All PCRs consisted of initial denaturation at 94degC for 5 min., 35 cycles of denaturation at 94degC for 40 s, annealing at 52degC (for the nested-PCR) or 55degC (standard PCR) for 40 s, and polynucleotide chain elongation at 72degC for 40s, and final extension at 72degC for 5 min.
The sequential PCR amplification consisted of initial denaturation at 96degC for 1 min, 25 cycles of denaturation at 96degC for 10 s, annealing at 50-52degC for 5 s, and polynucleotide chain synthesis at 60degC for 4 min.
All PCRs consisted of initial denaturation at 94C for 5 min., 35 cycles of denaturation at 94C for 40 s, annealing at 52C (for the nested-PCR) or 55C (standard PCR) for 40 s, and polynucleotide chain elongation at 72C for 40s, and final extension at 72C for 5 min.
The sequential PCR amplification consisted of initial denaturation at 96C for 1 min., 25 cycles of denaturation at 96C for 10 s, annealing at 50-52C for 5 s, and polynucleotide chain synthesis at 60C for 4 min.
After such chemical modification, the
polynucleotide chain becomes susceptible to cleavage by piperidine (30).
PCR was carried out in a total volume of 15uL according to the following temperature profile: initial denaturation of the DNA matrix for 5 minutes at 95degC followed by 33 cycles of denaturation for 1 minute at 95degC, annealing of primers for 1 min at 60degC, polynucleotide chain elongation for 2 min at 72degC, and final elongation for 10 min at 72degC.
PCR was carried out in a total volume of 15uL according to the following temperature profile: initial denaturation of the DNA matrix for 5 min at 95degC followed by 33 cycles of denaturation for 1 min at 95degC, annealing of primers for 1 min at 60degC, polynucleotide chain elongation for 2 min at 72degC, and final elongation for 10 min at 72degC.
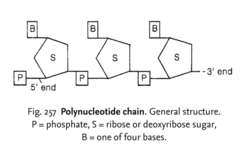
In 1953, the structure of DNA was correctly predicted by Watson and Francis Crick that DNA molecule consists of two long
polynucleotide chains each of these chains is known as a DNA chain, or a DNA strand which is made from simple subunits, called nucleotides.
One more important bioproperty- chemical polarity of the compounds and structures (water and hydrofuge organics, alkaline and acid parts of amino acids, polypeptide and polynucleotide chains)- was added to this group by the author.
The optimum temperature range for the synthesis of polynucleotide chains in Vitro is 50-60[degrees]C.
On one hand, the contrast interaction between a) water and hydrofuge organic compounds, b) amines and acids in polypeptide chains, and c) polypeptide and polynucleotide chains, which represent the chemically polar substance, support the repulsive forces in prebiotic bisystems.