fusiform gyrus
(redirected from lobulus fusiformis)gyrus
[ji´rus] (pl. gy´ri) (L.)one of the many convolutions of the surface of the cerebral hemispheres caused by infolding of the cortex, separated by fissures or sulci; called also cerebral gyrus.
angular gyrus one continuous anteriorly with the supramarginal gyrus.
annectent gyri various small folds on the cerebral surface that are too inconstant to bear specific names; called also gyri transitivi.
Broca's gyrus inferior frontal gyrus.
central gyrus, anterior precentral gyrus.
central gyrus, posterior postcentral gyrus.
cerebral gyrus gyrus.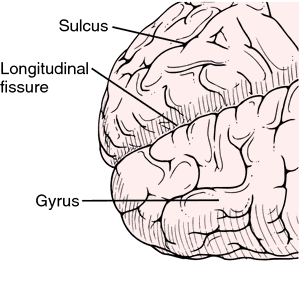

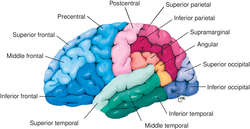
Cerebral gyri. From Applegate, 1996.
cingulate gyrus (gyrus cin´guli) an arch-shaped convolution situated just above the corpus callosum.
frontal gyrus any of the three (inferior, middle, and superior) gyri of the frontal lobe.
fusiform gyrus one on the inferior surface of the hemisphere between the inferior temporal and parahippocampal gyri, consisting of a lateral (lateral occipitotemporal gyrus) and a medial (medial occipitotemporal gyrus) part.
hippocampal gyrus (gyrus hippocam´pi) one on the inferior surface of each cerebral hemisphere, lying between the hippocampal and collateral fissures; called also parahippocampal gyrus.
infracalcarine gyrus (lingual gyrus) one on the occipital lobe that forms the inferior lip of the calcerine sulcus and, together with the cuneus, the visual cortex.
marginal gyrus the middle frontal gyrus.
occipital gyrus any of the three (superior, middle, and inferior) gyri of the occipital lobe.
occipitotemporal gyrus, lateral the lateral portion of the fusiform gyrus.
occipitotemporal gyrus, medial the medial portion of the fusiform gyrus.
orbital gyri irregular gyri on the orbital surface of the frontal lobe.
parahippocampal gyrus hippocampal gyrus.
paraterminal gyrus a thin sheet of gray matter in front of and ventral to the genu of the corpus callosum.
postcentral gyrus the convolution of the frontal lobe immediately behind the central sulcus; the primary sensory area of the cerebral cortex; called also posterior central gyrus.
precentral gyrus the convolution of the frontal lobe immediately in front of the central sulcus; the primary motor area of the cerebral cortex; called also anterior central gyrus.
gyrus rec´tus a cerebral convolution on the orbital aspect of the frontal lobe.
supramarginal gyrus that part of the inferior parietal convolution which curves around the upper end of the fissure of Sylvius.
temporal gyrus any of the gyri of the temporal lobe, including inferior, middle, superior, and transverse temporal gyri; the more prominent of the latter (anterior transverse temporal gyrus) represents the cortical center for hearing.
gy´ri transiti´vi annectent gyri.
uncinate gyrus the uncus.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
fu·si·form gy·rus
an extremely long convolution extending lengthwise over the inferior aspect of the temporal and occipital lobes, demarcated medially by the collateral sulcus from the lingual gyrus and the anterior part of the parahippocampal gyrus, and laterally by the inferior temporal sulcus from the inferior temporal gyrus.
Synonym(s): gyrus occipitotemporalis lateralis [TA], lateral occipitotemporal gyrus [TA], gyrus fusiformis, lobulus fusiformis
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
fu·si·form gy·rus
(fyū'si-fōrm jī'rŭs)An extremely long convolution extending lengthwise over the inferior aspect of the temporal and occipital lobes, demarcated medially by the collateral sulcus from the lingual gyrus and the anterior part of the parahippocampal gyrus, laterally by the inferior temporal sulcus from the inferior temporal gyrus.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
gyrus
(ji'rus) plural.gyri [L. gyrus fr. Gr. gyros, ring, circle]Any of the surface convolutions or rounded ridges that are packed along the cerebral hemispheres of the brain. Each gyrus is separated from its neighbor by a furrow called a sulcus. Details of the shape of gyri vary from individual to individual. Synonym: convolution; gyre See: illustration
angular gyrus
A gyrus of the ventral region of the parietal lobe; it caps the posterior (ascending) end of the superior temporal sulcus, and it is just ventral to the supramarginal gyrus. The cortex of the angular gyrus plays a role in the association of the visual and tactile perceptions of forms and shapes.
Synonym: gyrus angularisgyrus angularis
Angular gyrus.Broca gyrus
See: Broca, Pierre-Paulcallosal gyrus
A large gyrus on the medial surface of the cerebral hemisphere that lies directly above the corpus callosum and arches over its anterior end.
gyrus cerebelli
A layer of the cerebellum.
cingulate gyrus
A long curving gyrus on the medial surface of each cerebral hemisphere; it follows the arch of the corpus callosum, from which it is separated by a deep fissure, the callosal sulcus. The cortex of the cingulate gyrus and the underlying axon tract, the cingulum, are parts of the main circuitry of the limbic system.
Synonym: callosal convolutiondentate gyrus
A curved gyrus hidden along the medial surface of the temporal lobe of each cerebral hemisphere. It contains a cortex of three layers, with a single cell layer, that is part of the hippocampal formation, and it is folded inside the hippocampal sulcus, where it lies against the subicular edge of the parahippocampal gyrus. The surface of the dentate gyrus has regularly-spaced transverse grooves, which make the gyrus resemble a row of teeth.
