 The word “edema” comes from a Greek word meaning “swelling.” Medically, it refers to any swelling or puffiness in the body that is caused by fluid retention. The Lakeland pain management doctors at the Novus Spine & Pain Center vein clinic specialize in treating the pain of edema with cutting-edge therapies.
The word “edema” comes from a Greek word meaning “swelling.” Medically, it refers to any swelling or puffiness in the body that is caused by fluid retention. The Lakeland pain management doctors at the Novus Spine & Pain Center vein clinic specialize in treating the pain of edema with cutting-edge therapies.
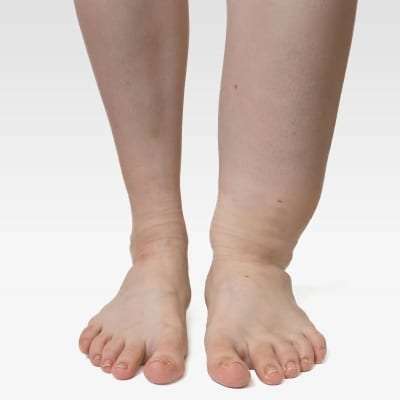
What Is Edema?
Edema is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the tissues of the body leading to swelling which can create pain. It is a common problem that can affect any part of the body, but most commonly affects the feet, ankles, legs, hands, and arms. Edema can be a sign of a serious condition. Although it is most often confined to a small area, edema can affect the entire body.
Pregnant women and older adults more commonly suffer from edema than others; however, it can happen to anyone. Medications, infections, and many other medical conditions can cause edema, in addition to pregnancy.
Causes of Edema
Edema is not contagious, nor is it genetic. It occurs when small blood vessels leak fluid into nearby tissues. When the extra fluid builds up, it causes the surrounding tissues to swell. The swelling can be the result of a twisted ankle, a bee sting, or a skin infection. In some cases, like an infection, edema helps the body heal by bringing more infection-fighting white blood cells to the swollen area.
In some cases, however, edema may be a sign of a more serious underlying medical condition. Edema can be the result of an imbalance of substances in the blood. Other causes include:
- Allergic reactions. In response to an allergen, nearby blood vessels leak fluid into the affected area. Edema is a part of most allergic reactions.
- Blood clots. Any blockage that prevents blood from flowing, such as a clot in a vein, can cause edema.
- A cyst, growth, or tumor. Any abnormal lump in the body can cause edema should it press against a lymph duct or a vein. As pressure builds up, fluids can leak into the surrounding tissue.
- Head trauma. A build-up of fluid in the cavities (ventricles) deep within the brain (hydrocephalus) can cause cerebral edema.
- Illness. Serious illnesses that can cause edema include:
- Heart failure.
- Kidney disease.
- Cirrhosis of the liver, or other liver conditions.
- Thyroid disorders.
- Blood clots.
- Infections.
- Severe allergic reactions.
- Prolonged immobility. People who are immobilized for a long time can develop edema. This type of edema can be due both to fluid pooling in gravity-dependent areas and the release of antidiuretic hormone from the pituitary.
- Varicose veins. Varicose veins are enlarged, knobby rough and twisted veins that bulge as the result of damaged valves in the vein. The increased pressure in the vein increases the risk of fluids leaking into the surrounding tissue.
Some high blood pressure and diabetic medications can cause edema. Other medications that can cause edema include:
- Calcium channel blockers.
- Corticosteroids (like prednisone and methylprednisolone).
- Estrogens.
- NSAIDs (such as ibuprofen and naproxen).
Symptoms of Edema
The symptoms of edema depend on the location in the body and the amount of swelling. Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet that is not injury-related could be edema. The swelling, or “puffiness,” can cause an uncomfortable feeling. In severe cases, the swelling can restrict the range of motion in the ankles and wrists.
In addition to swelling, a person with edema may notice:
- Stretched and shiny skin.
- Aching body parts and stiff joints.
