Abstract
Based on the current theory of sequence stratigraphy, this study employs stillstand normal regression (SNR) to replace the method of highstand normal regression (HNR) to establish shoreline trajectory and sediment supply models of off-lap and onlap-type sequences, respectively. The basic principle of the digital model-driven approach in this study is to decompose the shoreline trajectory (fst) and sediment supply trajectory (fss) into their vertical and horizontal projection vectors to establish periodic sufficient condition of shoreline trajectory and sediment supply trajectory, aiming to obtain a sequence model bounded by the remnant maximum flooding surface (RMFS) and/or its intersecting subaerial unconformity (ISU): HST (SNR)-FSST (FR)-LST (LNR)-TST (T). This model establishes the synchronic necessary condition of shoreline trajectory and sediment supply trajectory and obtains the periodic law patterns of sequence stratigraphy, proposed as “two rhombuses sandwiching one extension of subaerial unconformity”. This study defines a sequence as: a sequence is a stratigraphic unit (“two rhombuses sandwiching one extension of subaerial unconformity”) constrained by both periodic sufficient condition and synchronic necessary condition of shoreline and sediment supply trajectories, and is composed of a relatively conformable succession of genetically interrelated strata bounded at their top and base by RMFS and/or intersecting subaerial unconformities (ISU). Moreover, the periodic laws of sequence stratigraphy show that the RMFS is almost potentially correlative to the lower boundary of the stage B (global boundary stratotype section and point) of chronostratigraphic units and close to the biohorizon or first appearance datums (first appearance datums) of biostratigraphic units.


(modified from Grabau (1906), Barrell (1917), Sloss et al. (1949), Wheeler (1958), Mitchum et al. (1977), Haq et al. (1987), Posamentier et al. (1988, 1992), Van Wagoner et al. (1987, 1988, 1990), Cant (1989, 1991), Vail (1991), Christie-Blick (1991), Hunt and Tucker (1992, 1995), Helland-Hansen and Gjelberg (1994), Frazier (1974), Galloway (1989), Johnson and Murphy (1984), Embry and Johannessen (1992), Plint and Nummedal (2000), Donovan (2001), Catuneanu (2002), Catuneanu et al. (2009, 2011, 2012, 2017). (a) model of off-type sequence; (b) conceptual model of systems tract; and (c) entity model of the shoreline trajectory and sediment supply trajectory. LST-lowstand systems tract; TST-transgressive systems tract; HST-highstand systems tract; FSST-falling-stage systems tract; RMFS- remnant maximum flooding surface; ISU-intersecting subaerial unconformity; ESU-extension of subaerial unconformity; SNR- stillstand normal regression; FR-forced regression; LNR-lowstand normal regression; MRS-maximum regressive surface



(modified from Grabau (1906), Barrell (1917), Sloss et al. (1949), Wheeler (1958), Mitchum et al. (1977), Haq et al. (1987), Posamentier et al. (1988, 1992), Van Wagoner et al. (1987, 1988, 1990), Cant (1989, 1991), Vail (1991), Christie-Blick (1991), Hunt and Tucker (1992, 1995), Helland-Hansen and Gjelberg (1994), Frazier (1974), Galloway (1989), Johnson and Murphy (1984), Embry and Johannessen (1992), Plint and Nummedal (2000), Donovan (2001), Catuneanu (2002), Catuneanu et al. (2009, 2011, 2012, 2017), including (a) model of onlap-type sequence, (b) conceptual model of systems tract, and (c) entity model of the shoreline trajectory and sediment supply trajectory. LST-lowstand systems tract; TST-transgressive systems tract; HST-highstand systems tract; FSST-falling-stage systems tract; RMFS- remnant maximum flooding surface; ISU-intersecting subaerial unconformity; ESU-extension of subaerial unconformity; SNR-stillstand normal regression; FR-forced regression; LNR-lowstand normal regression; MRS-maximum regressive surface



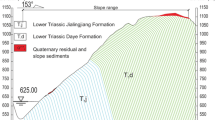
Modified from Li et al. (2017). LST-lowstand systems tract; TST-transgressive systems tract; HST-highstand systems tract; FSST-falling-stage systems tract; ISU-intersecting subaerial unconformity

