Maternal Pelvis
BONY PELVIS

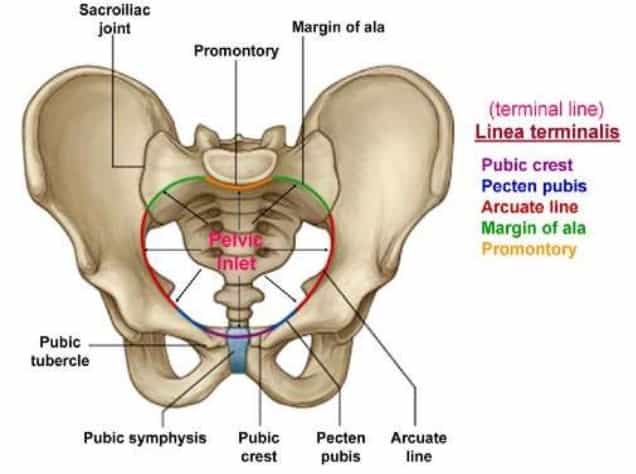
- The pelvis is made up of two innominate bones, sacrum, coccyx.
- The pelvis may be divided by linea terminalis into an upper part known as pelvis major or false pelvis and a lower part known as pelvis minor or true pelvis.
- Female pelvis as compared to the male pelvis has Shallow and wide symphysis pubis
PLANES :
4 imaginary planes:
- Plane of pelvic inlet or superior strait
- Plane of greatest pelvic dimensions
- Plane of midpelvis or least pelvic dimensions
- Plane of outlet or inferior strait
TRUE PELVIS
- Anterior wall and posterior wall of the true pelvis measures 5 cm and 10 cm respectively.
In the standing position:
- Upper part of pelvic canal is directed downwards and backwards
- Lower part curves and is directed downwards and forwards.
- The side walls of true pelvis converge a little.
The true pelvis is divided into 3 parts:
- Inlet
- Cavity
- Outlet

PELVIC INLET
Boundaries:
- Posteriorly: Sacral promontory and alae of the sacrum.
- Laterally: Linea terminalis.
- Anteriorly : Horizontal rami of Pubic bones and pubic symphysis.
- Typically round than ovoid.

