Table of Contents
SAP Product Costing Part 1
SAP
Controlling Configuration
Create Controlling area
Tcode: OKKP
Create Controlling Number Range
Tcode: KANK
In controlling CO document are saved are Business transaction types
E.g., of Business Transaction types are.
- KAUS: Calculate Scrap
- KAMV: Manual cost allocation
CO number range is assigned to business transaction type
Procedure: Click the create button. Now create the Group say Primary posting and create number range for this group say 1 to 199999. Now come back to the previous screen. Select the unassigned business transaction. Click button Element, select the group created earlier. This business transaction get assigned to the group and get’s the number range of the group
| Group | Number Range |
| Primary | 100000-200000 |
| Secondary | 200001-400000 |
| Planning | 400001-600000 |
Controlling Versions
Controlling data is stored in versions.
Default version is zero. Version zero is used for both actual and planning. Other versions are used only for planning.
IMG Path : SPRO-Controlling – General controlling – Organization – Maintain versions
Create Cost Element
Primary Cost Element
- Create Primary Cost Element: KA01/KA02 /KA03 in CO
- Create Primary CE in FI: FS00
Secondary Cost Element
- Create Secondary Cost Element in Controlling: KA06
List / Display Cost Element
Tcode : KA23
Primary Cost Element
| GL Acct | Description |
| 41069 | Raw Material Consumption |
| 41071 | Packing Material Consumption |
| 41072 | Purchased Components consumption |
| Secondary CE | Name | CE Category |
| 942000 | Canteen assessment cost element | 42: Assessment |
| 942001 | Material cost assessment OH cost element | 42 : Assessment |
| 942002 | marketing assessment OH cost element | 42 : Assessment |
| 941000 | Material Cost OH | 41 : OH |
| 941001 | Activity cost OH | 41 : OH |
| 943000 | Setup Activity Cost | 43: activity allocation |
| 943001 | Labor Activity cost | 43: activity allocation |
| 943002 | Machine Activity Cost | 43: activity allocation |
Cost Element Numbering rules can be similar to one shown below:
- 9: Starting Number.
- 41 / 42/43: CE Category
- 000/002: Sequence number
Create Cost Centers
Transaction: OKEON or KS01
Transaction to change / display Cost Center: KS02 / KS03
| Cost Center Group | Description | Cost Center | Cat | Co. Code | Co. Code |
| ADMIN_CTR | Administration | 3301002 | W | IST5 | IST5 |
| SERV_CTR | Canteen Dept | 3301001 | H | IST5 | IST5 |
| PROD_CTR | Production Div-1 | 3301005 | F | IST5 | IST5 |
| PROD_CTR | Production Div-2 | 3301006 | F | IST5 | IST5 |
Create Activity Type
- Transaction code: KL01 / KL02 /KL03
- For each activity type secondary cost element of category 43 is required
- Create secondary CE: KA06
| Act Type | Description | Act Unit | CCTR cat | Allocation CE | Act type cat | Price Indicator-Plan | Act Activity Type cat | Act Price Indicator |
| 330100 | Set Up activity cost | HR: Hours | * | 943000: Set Up activity cost | 1: Manual entry, manual allocation | 1: Plan price, automatically | 1: Manual entry, manual allocation | 5: Actual price, automatically based on activity |
| 330101 | Labor activity cost | HR: Hours | * | 943001: Labor activity cost | 1: Manual entry, manual allocation | 1: Plan price, automatically | 1: Manual entry, manual allocation | 5: Actual price, automatically based on activity |
| 330102 | Machine activity cost | HR: Hours | * | 943002: Machine activity cost | 1: Manual entry, manual allocation | 1: Plan price, automatically | 1: Manual entry, manual allocation | 5: Actual price, automatically based on activity |
Display Cost Center Report
Tcode: S_ALR_87013611
For detailed, step-by-step instructions on SAP Product Costing Advance, follow along with my video tutorial below
Activity Independent Cost Center Planning
Tcode: KP06
Layout : 1-101
CCTR# 3301001 – Canteen