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Barrell J (1917) Rhythms and the measurements of geological time. Bull Geol Soc Am 28:745–904
Cant DJ (1989) Simple equations of sedimentation: applications to sequence stratigraphy. Basin Res 2:73–81
Cant DJ (1991) Geometric modelling of facies migration: theoretical development of facies successions and local unconformities. Basin Res 3:51–62
Catuneanu O (2002) Sequence stratigraphy of clastic systems: concepts, merits, and pitfalls. J Afr Earth Sc 35(1):1–43
Catuneanu O (2012) International Subcommission on Stratigraphic Classification: Guideline for Sequence Stratigraphy, GeoConvention 2012: Vision:1–7
Catuneanu O (2017) Sequence stratigraphy: guidelines for a standard methodology. Stratigraphy & Timescales 2:1–57
Catuneanu O, Abreu V, Bhattacharya JP, Blum MD, Dalrymple RW, Eriksson PG, Fielding CR, Fisher WL, Galloway WE, Gibling MR, Giles KA, Holbrook JM, Jordan R, Kendall CGStC, Macurda B, Martinsen OJ, Miall AD, Neal JE, Nummedal D, Pomar L, Posamentier HW, Pratt BR, Sarg JF, Shanley KW, Steel RJ, Strasser A, Tucker ME, Winker C (2009) Towards the standardization of sequence stratigraphy. Earth Sci Rev 92:1–33
Catuneanu O, Galloway WE, Kendall CG, St. C, Miall AD, Posamentier HW, Strasser A, Tucker ME (2011) Sequence stratigraphy: methodology and nomenclature. Newsl Stratigr 44/3:173–245
Christie-Blick N (1991) Onlap, offlap, and the origin of unconformity-bounded depositional sequences. Mar Geol 97:35–56
Christie-Blick N, Pekar SF, Madof AS (2007) Is there a role for sequence stratigraphy in chronostratigraphy? Stratigraphy, 4 (2/3): 217–229
Cross TA (1988) Controls on coal distribution in transgressive-regressive cycles, Upper Cretaceous, Western Interior, U.S.A. In: Wilgus, C.K., Hastings, B.S., Kendall, C.G.St.C., Posamentier, H.W., Ross, C.A., Van Wagoner, J.C. (Eds.), Sea Level Changes — An Integrated Approach. Special Publication, vol. 42. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists (SEPM), 371–380
Donovan AD (2001) Free market theory and sequence stratigraphy. A.A.P.G. Hedberg Research Conference on “Sequence Stratigraphic and Allostratigraphic Principles and Concepts”, Dallas, August 26–29. Program and Abstracts Volume: 22
Donovan AD (2010) The sequence stratigraphy family tree: understanding the portfolio of sequence methodologies. In: Ratcliffe, K. T., and Zaitlin, B. A. (Eds.), Application of Modern Stratigraphic Techniques: Theory and Case Histories. Special Publication, vol. 94. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists (SEPM), 5–33
Embry AF (1988) Triassic changes: evidence from the Canadian arctic archipelago. In: Wilgus, C.K., Hastings, B.S., Kendall, C.G.St.C., Posamentier, H.W., Ross, C.A., Van Wagoner, J.C. (Eds.), Sea Level Changes — An Integrated Approach. Special Publication, vol. 42. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists (SEPM), 249–259
Embry AF (2009) Practical Sequence Stratigraphy. Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists, Online at www.cspg.org, 1–79
Embry AF (2010) Correlating siliciclastic successions with sequence stratigraphy. In: Ratcliffe, K. T., and Zaitlin, B. A. (Eds.), Application of Modern Stratigraphic Techniques: Theory and Case Histories. Special Publication, vol. 94. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists (SEPM), 35–53
Embry AF, Johannessen EP (1992) T-R sequence stratigraphy, facies analysis and reservoir distribution in the uppermost Triassic-Lower Jurassic succession, Western Sverdrup Basin, Arctic Canada. In: Vorren, T.O., Bergsager, E., Dahl-Stamnes, O.A., Holter, E., Johansen, B., Lie, E., Lund, T.B. (Eds.), Arctic Geology and Petroleum Potential. Special Publication, vol. 2. Norwegian Petroleum Society, 121–146
Embry A, Johannessen E, Owen D, Beauchamp B, Gianolla P (2007) Sequence stratigraphy as a “concrete” stratigrapic discipline. Report of the ISSC Task Group on Sequence Stratigraphy, 104 p