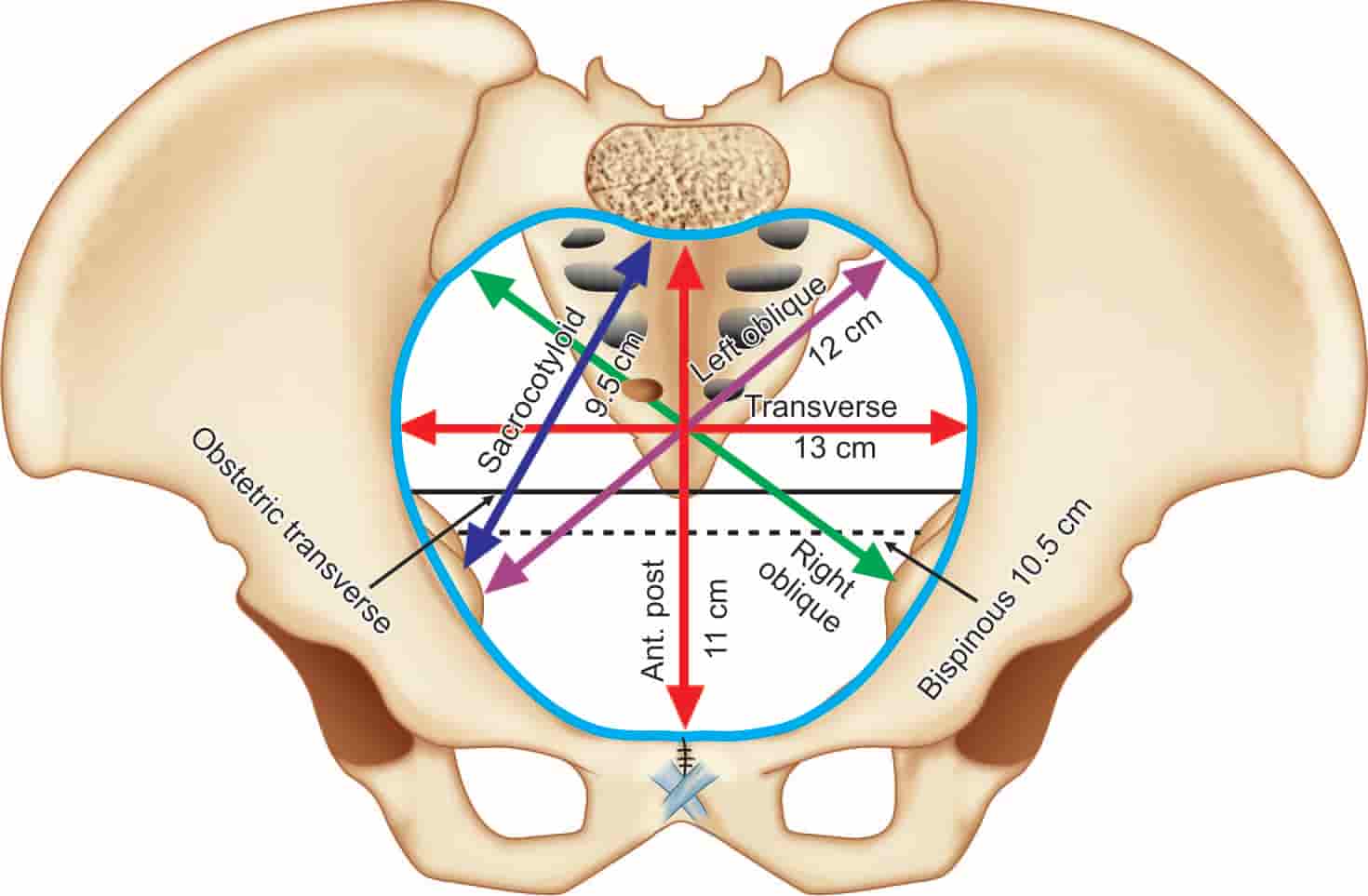
DIAMETERS :
- Anteroposterior diameter
- Obstetric conjugate(10.5 cm):
- Smallest anterioposterior diameter
- Shortest distance from symphysis pubis to the middle of sacral promontory.
- Presenting part of Fetus should pass through it.
- True conjugate/Anatomic conjugate/Conjugate vera(11 cm): Middle of sacral promontory to superior surface of the pubic symphysis.
- Diagonal Conjugate(12.5 cm) :Subpubic angle to middle of sacral promontory.
- Can be measured clinically :Subtracting 1.5 cm from this gives obstetric conjugate.
- The inlet is adequate for a normal fetus if the diagonal conjugate is 12cm or more.
- Obstetric conjugate(10.5 cm):
- Transverse diameter(13.5cm)
- Widest distance between iliopectineal lines
- Widest diameter of the inlet
- Most fetuses engage in transverse or oblique diameter
- Oblique diameters(12.5cm)
- Sacroiliac joint of one side to opposite iliopectineal eminence
- Posterior saggital diameters(5cm)
- Point of intersection of obstetric conjugate and transvese diameter to middle of sacral promontory
- Sacrocotyloid diameter(9.5cm)
- Midpoint of sacral promontory and ipsilateral iliopectineal eminence

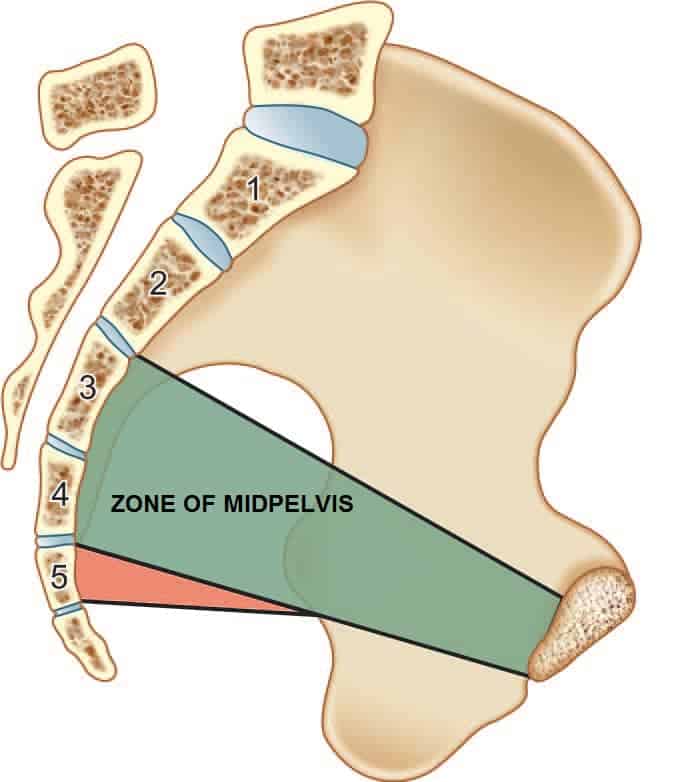
MIDPELVIS
- Cardinal movements of engagement and internal rotation occur here.
- Bounded by 4th & 5th sacral vertebrae,white line,ischial spines,sacrospinous ligaments and pubic symphysis .
Diameters :
- Anteroposterior diameter(11.5cm): Junction of 4th and 5th sacral vertebrae to lower border of public symphysis.
- Transverse diameter(10.5 cm)(smallest): Between ischial spines
- Posterior sagittal diameter(6 cm): Interspinous diameter to junction of 4th and 5th sacral vertebrae.

