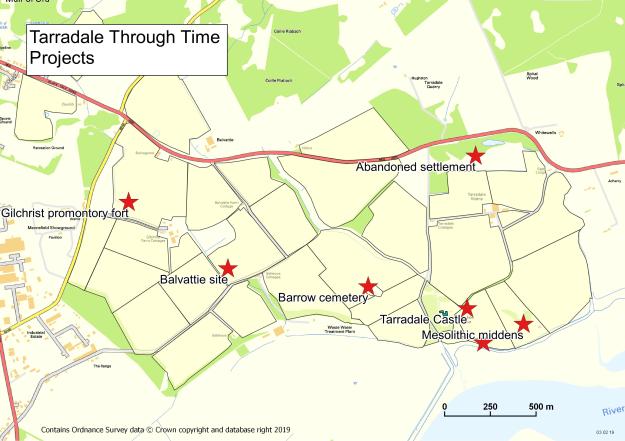
by Roland Spencer-Jones
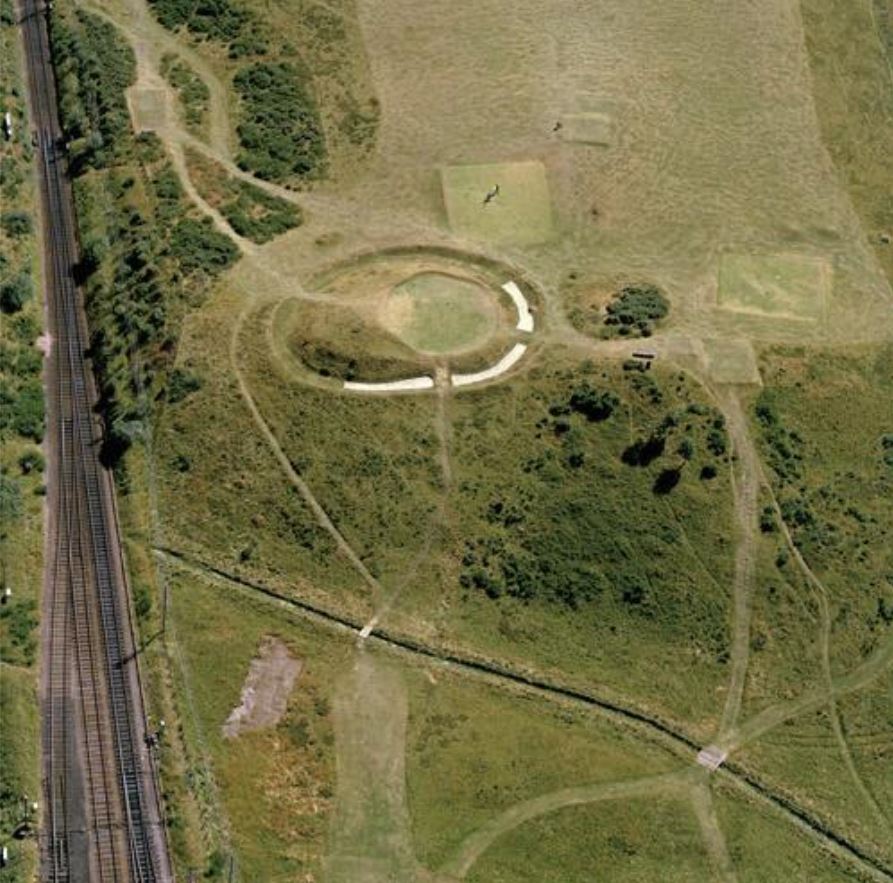
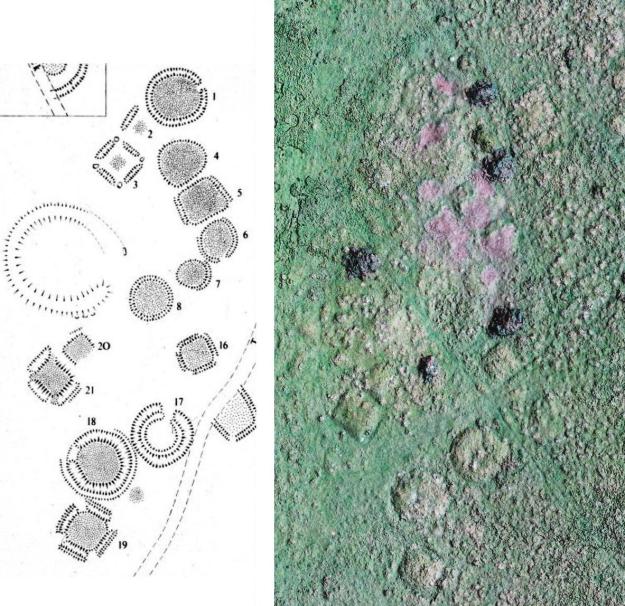
Muir of Ord Golf Club may be unique in having a green on top of a scheduled ancient monument. Castle Hill, the 13th green, is an artificially modified mound, standing at the north end of a ridge, proud of the surrounding flat ground. Its perimeter is delimited by a raised bank inside of which is a circular ditch, with two gaps at NW and SE. This bank and ditch enclose an oval flat area approximately 28 m by 21 m. The ridge probably represents an alluvial glacial moraine before the end of it was subsequently modified.
There has been considerable discussion and debate in the archaeological literature over the last 350 years as to the nature of this feature, when it was created, and for what purpose. However, whatever its nature, it is special, recognised as such by being included in the list of ancient monuments in Section 12 of the Ancient Monuments Consolidation and Amendments Act 1913. This important act of scheduling was reported to the Right Honourable Lord Lovat in a registered letter dated 11th April 1957. In the scheduling documentation[1] it was called Castle Hill Fort or Henge. Scheduling is the process that “identifies, designates and provides statutory protection for monuments and archaeological sites of national importance”, with damage to a scheduled site potentially incurring criminal charges. This became relevant in the early 1980’s, see later.
Early Descriptions of Castle Hill
The first historical mention of this prominent feature was towards the end of the 17th century in a massive volume of archaeological recording, the Monumenta Britannica, written by probably Britain’s first archaeologist, John Aubrey (Aubrey, 1665-93). In it, Aubrey records part of a letter he received in 1692 from a Dr James Garden, Professor of Theology in the King’s College at Aberdeen. Aubrey had written to many local dignitaries and antiquarians throughout Northern Britain asking for information about stone monuments. He was delighted to receive this full response from Dr Garden in which the latter refers to a sacred grove thus: “I … have gotten information of two groves yet standing which are reputed sacred. One of them (which stands near to a place called Taradale in the parish of Killernen and shire of Nairn) is enclosed with a trench or dry ditch having two entries to it where the ditch is filled up or rather the ground has never been broken: all that live near it hold it as sacred, and will not cut so much as a rod out of it: my informer adds that, hard by, there is a cornfield where he conjectures there has been one of the Monuments, because in it there are several big stones such as those Monuments use to consist of, fallen down and out of order.” Taradale, now Tarradale, is the name given to the settlement that later came to be called Muir of Ord once the railway arrived in 1862. Garden’s description of the “sacred grove” fits nicely with the structure now called Castle Hill. Also note the description of standing stones in the vicinity, which we will come on to later.
Continue reading