Frazier DE (1974) Depositional episodes: their relationship to the quaternary stratigraphic framework in the northwestern portion of the Gulf Basin. University of Texas at Austin, Bureau of Economic Geology. Geol Circular 4:1–28
Galloway WE (1989) Genetic stratigraphic sequences in basin analysis, I. Architecture and genesis of flooding-surface bounded depositional units. Am Assoc Pet Geol Bull 73:125–142
Grabau AW (1906) Types of sedimentary overlap. Bull Geol Soc Am 17:567–636
Haq BU, Hardenbol J, Vail PR (1987) Chronology of fluctuating sea levels since the Triassic. Science 235:1156–1167
Hedberg HD (1976) International Stratigraphic Guide – A guide to Stratigraphic classification. John Wiley and Sons, Terminology and Procedure, pp 1–200
Helland-Hansen W, Gjelberg JG (1994) Conceptual basis and variability in sequence stratigraphy: a different perspective. Sed Geol 92:31–52
Herdberg HD (1976) International stratigraphic guide. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Hunt D, Tucker ME (1992) Stranded parasequences and the forced regressive wedge systems tract: deposition during base-level fall. Sed Geol 81:1–9
ISSC (2013) International Subcomission on Stratigraphic Classification Newsletter no. 18, 4 p
ISSC Working Group on Sequence Stratigraphy (2003) Fate of the working groups and projects started during Alberto Riccardi Chairmanship (1996–2002). International Subcomission on Stratigraphic Classification Newsletter no. 1, pp 16–19
Jervey MT (1988) Quantitative geological modeling of siliciclastic rock sequences and their seismic expression. In: Wilgus, C.K., Hastings, B.S., Kendall, C.G.St.C., Posamentier, H.W., Ross, C.A., Van Wagoner, J.C. (Eds.), Sea Level Changes — An Integrated Approach. Special Publication, vol. 42. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists (SEPM), 47–69
Johnson JG, Murphy MA (1984) Time-rock model for Siluro-Devonian continental shelf, western United States. Geol Soc Am Bull 95:1349–1359
Kendall CG, St. C, Lerche I (1988) The rise and fall of eustasy. In: Wilgus, C.K., Hastings, B.S., Kendall, C.G.St.C., Posamentier, H.W., Ross, C.A., Van Wagoner, J.C. (Eds.), Sea Level Changes — An Integrated Approach. Special Publication, vol. 42. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists (SEPM), 3–17
Kolla V, Posamentier HW, Eichenseer H (1995) Stranded parasequences and the forced regressive wedge systems tract: deposition during base-level fall–discussion. Sed Geol 95:139–145
Li SH (2010) Thinking of international sequence stratigraphy development and L-H-T sequence stratigraphy. Acta Sedimentological Sinica 28(4):735–744 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li SH, Jia LC (2011) Adjustment to non-periodicity and sequence boundary in four-divided model of sequence stratigraphy. Acta Sedimentological Sinica 29(1):105–117 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li SH, Li SP, Hu YY, Wu W, Liu B, Li ZT (2017) Sequence stratigraphy: problems and discussion. Earth Sci 42(12):2312–2316 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Miall AD (1991) Stratigraphic sequences and their chronostratigraphic correlation. J Sediment Petrol 61:497–505
Miall AD (1995) Whither Stratigraphy? Sedimentary Geology 100:5–20
Miall AD, Miall CE (2001) Sequence stratigraphy as a scientific enterprise: the evolution and persistence of conflicting paradigms. Earth Sci Rev 54:321–348
Mitchum RM Jr, Vail PR, Thompson III, S (1977) In: Payton CE (ed) Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of sea-level, part 2: the depositional sequence as a basic unit for stratigraphic analysis. Seismic Stratigraphy — Applications to Hydrocarbon Exploration. Memoir, vol 26. American Association of Petroleum Geologists, pp 53–62
Owen DE (2009) How to use stratigraphic terminology in papers, illustrations, and talks. Stratigraphy 6(2):106–116
Plint AG (1988) Sharp-based shoreface sequences and ‘offshore bars’ in the Cardium Formation of Alberta: their relationship to relative changes in sea level. In: Wilgus, C.K., Hastings, B.S., Kendall, C.G.St.C., Posamentier, H.W., Ross, C.A., Van Wagoner, J.C. (Eds.), Sea Level Changes – An Integrated Approach. Special Publication, vol. 42. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists (SEPM), 357–370
