Abstract
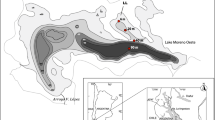
The horizontal distributions of the benthic stages of Chaoborus flavicans and Cyclops vicinus were studied in a eutrophic stratified lake in the Massif-Central (France) over one year, at 5 stations from the shore to the centre of the lake. Their distribution was investigated in relation to temperature, dissolved oxygen, sediment grain-size and other benthic organisms. The dominant taxa of the benthic fauna of Lake Aydat were dipterans, crustaceans and oligochaetes and their distributions were independent of the grain size. In contrast to chironomids which preferentially inhabited the sublittoral zone, chaoborids and crustaceans were more numerous in the profundal zone. The sediment-dwelling oligochaetes remained numerous in both zones, according to the season. The fourth copepodite stages of Cyclops and Tubifex are tolerant to low oxygen concentrations in contrast to the fourth instar larvae of Chaoborus whose distribution was positively correlated with oxygen. The guts of these dipteran larvae were found to be empty and we assumed that, in contrast to the chironomids and oligochaetes, the resting stages of Cyclops vicinus and the benthic stages of Chaoborus flavicans did not use benthic resources. The former are activated at the autumn overturn, while the latter escape from the bottom at the start of the spring oxygen depletion. This suggests that physical factors are largely responsible for their reactivation. Both animals suffered of the effects of starvation and probably lost weight. The reactivation of the copepod at the autumn overturn would be facilitated by fluid mechanical disturbance. In addition, after the spring overturn, a small increase in temperature near 4 °C would be a reliable environmental signal for the dipteran. Food limitation does not occur, invertebrate predation pressure seems to be negligible and the predation by fish on the macrobenthic fauna and by chance on the meiofauna, clearly remains limited in both space and time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. F. NOR., 1990. Normes X 31–101 & 31–107. In Association Française de Normalisation (ed.). Recueil des normes.
Azam, F., T. Fenchel, J. G. Field, J. S. Gray, L. A. Meyer-Reil & F. Thingstad, 1983. The ecological role of water-column microbes in the sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 10: 257–263.
Buchanan, J. B., 1984. Sediment analysis. In N.A. Holme & A.D. McIntyre (eds), Methods for the Study of Marine Benthos. Blackwell Scientific Publications; Oxford: 41–65.
Campy, M. & M. Meybeck, 1995. Les sédiments lacustres. In R. Pourriot & M. Meybeck (eds), Limnologie Générale. Masson, Paris: 185–226.
Dahms, H. U., 1995. Dormancy in the Copepoda-an overview. Hydrobiologia 306: 199–211.
Dawidowicz, P., J. Pijanowska & K. Ciechomski, 1990. Vertical migration of Chaoborus larvae induced by the presence of fish. Limnol. Oceanogr. 35: 1631–1637.
Depiereux, E., 1988. Multivariate analysis in the description of community structure: principal component and cluster analysis. In M. Hermy & A. Wilmotte (eds), Multivariate Analysis of Biological Data. Bull. Soc. Roy. Belg.: 127–158.
Durieu, M., 1995. Cycle biologique de Chaoborus flavicans (Diptera: Chaoboridae), valorisation de la production de biomasse en bassin de lagunage et optimisation en condition expérimentales. Doctorat d'Université, Université Paul Sabatier, Toulouse, France, 325 pp.
Eaton, K. A., 1983. The life-history and production of Chaoborus punctipennis (Diptera: Chaoboridae) in lake Norman, North Carolina, USA. Hydrobiologia 106: 247–252.
Fedorenko, A. Y., 1975. Feeding characteristics and predation impact of Chaoborus (Diptera: Chaoboridae) larvae in small lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 20: 250–258.
George, D. G., 1976. Life cycle and production of Cyclops vicinus in a shallow eutrophic reservoir. Oikos 27: 101–110.
Gerdeaux, D., J. Guillard & J. L. Jamet, 1989. Abundance estimation of Chaoborus larvae and fishes in Lake Aydat by echo-integration. Proc. I. O. A. 11: 231–237.
Giani, N. & H. Laville, 1995. Réseau trophique benthique. In R. Pourriot & M. Meybeck (eds), Limnologie générale. Masson; Paris: 565–587.
Hansen, A. M. & B. Santer, 1995. The influence of food resources on the development, survival and reproduction of the two cyclopoid copepods: Cyclops vicinus and Mesocyclops leuckarti. J. Plankton Res. 17: 631–646.
Hartmann, H. J., H. Taleb, L. Aleya & N. Lair, 1993. Predation on ciliates by the suspension-feeding calanoid copepod Acanthodiaptomus denticornis. Can. J. Fish. aquatic. Sci. 50: 1382–1393.
