Argyrosomus regius

Argyrosomus regius, also known as the meagre or croaker, is a species of drum that belongs in the genus Argyrosomus. It is found in the Atlantic Ocean and also the Mediterranean and Black Sea.
Etymology[change | change source]
The specific name regius means "royal".
Classification[change | change source]
Argyrosomus regius was described in 1801 as Perca regia by Ignacio Jordán Claudio de Asso y del Río. Later though, the species name was changed and is now a synonym.
Synonyms[change | change source]
- Sciaena aquila Cuvier, 1817
- Perca regia Asso, 1801
- Argyrosomus regium Asso, 1801
- Sciaena regius Asso, 1801
- Cheilodipterus aquila Lacepède, 1803
- Sciaena aquila Lacepède, 1803
- Perca vanloo Risso, 1810
- Argyrosomus procerus De la Pylaie, 1835
- Johnius hololepidotus Lacepède, 1801
Description[change | change source]
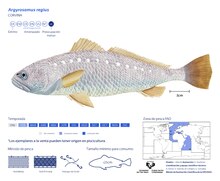
The meagre is a relatively large fish with tiny eyes. It has a body that looks like that of a cod, but with a smaller dorsal fin and a slightly longer body. It can reach up to 2.3 m (7.5 ft) in length and 103 kg (227 lb) in weight. You can easily see the lateral line.
Ecology[change | change source]
Life history[change | change source]
Breeding takes place from May to July. The juveniles leave the estuary and move to coastal waters where they spend the winter months. They go back to the estuary when it is spring from the middle of May. The females produce about 800,000 eggs. When the water temperature is 17–22 °C (63–72 °F), spawning will happen.
What they eat[change | change source]

The juveniles eat small demersal fish and crustaceans. When they've grown to 30–40 cm, they will start feeding on pelagic fish and cephalopods.
Human uses[change | change source]
Fisheries[change | change source]
Argyrosomus regius is fished using trawls. The main fisheries are in Mauritania, Morocco, and Egypt.
Aquaculture[change | change source]
The aquaculture of this fish is experimental. There are a few facilities in southern France.
Image gallery[change | change source]



Related pages[change | change source]
References[change | change source]
- "Argyrosomus regius". British Marine Life Study Society. Retrieved 26 December 2016.
- Pollard, D.A.; Bizsel, K. (2020). "Argyrosomus regius". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