| Cost Element | Description |
| 63510 | Electricity |
| 63520 | Water |
| 63581 | Cleaning Services |
Activity Dependent Planning
Activity Hours Planning for Cost Center
Tcode: KP26
Cost Center # 3301005 – Production Division -1
Plan Activity Dependent Cost
Tcode: KP06
CCTR # 3301005
Activity Type: 330100 to 330102
Cost Element
- Raw Material Consumption: 41070
- Packing Material Consumption: 41071
- Purchased Components: 41072
- Wages: 60000
Plan Cost Splitting
Transaction code: KSS4
Cost Center # 3301005
Plan Cost Splitting: KSS4
This will split activity independent cost equally among cost center activities. Let’s post planned activity independent cost
Electricity Cost # 63510
Water # 63520
Plan Price Calculation
Tcode: KSPI
| KP26 Planned Act CCTR#3301004- Prod Div | KP06 Act Dependent Cost | KSS4 | KSPI | KSPI | |||||
| Act Type | Description | Allocation CE | Plan Act Hr./Month | Wages:60000 | RM:41070 | PM:41071 | KSS4/period | KSPI | KSPI |
| 330100 | Setup | 943000 | 100 | 1000 | – | – | 1000 | (KP06+KSS4)Hr | 20 |
| 330101 | Labor | 943001 | 200 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | (KP06+KSS4)Hr | 20 |
| 330102 | Machine | 943002 | 200 | 1000 | 1000 | – | 1000 | (KP06+KSS4)Hr | 15 |
Verify Activity Prices
Tcode: KSBT
For detailed, step-by-step instructions on SAP Product Costing Advance, follow along with my video tutorial below SAP Product Costing Advance
FI-MM Integration
Define Plant
- A ‘Plant’ is an operating area or a branch or a location within a company. Each ‘Plant’ is assigned to a single ‘company code’. A ‘company code’ can have several ‘Plants.’
- IMG Path: Enterprise Structure -Definition – Logistics general – Define, copy, delete, check plant
Define Storage Location
A storage location is the place where stock is physically kept within a plant. There may be one or more storage locations within a plant.
- IMG Path: Enterprise Structure -Definition – Materials Management – Maintain Storage Location
- Tcode: OX09
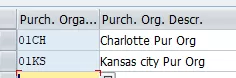
Maintain Purchase Organization
The purchasing organization is the highest level of aggregation (after the organizational unit “client”) for purchasing statistics.
IMG Path: Enterprise Structure – Definition – Materials Management – Maintain Purchasing Organization
Assign Plant to Company Code
A Plant needs to be assigned to one of the Company Codes, the relation is always one to one i.e. One Plant can be assigned to only one company code
However, before plant is assign to company code, we have to define Valuation Level. Materials are valued at valuation level.
Define Valuation Level
OX14
Assign Plant to Company Code
Path: Enterprise Structure -Assignment – Logistics general – Assign Plant to Company Code
Assign Purchase Organization to Company code
IMG Path: Enterprise Structure – Assignment – Material Management – Assign purchasing organization to company code
Assign Purchase Org to Plant
IMG Path: Enterprise Structure -Assignment – Logistics general – Assign purchasing organization to Plant.
Purchasing Groups
Path: SPRO – Material Management – Purchasing – Create Purchasing Group
A Purchasing group refers to a people or a group of people who are dealing with specific material or a group of material.
Define Attributes for Material Type
Material Type is a Logical grouping of materials that are similar in characteristics. Any material master record created in SAP ERP must be assigned to a material type.
IMG Path: Logistics – General – Material Master – Basic Settings- Material Types- Define Attributes of Material Types
- Transaction Code: OMS2
| Material Type | Description |
| ROH | Raw Material |
| FERT | FG Type |
| HALB | Semi FG type |
Maintain Posting Period
This activity is done for making a Company Code relevant for materials Management and to define the starting posting period.