Heinis, F. & T. Crommentuijn, 1992. Behavioural responses to changing oxygen concentrations of deposit feeding chironomid larvae (Diptera) of littoral and profundal habitats. Arch. Hydrobiol. 124: 173–185.
Hillbricht-Ilkowska, A., Z. Kajak, J. Ejsmont-Karabin, A. Karabin & J. Rybak, 1975. Ecosystem of the Mikolajskie lake. The utilization of the consumers production by invertebrate predators in pelagic and profundal zone. Pol. Arch. Hydrobiol. 22: 53–64.
Howmiller, R. P., 1977. On abundance of Tubificidae (Annelida: Oligochaeta) in the profundal benthos of some Wisconsin lakes. Am. Midl. Nat. 97: 211–215.
Jamet, J. L., 1991. Importance de la faune ichtyologique dans le lac d'Aydat, milieu eutrophe de la zone tempérée Nord, ses relations trophiques avec les autres composants de l'écosystème. Doctorat d'Université, Université Blaise Pascal, Clermont-Ferrand, France, 263 pp.
Jønasson, P. M., 1955. The efficiency of sieving techniques for sampling freshwater bottom fauna. Oikos 6: 183–207.
Jønasson, P. M., 1972. Ecology and production of the profundal benthos in relation to phytoplankton in Lake Esrom. Oikos (suppl.) 14: 139 pp.
Jønasson, P. M., 1996. Limits for life in the lake ecosystem. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 26: 1–33.
Kajak, Z. & B. Ranke-Rybicka, 1970. Feeding and production efficiency of Chaoborus flavicans MEIGEN (Diptera; Culicidae) larvae in eutrophic and dystrophic lake. Pol. Arch. Hydrobiol. 30: 225–232.
Kajak, Z., J. Rybak & B. Ranke-Rybicka, 1978. Fluctuations in numbers and changes in the distribution of Chaoborus flavicans (Meigen) (Diptera, Chaoboridae) in the eutrophic Mikolajskie lake and dystrophic lake Flosek. Ekol. pol. 26: 259–272.
Kajak, Z. & J. Rybak, 1979. The feeding of Chaoborus flavicans MEIGEN (Diptera: Chaoboridae) and its predation on lake zooplankton. Int. Rev. ges. Hydrobiol. 64: 361–378.
Kerfoot, W. C., D. L. Kellogg Jr & J. R. Strickler, 1980. Visual observations of live zooplankters: evasion, escape, and chemical defences. In W. C. Kerfoot (ed.), Evolution and Ecology of Zooplankton Communities. The University Press of New England, Hanover (N.H.); Lond.: 10–27.
Lair, N., 1990. Effect of invertebrate predation on seasonal succession of a zooplankton community: a two year study in lake Aydat. Hydrobiologia 198: 1–12.
Lair, N. & A. Ayadi, 1989. The seasonal succession of planktonic events in Lake Aydat, France. A comparison with the PEG model. Arch. Hydrobiol. 115: 589–602.
Lair, N. & Y. El Ghachtoul, 1989. La diapause de Cyclops vicinus vicinus (Ulianine, 1875) dans un lac eutrophe du Massif-Central Français. SITE Atti 7: 289–295.
Leaner, M. A., G. Lochhead & B. D. Hughes, 1978. A review of the biology of British Naididae, with emphasis on the lotic environment. Freshwat. Biol. 8: 357–375.
Maier, G., 1989. Variable life cycles in the freshwater copepod Cyclops vicinus (Uljanin, 1875): Support for the predator avoidance hypothesis ? Arch. Hydrobiol. 115: 203–219.
Mumm, H. & A. F. Sell, 1995. Estimating the impact of Chaoborus predation on zooplankton: A new design for in situ enclosures studies. Arch. Hydrobiol. 134: 195–206.
Neill, W. E., 1981. Impact of Chaoborus predation upon the structure and dynamics of a crustacean zooplankton community. Oecologia 48: 164–177.
Neill, W. E., 1990. Induced vertical migration in copepods as a defence against invertebrate predation. Nature 345: 524–526.
Nilssen, J. P. & K. Elgmork, 1977. Cyclops abyssorum-Life cycle dynamics and habitat selection. Mem. Ist. ital. Idrobiol. 34: 197–238.
Nilssen, J. P., 1978. On the evolution of life histories of limnetic cyclopoid copepods. Mem. Ist. ital. Idrobiol. 36: 193–214.
Parma, S., 1971. The morphology of the larval instars of Chaoborus flavicans (Meigen, 1818) (Diptera, Chaoboridae). Beaufortia, 238: 173–181.