Plint AG, Nummedal D (2000) The falling stage systems tract: recognition and importance in sequence stratigraphic analysis. In: Hunt D, Gawthorpe RL (eds) Sedimentary response to forced regression, vol 172. Geological Society, London,Special Publication, pp 1–17
Posamentier HW (2001) Ruminations on sequence terminology with specific reference to “sequence” and sequence boundary types. A.A.P.G. Hedberg Research Conference on “Sequence Stratigraphic and Allostratigraphic Principles and Concepts”, Dallas, August 26–29. Program and Abstracts Volume, 39–40
Posamentier HW, Vail PR (1988) Eustatic controls on clastic deposition II — sequence and systems tract models. In: Wilgus, C.K., Hastings, B.S., Kendall, C.G.St.C., Posamentier, H.W., Ross, C.A., Van Wagoner, J.C. (Eds.), Sea Level Changes — An Integrated Approach. Special Publication, vol. 42. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists (SEPM), 125–154
Posamentier HW, Allen GP (1999) Siliciclastic sequence stratigraphy—concepts and applications, concepts in sedimentology and paleontology, vol 7. Econ. Paleo. and Mineral. (SEPM), Tulsa
Posamentier HW, Jervey MT, Vail PR (1988) Eustatic controls on clastic deposition I — conceptual framework. In: Wilgus, C.K., Hastings, B.S., Kendall, C.G.St.C., Posamentier, H.W., Ross, C.A., Van Wagoner, J.C. (Eds.), Sea Level Changes — An Integrated Approach. Special Publication, vol. 42. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists (SEPM), 110–124
Posamentier HW, Allen GE, James DE, Esson M (1992) Forced regressions in a sequence stratigraphic framework: concepts, examples and exploration significance. Am Assoc Pet Geol Bull 76:1687–1709
Salvador A (ed) (1994) International Stratigraphic Guide – Guide to Stratigraphic classification, terminology, and Procedure, 2nd edn. The International Union of Geological Sciences and the Geological Society of America, Colorado, pp 1–214
Salvador A (2001a) Review the basic concepts and terminology not only of sequence stratigraphy but of all unconformity-related units. A.A.P.G. Hedberg Research Conference on “Sequence Stratigraphic and Allostratigraphic Principles and Concepts”, Dallas, August 26–29. Program and Abstracts Volume, 46–47
Salvador A (2001b) The correlative conformities. A.A.P.G. Hedberg Research Conference on “Sequence Stratigraphic and Allostratigraphic Principles and Concepts”, Dallas, August 26–29. Program and Abstracts Volume, 48–49
Sarg JF (1988) Carbonate sequence stratigraphy. In: Wilgus, C.K., Hastings, B.S., Kendall, C.G.St.C., Posamentier, H.W., Ross, C.A., Van Wagoner, J.C. (Eds.), Sea Level Changes — An Integrated Approach. Special Publication, vol. 42. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists (SEPM), 155–181
Sloss LL (1963) Sequences in the cratonic interior of North America. Geol Soc Am Bull 74:93–114
Sloss LL, Krumbein WC, Dapples EC (1949) Integrated facies analysis. In: Longwell, C.R. (Ed.), Sedimentary Facies in Geologic History. Memoir, vol. 39. Geological Society of America, 91–124
Vail PR (1987) Seismic stratigraphy interpretation using sequence stratigraphy. In: Bally, A.W. (Ed.), Atlas of Seismic Stratigraphy, volume 1. Studies in Geology, vol. 27. American Association of Petroleum Geologists, 1–10
Vail PR, Mitchum RM Jr, Thompson S III (1977a) Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of sea level, part 3: relative changes of sea level from coastal onlap. In: Payton CE (ed) Seismic stratigraphy — applications to Hydrocarbon Exploration. Memoir, vol 26. American Association of Petroleum Geologists, pp 63–81
Vail PR, Mitchum RM Jr, Thompson III S (1977b) Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of Sea Level, Part 4: global cycles of relative changes of Sea level. In: Payton CE (ed) Seismic stratigraphy — applications to Hydrocarbon Exploration. Memoir, vol 26. American Association of Petroleum Geologists, pp 83–97