IMG Path: Logistics – General -Material Master – Basic Settings- Maintain Company Codes for Materials Management
Transaction Code: OMSY
Creation of Plant Parameters
Transaction code: OMI8
Copy from plant 1000 to our plant IST5
Default values of Tax code for Invoice Verification
Path: SPRO -Materials Management – Logistic Invoice verification – Incoming Invoice – Maintain Default Tax code
GR Tolerance Group
In this step, we set the tolerance limits for goods receipts. When processing a goods receipt, the system checks each item to determine whether the goods receipt varies from the purchase order or the material master data. The different types of variances are defined by tolerance keys. For each tolerance key, tolerance limits can be set per
company code.
Path: SPRO -Material Management – Inventory Management – Good Receipt – Set Tolerance
Copy Tolerance B1, B2 and VP from company code 1000 to IST5
Set Tolerance limit for Price Variance.
When processing a purchase order, the system checks whether the effective price of a PO item shows variances compared with the valuation price stored in the material master record. In addition, it checks whether the specified cash discount value is admissible.
Variances are allowed within the tolerance limits. If a variance exceeds a tolerance limit, the system issues a warning or error message. In SAP, the types of variance are represented by the tolerance keys.
Path: SPRO –Material Management – Purchasing – PO – Set Tolerance limit for price variance
Copy Tolerance limit PE, SE from company code 1000 to IST5.
Set Tolerance limit for price difference between Invoice and Purchase order
IMG Path: Material Management – Logistic Invoice verification – Invoice block – Set Tolerance.
Copy price variance PP and VP from company code 1000 to IST5.
Define Automatic Status Change
Transaction Code: OMRV
Invoice verified in the background. If found correct, status automatically set to completed.
Define Valuation Control
It defines if the valuation areas will be grouped by activating the valuation grouping code. In the standard SAP R/3 System, the valuation grouping code is set to active as default setting.
Transaction code: OMWM
IMG Path: Materials Management -> Valuation and Account Assignment -> Account Determination -> Account Determination without Wizard-> Define Valuation Control
Group Together Valuation area plant
Path: Material Management – Valuation and Account Assignment – Account Determination – Account Determination without wizard – Group together valuation area
Transaction Code: OMWD
In the standard SAP system, valuation is predefined at plant level. All plants are grouped together via valuation grouping code 0001. Assign SAP define valuation grouping 0001 to Plant IST5.
Define Valuation Classes
IMG Path: Materials Management -> Valuation and Account Assignment -> Account Determination -> Account Determination without Wizard->Define Valuation Classes.
Transaction Code: OMSK
| Valuation Class / Acct Cat Reference | Description |
| Valuation Class | A grouping of Material |
| Account Category Reference | Grouping of Valuation Classes |
| Material Type | Logical Grouping of material with similar characteristic |
| Material Type and Account Category Reference assignment | Material Types are assigned to Account category Reference. This links Material types to valuation class and to GL accounts to which posting should happen |
Account Category Reference
Valuation Class
Transaction Code: OMSK
Material Type and Account Category Reference
Transaction Code: OMSK
FI-MM Integration Configuration
Transaction Code: OBYC
| Transaction | Valuation Class | GL | Description |
BSX Inventory Postings | 01FG | 13200 | FG Inventory |
| 01SF | 13100 | SFG Inventory | |
| 01RM | 13000 | RM Inventory | |
WRX GRIR Clearing Account | 01FG | 20100 | GRIR Clearing Account |
| 01SF | 20100 | ||
| 01RM | 20100 | ||
| GBB-BSA | 01FG | 13997 | Inventory Data Load |
| GBB-VAX | 01FG | 41000 | Cost of Goods Sold |
| GBB-VBR | 01RM | 41070 | Consumption Raw Materials |
| GBB-AUF | 01FG | 41076 | Production Receipts |
| GBB-AUF | 01SF | 41076 | Production Receipts |
For detailed, step-by-step instructions on SAP Product Costing Advance, follow along with my video tutorial below SAP Product Costing Advance
Product Costing
Define Costing Sheet Components- Calculation base
Path: SPRO – Controlling – Product Cost Controlling – Product Cost Planning – Basic settings for material costing – Overhead – Costing sheet components – Define Calculation base
The calculation base determines to which cost elements overhead is applied together.