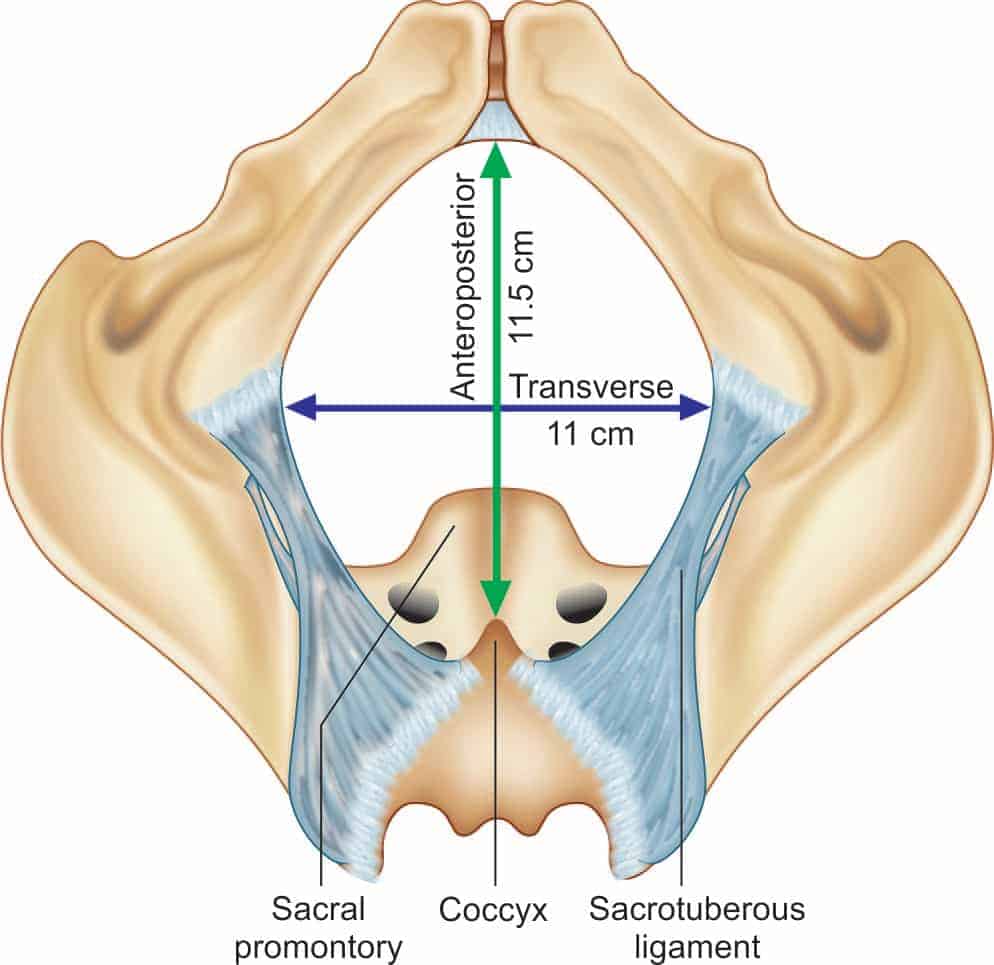
PELVIC OUTLET:
- Made up of 2 triangles with a common base
- Anterior triangle has subpubic angle as apex and pubic rami and ischial tuberosities as sides.
DIAMETERS:
- Anteroposterior diameter(12 cm):Lower margin of pubic symphysis to sacrococcygeal junction.
- Transverse Diameter (10.5 cm): Between inner edges of ischial tuberosity. Most important diameter of pelvis during labour.
- Posterior sagittal diameter(7 cm): Middle of transverse diameter to sacrococcygeal junction.
- Subpubic angle:Meeting of the two descending pubic rami.
- In females, it measures 85-90 degrees.
- <85o :transverse diameter of outlet will also be less.
- Waste space of Morris: Distance between pubic symphysis and edge of a round disc of diameter 9.3 cm.
Axis Of Birth Canal:
- Obtained by joining the axes of inlet, cavity and outlet.
- It is a curve with the convexity fitting the sacral curvature and is called anatomical pelvic axis or the curve of Carus.
- Inclination of Pelvis(assessed in standing position): The plane of inlet makes 60 degree with the horizontal.
- Affect engagement of the fetal head.
Obstetric axis:
- Course taken by the presenting part as it moves down through the pelvis.
- At first it goes downwards and backwards upto the level of ischial spine.
- Then, the direction changes and at the outlet it moves downwards and forwards.