Vail PR, Audemard F, Bowman SA, Eisner PN, Perez-Cruz C (1991) The stratigraphic signatures of tectonics, eustasy and sedimentology — an overview. In: Einsele G, Ricken W, Seilacher A (eds) Cycles and events in Stratigraphy. Springer-Verlag,, Berlin, pp 617–659
Van Wagoner JC (1998) Sequence stratigraphy and marine to nonmarine facies architecture of foreland basin strata, Book Cliffs, Utach, U.S.A.: reply. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 82 (8):1607–1618
Van Wagoner JC, Mitchum RM, Posamentier HW, Vail PR (1987) An overview of sequence stratigraphy and key definitions. In: Bally AW (ed) Atlas of Seismic Stratigraphy. Studies in Geology, vol 1. vol. 27. American Association of Petroleum Geologists, pp 11–14
Van Wagoner JC, Posamentier HW, Mitchum RM, Vail PR, Sarg JF, Loutit TS, Hardenbol J (1988) An overview of sequence stratigraphy and key definitions. In: Wilgus, C.K., Hastings, B.S., Kendall, C.G.St.C., Posamentier, H.W., Ross, C.A., Van Wagoner, J.C. (Eds.), Sea Level Changes – An Integrated Approach. Special Publication, vol. 42. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists (SEPM), 39–45
Van Wagoner JC, Mitchum RM Jr, Campion KM, Rahmanian VD (1990) Siliciclastic sequence stratigraphy in well logs, core, and outcrops: concepts for high-resolution correlation of time and facies. Am Association Petroleum Geol Methods Explor Ser 7:1–55
Walliser OH (1996) Patterns and causes of global events. In: Walliser OH (ed) Global events and event stratigraphy in the Phanerozoic. Springer, Berlin, pp 7–19
Wang X (1999) Several basic theoretical problems of outcrop sequence stratigraphy. Sci China (Series D) 29(1):22–30 (in Chinese with no English abstract)
Wheeler HE (1958) Time stratigraphy. Am Assoc Pet Geol Bull 42:1047–1063
Wilson RCL (1998) Sequence stratigraphy: a revolution without a cause? In: Blundell, D. J. & Scott, A. C. (eds) Lyell: the Past is the Key to the Present. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 143: 303–314
Yoshida S (2000) Sequence stratigraphy and facies architecture of the upper Blackhawk formation and the Lower Castlegate Sandstone (Upper cretaceous), Book Cliffs, Utah, USA. Sed Geol 136:239–276
Yoshida S, Miall AD, Willis A (1998) Sequence stratigraphy and marine to nonmarine facies architecture of foreland basin strata, Book Cliffs, Utach, U.S.A.:discussion. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 82 (8): 1596–1606
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the Foundation of Department of Science and Technology of Guizhou Province, China (No. [2022]ZD003). The author is grateful to all the sequence stratigraphers who have contributed to the development of sequence stratigraphy. Their outstanding achievements have guided the author to establish the periodic sufficient conditions of shoreline trajectory and sediment supply trajectory so as to obtain RMFS and /or ISU bounded sequence model, and establish their synchronic necessary conditions, so as to obtain periodic law of sequence stratigraphy. All these originated from the Jijihu modern subaqueous aggradational fan discovered by Li in the Gurbantonggute desert in Northwest China in the summer of 2007. Li spent more than 15 years to continue this research without any financial support. Therefore, Li should especially thank Dr. Andrew Miall, who encouraged the author not to give up and kindly sent the author two papers (Cant 1989, 1991). Li also wants to express his heartfelt thanks to Drs. Octavian Catuneanu, Dag Nummedal, Christopher R. Fielding, Christopher G. St C. Kendall, Gert Jan Weltje, Frits Agterberg, Marshall X Ma, Yinye Wu, Longyi Shao, Zaixing Jiang, Xinong Xie, and many others for their help and suggestions on this work through email. Many thanks Drs. Baoqing Li and Bei Liu for English editing and figure presentation.
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Xiang Que.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S. Periodic law patterns of sequence stratigraphy. Earth Sci Inform 16, 4257–4271 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-01085-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-01085-6