Define Costing Sheet Components
Percentage OH Rates
Path: SPRO – Controlling – Product Cost Controlling – Product Cost Planning – Basic settings for material costing – Overhead – Costing sheet components – Define Percentage OH rates
Define percentage overhead rates, for example, 10% in controlling area AUM1.
Select OH Rate 19MH and below entries.
Select 19AH OH rate and make the below entries
Define Costing Sheet Components- Credits
Path: SPRO – Controlling – Product Cost Controlling – Product Cost Planning – Basic settings for material costing – Overhead – Costing sheet components – Define Credits
Here you define Cost center which is to be credited with OH cost. Further this credit is recorded under secondary cost element of category 41 (overhead rates)
Define Costing Sheet
Path: SPRO – Controlling – Product Cost Controlling – Product Cost Planning – Basic settings for material costing – Overhead – Costing sheet
Define Costing Variant
Costing Variant contain Costing Type, Valuation Variant, Date Control, Quantity structure control, Transfer control and reference variant. We will create three costing variants – Standard cost, Planning cost and Actual cost variant
Costing variants is the link between product costing and Customizing,
The costing variant contains all the control parameters for costing.
The costing variant for a material cost estimate contains the following control parameters:
- Costing type
- Valuation variant
- Date control
- Quantity structure control
- (only relevant for cost estimates with quantity structure)
- Transfer control (optional)
- Reference variant (optional)
Note:
Costing Type: Determine type of cost is calculated., whether standard cost, Cost for reporting, etc.
Valuation variants determine how Material, Activities, Subcontract, External Operations and OH are valued.
Date Control: Determine validity period of costing run
Define Costing Variant Components
Define Costing Variant Components -Costing Type
Path: Controlling – Product Cost controlling – Product Cost planning – Material Cost estimate with quantity structure – Costing variant components – Define costing type
Here you define the purpose of a material cost estimate by specifying, field in the material master record to which the costing results can be transferred to:
| Update – Material master Fields | Cost Estimate (CK40N) |
| Standard price | Standard cost estimate (01) |
| Tax-based price | Inventory cost estimate |
| Commercial price | Inventory cost estimate |
| Price other than std. price | Modified standard cost estimate |
In a client there can be only one costing type for standard price. We will keep SAP standard costing type 01 for standard price
Define Valuation Variant
Path: Controlling – Product Cost controlling – Product Cost planning – Material Cost estimate with quantity structure – Costing variant components
Here you specify parameters to be used for cost estimate.
- Material Valuation: define the sequence in which the system searches for prices from the accounting view or costing view of the material master record to valuate materials. E.g., We can specify the sequence in which material price is picked – use moving average price, if not available use Standard Price, if not available use Purchase Info record and so on
- Activity Price: Sequence in which activity price is picked. For e.g. take Plan activity price, if not available take actual activity price and so on
- Overhead costs: Link the costing sheet prepared in earlier steps to pick the OH cost for cost estimates.
Activity type price priority
Sub-contracting price sequence
External Operations price sequence
Under OH select the costing sheet created earlier
OH, on Material Components. Not required in our scenario. If costing sheet assigned here OH 10% and 15% defined in costing sheet will be added to the raw material
To display Number in the drop down enable visualization in the options as below.
Valuation variant is defined at plant level
Click and assign Valuation variant I5 to our plant IST5
Define Date Control
Path: Controlling – Product Cost controlling – Product Cost planning – Material Cost estimate with quantity structure – Costing variant components
Tcode: OKK6
Date control determines which dates are proposed or displayed when a cost estimate is created, and whether these dates can be changed by the user.