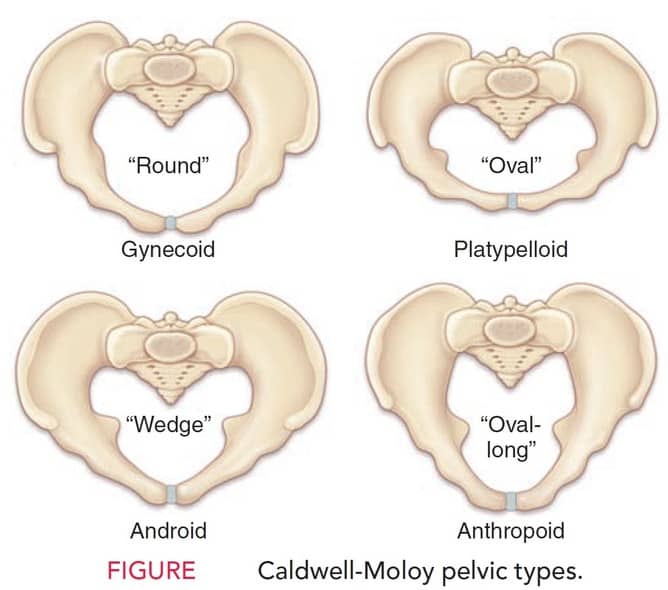
CLASSIFICATION OF PELVIS (BY CALDWELL AND MOLOY)
Based on shape of pelvis:
Gynaecoid pelvis(Commonest) :
- Transverse diameter equal to or greater than AP diameter
- In the midpelvis, sidewalls of pelvis are straight and the spines are not prominent.
- At the outlet, pubic arch is wide.
Android Pelvis
- At the inlet, posterior sagittal diameter.
- Deep transverse arrest
Anthropoid Pelvis
- At the inlet, AP diam.>Transverse diam.
- In the midpelvis, sidewalls are convergent, ischial spines are likely to be prominent.
- At the outlet, subpubic arch is narrowed, but well shaped.
Platypelloid pelvis:
- Flattened gynaecoid pelvis with a short AP and a wide transverse diameter.

Exam Important
- Most important diameter of pelvis during labour is Interspinous diameter of outlet
- Female pelvis as compared to the male pelvis has Shallow and wide symphysis pubis
- Maximum diameter of pelvic inlet is Transverse diameter
- Diagonal conjugate measurement at pelvic inlet can be assessed directly
- To obtain true conjugate 1.5 cm should be subtracted from the diagonal conjugate
- True pelvis refers to Lower part of pelvis
- Shortest diameter of the pelvic outlet is Posterior sagittal diameter
- Diagonal conjugate is defined as the distance between Lower border of symphysis pubis and the sacral Promontory
- Interspinous diameter is the smallest diameter of the pelvis in the midplane
- A pelvis characterized by an anteroposterior diameter of the inlet greater than the transverse diameter is classified as Anthropoid
- The smallest anteroposterior diameter of the pelvic inlet is called the Obstetric conjugate
- Deep transverse arrest is most commonly seen in Android pelvis
- Gynecoid is the most common type of female pelvis
- Subpubic angle is 85°
- The distance from the upper end of sacrum to lower border of pubis corresponds to Diagonal conjugate
- Transverse diameter of the female mid-pelvic plane is 10.5
Don’t Forget to Solve all the previous Year Question asked on Maternal Pelvis
Click Here to Start Quiz
Click Here to Start Quiz
