Abstract
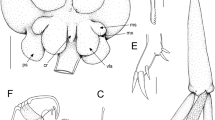
Four species of Copepoda Poecilostomatoida are recorded from the mantle cavity of bivalve molluscs collected in West New Guinea (Irian Barat, Indonesia). Two of these are new to science: Pseudanthessius dimorphus and Lichomolgus hoi n. spp.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gotto, R. V., 1975. Lichomolgus eganae n.sp. (Copepoda, Cyclopoida): an ascidicolous copepod from New South Wales. Bull. zoöl. Mus. Univ. Amsterdam 5: 1–5.
Ho, Ju-shey, 1980. Origin and dispersal of Mytilus edulis in Japan deduced from its present status of copepod parasitism. Publs. Seto mar. biol. Lab. 25: 293–313.
Ho, Ju-shey & Il-Hoi Kim, 1991. Copepod parasites of commercial bivalves in Korea, II. Copepods from cultured bivalves. Bull. Korean Fish. Soc. 24: 369–396.
Humes, A. G., 1972. Pseudanthessius comanthi n.sp. (Copepoda, Cyclopoida) associated with a crinoid at Eniwetol Atoll. Pacific Science 26: 373–380.
Humes, A. G., 1976. Cyclopoid copepods associated with Tridacnidae (Mollusca, Bivalvia) in the Moluccas. Proc. biol. Soc. Wash. 89: 491–508.
Humes, A. G., 1977. Pseudanthessiid copepods (Cyclopoida) associated with crinoids and echinoids (Echinodermata) in the tropical western Pacific Ocean. Smiths. Contr. Zool. 243: i-iii, 1–43.
Humes, A. G., 1978. A new cyclopoid copepod, Pseudanthessius limatus, associated with an ophiuroid in Panama (Atlantic side). Proc. biol. Soc. Wash. 91: 242–249.
Humes, A. G. & J. H. Stock, 1973. A revicion of the family Lichomolgidae Kossmann, 1877, cyclopoid copepods mainly associated with marine invertebrates. Smiths. Contr. Zool. 127: i-v, 1–368.
Illg, P. L., 1950. A new copepod, Pseudanthessius latus (Cyclopoida. Lichomolgidae) commensal with a marine flatworm. J. Wash. acad. Sci. 40: 129–133.
Jones, J. B., 1976. Lichomolgus uncus n.sp. (Copepoda: Cyclopoida) an associate of the mussel Perna canaliculus Gmelin. J. r. Soc. N.Z. 6: 301–305.
Kim, Il-Hoi & Ju-shey Ho, 1991. Copepod parasites on commercial bivalves from Korea, I. Two new poecilostomatoid species from Solen grandis Dunker in the Yellow Sea. Korean J. syst. Zool. 7: 1–12.
Matsuzaki, K. & K. Ogawa, 1989. A new lichomolgid copepod associated with the simple ascidian Halocynthia roretzi. Proc. Jap. Soc. syst. Zool. 40: 13–20.
Nicholls, A. G., 1944. Littoral Copepoda from South Australia, II. Calanoida, Cyclopoida, Notodelphyoida, Monstrilloida and Caligoida. Recs. S. Aust. Mus. 8: 1–62.
Stock, J. H., 1964. Sur deux espèces d'Anthessius (Copepoda) des Indes Orientales. Zoöl. Mededel., Leiden 39: 111–124.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stock, J.H. Copepoda Poecilostomatoida associated with Bivalvia from New Guinea. Hydrobiologia 312, 37–45 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018885
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018885