- The validity period of the cost estimate
- The date on which the quantity structure is determined ( quantity structure date)
- The date on which the quantity structure is valuated ( valuation date)
Define Quantity Structure Control
Path: Controlling – Product Cost controlling – Product Cost planning – Material Cost estimate with quantity structure – Costing variant components
Tcode: OKK5
Check BOM Selection
Path: Controlling – Product Cost controlling – Product Cost planning – Material Cost estimate with quantity structure – Settings for qty structure – BOM Selection – Check BOM selection
Tcode: OPJI
BOM: BOM (Bill of Material): This is list of Raw material along with the quantities required to produce Finished Goods
Specify different sequences of priorities of BOM usages according to your requirements
Check BOM Application
Path: Controlling – Product Cost controlling – Product Cost planning – Material Cost estimate with quantity structure – Settings for qty structure – BOM Selection – Check BOM application
Tcode: OPJM
Here you define BOM application area. Now you assign BOM selection ID created earlier to this BOM application area. Selection ID decides the sequence in which BOM are selected during cost estimate for this BOM application area
Check Routing Selection
Path: Controlling – Product Cost controlling – Product Cost planning – Material Cost estimate with quantity structure – Settings for qty structure – Routing Selection – Check automatic routing selection
Tcode: OPJF
Routing: It is sequence of activities. It specifies on which Work Center (A work center typically refers to a machine) what activities are to be performed for how many hours. Raw Material is converted into finished goods at work center
Define a Routing selection ID
Assign it to alternative selection priorities
Specify selection priority for each of these scenarios
- ID: A6: Can be any identifier
- SP: Selection Priority
- Task List: N: Routing, R: Rate Routing
- Plan Usage: 1: Production
- Status: 4: Released general
Assign BOM application ID and routing selection ID in Quantity structure control
Tcode: OKK5
Define Transfer Control
Path: Controlling – Product Cost controlling – Product Cost planning – Material Cost estimate with quantity structure – costing variant component – define transfer control
Tcode: OKKM
Transfer Control: The transfer control specifies how the existing cost estimate is to be used in the cost estimate of the other product. For e.g. Costing done at beginning of the year. All components of the product cost have to be costed to arrive at final Standard Cost. Costing of new component during the year. We can use standard cost of components costed at the beginning of the year if they are being used in manufacture of this new Product. Here we will use the transfer control
In this step you define parameters for partial costing. The purpose of partial costing is to prevent the system from creating a new cost estimate for a material when costing data already exists. Instead, the existing costing data is simply transferred into the new cost estimate. This improves performance.
Current and Future cost kept for 6 months before archiving
Define Costing Variant
Path: Controlling – Product Cost controlling – Product Cost planning – Material Cost estimate with quantity structure – Define costing variant
Tcode: OKKN
Select costing component created in earlier steps and assign to Costing variant MK14. Costing type assigned is 01 Standard Cost and not one created earlier as we want to do standard costing
Qty Structure selection
Additive cost. These are transportation, packing cost added to COGM.
Update selection
Itemization: Detailed break up of cost based on its components
Error management selection
Assignment is optional so ignored for now
For detailed, step-by-step instructions on SAP Product Costing Advance, follow along with my video tutorial below SAP Product Costing Advance Training
Define Cost Component Structure
Path: Controlling – Product Cost controlling – Product Cost planning – Basic settings for material costing – Define Cost component structure
Tcode: OKTZ
It gives the breakup of the cost estimate of products like material cost, packing mat cost, consumables etc. The cost component structure contains the cost components (grouping of costs or cost elements)
Each cost component specifies whether it is relevant for valuation of inventory or not and also it specifies under which cost components to be updated. Eg. COGM, COGS, Inventory, and Tax inventory etc. Each cost component specifies whether it is to be rolled up or not.
Any component which is relevant for inventory should be rolled up and shown under COGM view.
The cost component can have maximum of 40 components in case of all components are variable. In case of all components are fixed, then the CCS can have maximum of 20 components.
Define cost component Group (CCG)
Path: Controlling – Product Cost controlling – Product Cost planning – Basic settings for material costing – Define Cost component structure
Tcode: OKTZ
Define Cost Component Structure
Define Cost Component with attributes
Select CCS B1 and double click Cost component with attributes. Define as below:
Material Cost
Packing Cost component
Purchased cost component.
Setup Activity Cost
Machine Activity Cost
Labor Activity Cost
Material OH
Activity OH Cost Component
Assign Cost Components to Cost Elements
Select the views for this cost component structure.