- Higher pulse rate and blood pressure.
- Headache.
Individual symptoms depend on the underlying cause, the type of edema, and where the edema is located.
Edema Treatments
The only treatment for edema is to treat the underlying condition. Temporary edema can often be improved by reducing the amount of salt in the patient’s diet. The doctor may prescribe a diuretic (water pill) to help flush extra fluid out of the body by increasing the rate of urine production. However, diuretics do not work when edema is the result of medications.
Mild edema usually goes away on its own, especially if the patient helps the body eliminate the fluid by raising the affected limb higher than the heart.
Edema Self-Care Techniques
Some self-care techniques that can help prevent or reduce edema include:
- Avoid tobacco and alcohol.
- Compression. The doctor may recommend the patient wear compression (support) stockings, sleeves, or gloves, usually after the swelling has gone down, to prevent further swelling.
- Healthy eating. Avoid packaged and processed foods with a high salt content.
- Elevation. Elevating the swollen body part above the level of the heart, several times a day, helps improve circulation. In some cases, elevating the affected body part while you sleep may be helpful.
- Maintain a healthy weight, if appropriate.
- Movement/Exercise. Moving and using the muscles in the affected body part, especially the legs, may help pump the excess fluid back toward the heart. Avoid sitting or standing still for extended periods. Get up and walk when traveling, especially during air travel.
Minimally Invasive Edema Treatments
Edema can be an external sign of venous insufficiency (a vein problem). Patients with vein-related symptoms can experience chronic pain and discomfort as well as, leg heaviness, leg fatigue, leg swelling, itching, or leg cramping.
Endovenous ablation (also called Endovenous Thermal Ablation or Venus Ablation) is a frequently used method for treating varicose veins which can also help treat edema. There are three types of endovenous ablation treatments for varicose veins that can be performed with local anesthesia in an outpatient setting at the pain clinic in Lakeland, Florida:
- Laser Ablation. An advantage of laser ablation is the ability to control the amount of energy delivered inside the vein
- Radiofrequency. Similar to laser ablation, radiofrequency uses small electrodes in direct contact with the vein wall emitting high radiofrequency energy to heat, cauterize, and close the vein.
- Steam Ablation. The newest method of thermal vein ablation. A very small volume of sterile water is used with a steam catheter to cauterize and close varicose veins.
Is Edema Preventable?
The prevention of edema may not be possible, depending on the cause. If edema is the result of health problems, such as congestive heart failure, liver disease, or kidney disease, the swelling can only be managed.
To help prevent edema, your doctor may recommend staying as physically active as possible and avoiding excess sodium in your diet. In addition:
- Elevate the legs when seated or lying down.
- Wear support stockings if you have edema of the legs.
- Keep moving, as much as possible. Avoid sitting or standing for long periods without moving around.
- Limit the amount of salt in your diet.
Any underlying disease or condition needs treatment to prevent it from becoming more serious.
Novus Spine & Pain Center
The Novus Spine & Pain Center is in Lakeland, Florida, and specializes in treating edema (swelling). By using a comprehensive approach and cutting-edge therapies, we work together with patients to restore function and regain an active lifestyle, while minimizing the need for opiates.
Our Mission Statement: To provide the best quality of life to people suffering from pain, by providing state of the art treatments, knowledge and skill, compassion, and respect for all.
For your convenience, you may schedule an appointment online, request a call back, or call our office at 863-583-4445.
Edema Resources
What is Edema? (WebMD)
Edema – Symptoms & Causes (Mayo Clinic)
Edema – Diagnosis & Treatment (Mayo Clinic)
Leg Swelling (Mayo Clinic)
Hydrocephalus (Mayo Clinic)
Edema (MedicineNet)
Everything You Need To Know About Edema (Medical News Today)
Edema (Wikipedia)
What Causes Edema? (Healthline)
Edema (Family Doctor)
C3: Edema (American Vein and Lymphatic Society)
Updated: April 18, 2022