Synonym: fascia dentata See: limbic system for illusgyrus fornicatus
The ring along the medial surface of each cerebral hemisphere that forms a large segment of the limbic circuitry. The gyrus fornicatus comprises the subcallosal gyrus, the cingulate gyrus, the retrosplenial area, the parahippocampal gyrus, and the uncus.
fusiform gyrus
Occipitotemporal gyrus.Heschl gyrus
See: Heschl gyrushippocampal gyrus
Parahippocampal gyrus.inferior frontal gyrus
The inferior-most of the three major longitudinal gyri of the lateral surface of the frontal lobe of each cerebral hemisphere; it is part of the prefrontal cortex. In the dominant hemisphere, the posterior two-thirds of the inferior frontal gyrus are Broca speech area, which is involved in activating the muscle groups used when speaking
inferior occipital gyrus
A stubby, knuckle-shaped gyrus on the lateral surface of the occipital lobe of each cerebral hemisphere, just below the lateral occipital sulcus.
inferior parietal gyrus
Inferior parietal lobule.inferior temporal gyrus
The inferior-most of the three longitudinal gyri that cover the lateral surface of the temporal lobe.
lingual gyrus
A tongue-shaped gyrus that, at its anterior end (tip), abuts the parahippocampal gyrus on the under surface (ventral) of the occipital lobe. The calcarine fissure (calcarine sulcus) forms the medial (upper) edge of the lingual gyrus, and the collateral sulcus forms the lateral (lower) edge. Part of the primary visual cortex is found along the wall of the lingual gyrus inside the calcarine fissure.
gyrus longus insulae
A lengthy gyrus composing the postinsula.
medial frontal gyrus
The major anterior gyrus of the medial surface of the frontal lobe of each cerebral hemisphere; it is part of the prefrontal cortex. The medial frontal gyrus curves over the cingulate gyrus, separated from it by the cingulate sulcus.
middle frontal gyrus
The middle of the three major longitudinal gyri of the lateral surface of the frontal lobe of each cerebral hemisphere; it is part of the prefrontal cortex.
middle temporal gyrus
The middle the three longitudinal gyri that cover the lateral surface of the temporal lobe.
occipital gyrus
The inferior or the superior occipital gyrus.
occipitotemporal gyrus
The lateral or the medial occipitotemporal gyrus, both of which run longitudinally along the bottom (ventral surface) of the temporal lobe of each cerebral hemisphere.orbital gyrus
Any of the gyri forming the inferior, concave surface of the frontal lobe, which lies along the orbital surface of the frontal bone.
paracentral gyrus
Paracentral lobule.parahippocampal gyrus
A gyrus along the medial (inner) edge of the temporal lobe of each cerebral hemisphere; it is bounded by the hippocampal fissure medially and the collateral sulcus laterally. The medial edge of the parahippocampal gyrus is called the subiculum; the remainder of the gyrus is called the entorhinal cortex. Together, the ventricular side of the subiculum and dentate gyrus form the hippocampus.
Synonym: hippocampal gyrus See: limbic system for illusparaterminal gyrus
A small area of the cerebral cortex anterior to the lamina terminalis and below the rostrum of the corpus callosum.
parietal gyrus
The inferior or the superior parietal lobule.
postcentral gyrus
A major dorsoventral gyrus in the parietal lobe of each cerebral hemisphere; its anterior border is the central sulcus, and its posterior border is the postcentral sulcus. This gyrus contains the primary somatosensory cortex. Synonym: ascending parietal convolution
posterior central gyrus
Postcentral gyrus.precentral gyrus
A major dorsoventral gyrus in the parietal lobe of each cerebral hemisphere; its anterior border is the precentral sulcus, and its posterior border is the central sulcus. This gyrus contains the primary motor cortex. Synonym: ascending frontal convolution
gyrus profundus cerebri
One of the very deep gyri of the cerebrum.
gyrus rectus
A longitudinal gyrus on the medial edge of the orbital (ventral) surface of the frontal lobe of each cerebral hemisphere; the lateral edge of the gyrus rectus is the olfactory sulcus.
Retzius gyrus
See: Retzius, Anders Adolfsubcallosal gyrus
The short gyrus at the head of the cingulate gyrus, just below the rostrum of the corpus callosum, on the medial surface of each cerebral hemisphere. It is the anterior-most segment of the gyrus fornicatus.
Synonym: limbic system for illussuperior frontal gyrus
The superior-most gyrus of the three major longitudinal gyri of the lateral surface of the frontal lobe of each cerebral hemisphere; it is part of the prefrontal cortex.
superior occipital gyrus
A stubby, knuckle-shaped gyrus on the lateral surface of the occipital lobe of each cerebral hemisphere, just above the lateral occipital sulcus.
superior parietal gyrus
Superior parietal lobule.superior temporal gyrus
The superior of the three longitudinal gyri that cover the lateral surface of the temporal lobe.
supracallosal gyrus
Indusium griseum.supracallosus gyrus
The gray matter layer covering the corpus callosum.
supramarginal gyrus
A V-shaped gyrus capping the posterior end of the Sylvian fissure in the parietal lobe of each cerebral hemisphere, just dorsal to the angular gyrus. The supramarginal gyrus plays a role in auditory comprehension.
temporal gyrus
The superior, the middle, or the inferior temporal gyrus.
transverse temporal gyrus
See: Heschl gyrusuncinate gyrus
Uncus.Medical Dictionary, © 2009 Farlex and Partners