Assign Cost component structure to Organizational Units (Co Code and Plant)
Activate Cost Component structure
Activate CCS to Controlling area currency
Path: Controlling – Product Cost controlling – Product Cost planning – Select functions in material costing – activate CCS in CO Area currency
Difference between Plan Cost, Standard Cost and Actual Cost
| Plant Cost | Standard Cost | Actual Cost |
| Plan cost for a job order | Estimated cost per unit | Actual cost |
Difference between plan cost and actual cost is of Fixed Cost. Fixed cost does not change in plan cost.
Define Costing variant for Plan.
Tcode: OPL1
Path: Controlling- Product Cost Planning – Cost Object Controlling – Product Cost by order – manufacturing orders- Check costing variant for manufacturing orders – new entries
We will use Valuation variant I5 created earlier.
Costing Type, we will use SAP standard: 06 Planned Production Order
Define Costing variant for Actual.
Tcode: OPL1
WIP Settings
Define RA Key
Path: Controlling- Product Cost Planning – Cost Object Controlling – Product Cost by order – Period end closing – work in progress – Define RA Key
Tcode: OKG1
Path: Controlling- Product Cost Planning – Cost Object Controlling – Product Cost by order – Period end closing – work in progress
Create below secondary (31 category CE): KA06
| Sec CE | Name | CE Category |
| 931000 | WIP Material Cost | 31: Prod Order/ Project Result |
| 931001 | WIP Direct OH | 31: Prod Order/ Project Result |
| 931002 | WIP Indirect OH | 31: Prod Order/ Project Result |
| 931003 | WIP Technical (Total of all WIP) | 31: Prod Order/ Project Result |
Define RA version
Path: Controlling- Product Cost Planning – Cost Object Controlling – Product Cost by order – Period end closing – work in progress
All results analysis data calculated in results analysis is updated on the order with reference to the results analysis version. This enables you to calculate work in process on the basis of multiple results analysis versions. This means that you can use different results analysis versions to define different methods of WIP calculation
Save and deselect Transfer to Financial Accounting. This will be reselected after completing subsequent steps.
Define valuation methods actual
Path: Controlling- Product Cost Planning – Cost Object Controlling – Product Cost by order – Period end closing – work in progress
- In this step you define a valuation method for the calculation of work in process.
- In the Product Cost by Period component the work in process is valuated at target costs. The valuation is made based on the quantities confirmed at the operations point
- In the Product Cost by Order component the work in process is normally valuated at actual costs. The value of the work in process is the difference between the debit and the credit of an order if the order has the status PREL (partially released) or REL (released).
Define Line ID
Path: Controlling- Product Cost Planning – Cost Object Controlling – Product Cost by order – Period end closing – work in progress
Define Line ID. In next step you assign CE to these Line ID. Line ID receive WIP value from these CE at the time of Production Order Settlement. Create a Secondary CE of category 31 and assign to these Line ID. Secondary CE receive the settled cost. Secondary CE is mapped to FI BS and PL account. This enable posting of FI documents for WIP balance at the time of production Order settlement
Line ID show WIP breakup. New entries and below entries
Define Assignment
Path: Controlling- Product Cost Planning – Cost Object Controlling – Product Cost by order – Period end closing – work in progress
19M – Material Cost: 41069, 41070, 41071, 41072
19D – Direct OH: 943000-943002
19I – Indirect OH: 941000-941001
19S – Settlement CE: 41077
Assign CE / GL accounts to WIP line ID’s created in above step
SAP GL account length is 10 digits. When masking prefix zeroes if length less than 10 digit
Define Update
Path: Controlling- Product Cost Planning – Cost Object Controlling – Product Cost by order – Period end closing – work in progress
Tcode: OKGA
K : Cost
A : Settled Cost
CE category is 31. This is created for WIP
For each line ID, you specify the results analysis cost element under (31 category) which the work in process is updated, and assign each line ID to a category.