Santer, B., 1993. Potential importance of algae in the diet of adult Cyclops vicinus. Freshwat. Biol. 30: 269–278.
Santer, B. & F. van den Bosch, 1994. Herbivorous nutrition of Cyclops vicinus: the effect of a pure algal diet on feeding, development, reproduction and life cycle. J. Plankton Res. 16: 171–195.
Särkkä, J., 1993. Diversity of meiofauna in the lacustrine profundal zone: Bathymetric differences and influence of environmental factors. Aquat. Sci. 55: 197–205.
Särkkä, J., 1995. Profundal meiofauna in two large lakes: Influence of pollution and bathymetric differences. Arch. Hydrobiol. 32: 453–493.
Sikorowa, A., 1968. The behaviour of Chaoborus LICHT. larvae under unfavorable oxygen conditions. Ekol. pol. A 16: 1–7.
Smyly, W. J. P., 1974. The effect of temperature on the development time of the eggs of three freshwater cyclopoid copepods from the English Lake District. Crustaceana 27: 278–284.
Stahl, J. B., 1966. The ecology of Chaoborus inMyers lake, Indiana. Limnol. Oceanogr. 11: 177–183.
Strayer, D., 1985. The benthic micrometazoans of Mirror Lake, New Hampshire. Arch. Hydrobiol. (Suppl.) 72: 287–426.
Strayer, D., 1991. Perspectives on the size structure of lacustrine zoobenthos, its causes and its consequences. J. n. am. benthol. Soc. 10: 210–221.
Strommer, J. L. & L. A. Smock, 1989. Vertical distribution and abundance of invertebrates within the sandy substrate of a low gradient headwater stream. Freshwat. Biol.: 22, 263–274.
Swift, M. C. & A. Y. Fedorenko, 1975. Some aspect of the prey capture by Chaoborus larvae. Limnol. Oceanogr. 20: 418–425.
Swüste, H. F. J., R. Cremer & S. Parma, 1973. Selective predation by larvae of Chaoborus flavicans (Diptera, Chaoboridae). Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 18: 1559–1563.
Taleb, H., N. Lair & J. L. Jamet, 1992. Estival diel vertical migration of Acanthodiaptomus denticornis (Wierzejski, 1887) (Calanoïda: Copepoda) in a eutrophic lake of the temperate zone as a mean of predator avoidance. Ann. Nat. Zool. 13: 149–156.
Taleb, H., N. Lair, P. Reyes-Marchant & J. L. Jamet, 1993. Observations on vertical migrations of zooplankton at four different stations of a small, eutrophic, temperate zone lake, in relation to their predators. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. 39: 199–216.
Ten Winkel, E. H. & C. Davids, 1987. Population dynamics aspects of chironomid larvae of the littoral zone of Lake Maarsseveeb I. Hydrobiol. Bull. 21: 81–94.
Tinson, S. & J. Laybourn-Parry, 1986. The distribution and abundance of benthic cyclopoid copepods in Esthwaite Water, Cumbria. Hydrobiologia 131: 225–234.
Traunspurger, W., 1996. Distribution of benthic nematodes in the littoral of an oligotrophic lake (Königssee, National Park Berchtesgaden, FRG). Arch. Hydrobiol. 135: 393–412.
Van de Bund, W. J. & D. Groenendijk, 1994. Seasonal dynamics and burrowing of littoral chironomid larvae in relation to competition and predation. Arch. Hydrobiol. 132: 213–225.
Walter, R. A., 1985. Benthic macroinvertebrates. In G.E. Lickens (ed.), An Ecosystem Approach to Aquatic Ecology: Mirror Lake and its Environment. Springer Verlag, New York: 204–228
Wyngaard, G. A., B. E. Taylor & D. L. Mahoney, 1991. Emergence and dynamics of cyclopoid copepods in an unpredictable environment. Freshwat. Biol. 25: 219–232.
Yan, N. D., W Keller, H. J. Mac Isaac & L. J. Mac Eachern, 1991. Regulation of zooplanktonic community structure of an acidified lake by Chaoborus. Ecol. Appl. 1: 52–65.
Yurista, P. M., 1997. Bythotrephes cederstroemi diapausing egg distribution and abundance in Lake Michigan and the environmental cues for breaking diapause. J. Great Lakes Res. 23: 202–209.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rabette, C., Lair, N. Spatial and temporal distribution of benthic stages of Cyclops vicinus and Chaoborus flavicans in relation to abiotic factors and benthic fauna. Hydrobiologia 390, 61–72 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003559832628
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003559832628