), 208701.
Newman, M. E. (2006). Finding community structure in networks using the eigenvectors of matrices. Physical Review E, 74(3), 036104.
Newman, M. E., & Girvan, M. (2004). Finding and evaluating community structure in networks. Physical Review E, 69(2), 026113.
Ostrowsky, K., Isnard, J., Ryvlin, P., Guenot, M., Fischer, C., & Mauguiere, F. (2000). Functional mapping of the insular cortex: Clinical implication in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia, 41(6), 681–686.
Ravasz, E., & Barabási, A.-L. (2003). Hierarchical organization in complex networks. Physical Review E, 67(2), 026112.
Schnitzler, A., & Ploner, M. (2000). Neurophysiology and functional neuroanatomy of pain perception. Journal of Clinical Neurophysiology, 17(6), 592–603.
Spiegel, B., Bolus, R., Harris, L. A., Lucak, S., Naliboff, B., Esrailian, E., et al. (2009). Measuring irritable bowel syndrome patient-reported outcomes with an abdominal pain numeric rating scale. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 30(11–12), 1159–1170.
Stephani, C., Vaca, G. F.-B., Maciunas, R., Koubeissi, M., & Lüders, H. (2011). Functional neuroanatomy of the insular lobe. Brain Structure and Function, 216(2), 137–149.
Strickland, A., Spiegel, B., Naliboff, B. D., Mayer, E. A., & Chang, L. (2008). Predictors of patient-assessed illness severity in irritable bowel syndrome. The American Journal of Gastroenterology, 103(10), 2536.
Tillisch, K., Mayer, E. A., & Labus, J. S. (2011). Quantitative meta-analysis identifies brain regions activated during rectal distension in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology, 140(1), 91–100.
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Landeau, B., Papathanassiou, D., Crivello, F., Etard, O., Delcroix, N., et al. (2002). Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage, 15(1), 273–289.
Wang, J., Zuo, X., & He, Y. (2010). Graph-based network analysis of resting-state functional MRI. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 4.
Wang, J., Wang, X., Xia, M., Liao, X., Evans, A., & He, Y. (2015). GRETNA: A graph theoretical network analysis toolbox for imaging connectomics. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 9, 386.
Wood, J. (1987). Physiology of the enteric nervous system. Physiology of the gastrointestinal tract.
Yan, C.-G., Wang, X.-D., Zuo, X.-N., & Zang, Y.-F. (2016). DPABI: Data processing & analysis for (resting-state) brain imaging. Neuroinformatics, 14(3), 339–351.
Zang, Y., Jiang, T., Lu, Y., He, Y., & Tian, L. (2004). Regional homogeneity approach to fMRI data analysis. Neuroimage, 22(1), 394–400.
Zeng, F., Qin, W., Yang, Y., Zhang, D., Liu, J., Zhou, G., et al. (2013). Regional brain structural abnormality in meal-related functional dyspepsia patients: A voxel-based morphometry study. PLoS One, 8(7), e68383.
Zhong, Y., Lu, G., Zhang, Z., Jiao, Q., Li, K., & Liu, Y. (2011). Altered regional synchronization in epileptic patients with generalized tonic–clonic seizures. Epilepsy Research, 97(1), 83–91.
Zung, W. W. K. (1971). A rating instrument for anxiety disorders. Psychosomatics, 12(6), 371–379.
Zung, W. W. K., Richards, C. B., & Short, M. J. (1965). Self-rating depression scale in an outpatient clinic: Further validation of the SDS. Arch Gen Psychiat, 13(6), 508–515.
Funding
This work was supported by the Project for the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant numbers 81501547, 61602423, and 81501548]; and the Science and Technology Planning Program of Henan Province [grant numbers 172106000074, 172102410080, 172102410088 and 172102210063].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jiaofen Nan: processing data, interpreting data and drafting the article; Wenya Yang and Panting Meng: processing data and interpreting data; Wei Huang: analyzing data; Qian Zheng: processing data; Yongquan Xia: designing the study and collecting the data; Feng Liu: providing numerous helpful suggesstions for writing the manuscript and discussing the results.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nan, J., Yang, W., Meng, P. et al. Changes of the postcentral cortex in irritable bowel syndrome patients. Brain Imaging and Behavior 14, 1566–1576 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00087-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00087-7