The line IDs put the costs incurred for an order into groups such as the following:
Path: Controlling- Product Cost Planning – Cost Object Controlling – Product Cost by order – Period end closing – work in progress
Tcode: OKGA
Create below GL accounts: FS00.
| GL Acct | Description | Type | Account Group | FSG | Line Item | Sort key |
| 200126 | WIP Mat Cost BS | BS | Current Assets | G006 | X | 001 |
| 200127 | WIP DOH Cost BS | BS | Current Assets | G006 | X | 001 |
| 200128 | WIP IOH Cost BS | BS | Current Assets | G006 | X | 001 |
| 400205 | WIP Mat Cost PL | PL | Manufacturing Expenses | G001 | X | 001 |
| 400206 | WIP DOH Cost PL | PL | Manufacturing Expenses | G001 | X | 001 |
| 400207 | WIP IOH Cost PL | PL | Manufacturing Expenses | G001 | X | 001 |
MTS: Make to Stock use WIPR.
MTO: Make to Order use RUCR.
Secondary CE 931000 post WIP material cost to BS:200126 and PL 400205 account
Select Transfer to FI in RA version
Path: Controlling- Product Cost Planning – Cost Object Controlling – Product Cost by order – Period end closing – work in progress
For detailed, step-by-step instructions on SAP Product Costing Advance, follow along with my video tutorial below
Variance Calculations
Variance Calculation determines differences between the actual costs incurred on a production order and the standard costs of the material produced. Variances are calculated not at once, but for different variance categories.
Define Variance Keys
Path: Controlling – Product Cost Controlling – Cost Object Controlling – Product Cost by Order – Period End Closing – Variance Calculation
Tcode: OKV1
Variance key is added to Finished Goods material Master. From the material master it is transferred to production order and control variance calculation
Define default variance keys for plants.
Path: Controlling – Product Cost Controlling – Cost Object Controlling – Product Cost by Order – Period End Closing – Variance Calculation
Tcode: OKVW
Define variance variant.
Path: Controlling – Product Cost Controlling – Cost Object Controlling – Product Cost by Order – Period End Closing – Variance Calculation
Tcode: OKVG
Define target cost version.
Path: Controlling – Product Cost Controlling – Cost Object Controlling – Product Cost by Order – Period End Closing – Variance Calculation
Tcode: OKV6
Variance Formula = Control Cost – Target cost
Now Control cost can be Actual Cost or Plan cost depending on version.
Target cost can be current standard cost or any other cost depending on version.
Define Controlling area version for Plan.
Tcode: OKEQ
Select and Click controlling area settings
Select and click settings for each Fiscal Year
Define Number Range for Variance Documents
Path: Controlling – Product Cost Controlling – Cost Object Controlling – Product Cost by Order – Period End Closing – Variance Calculation
Tcode: KANK
Business Transaction: KVAR : assign to secondary postings
Settlement
Create Settlement Profile
Path: Controlling – Product Cost Controlling – Cost Object Controlling – Product Cost by Order – Period End Closing- Settlement
Settlement profile used for settlement of Production order.
To be Settled in Full: Production order can be settled only when balance is zero.
Can Be settled: Order can be settled even with the balance.
Not for settlement: WIP can be settled. Variances cannot be settled.
Max no. Dst rls: Maximum 6 receiver allowed in settlement profile.
Residence time: 6 months before it is archived.
Maintain Number Range for Settlement Documents
Path: Controlling – Product Cost Controlling – Cost Object Controlling – Product Cost by Order – Period End Closing- Settlement
Tcode: SNUM
Create Group
Click Change group
Click create and create below group
Search MK14 (settlement profile created in last step) and assign to the group
(Details Product Costing video 3: 1:20:00)
PP Settings
Define PP Order Type
Path: Production- Shop Floor control – master data – Order – define order type
Tcode: OPJH
Select PP01
Copy SAP standard Production order PP01 as IST5
Define Order Type Dependent Parameters
Path: Production- Shop Floor control – master data – Order – define order type dependent parameters
Tcode: OPL8
Copy from plant 1000 and Order type PP01. Change Plant to IST5 and Order type to IST5.
Define Scheduling Parameters for Production Order
Path: Production- Shop Floor control – operations – scheduling -define scheduling parameters for production orders
Tcode: OPU3
Copy Plant 1000 and Order type PP01 as Plant IST5 and Order type IST5
Production Scheduling Profile
Tcode : OPKP
Define Confirmation Parameters
Path: Production- Shop Floor control – operations – confirmation – define confirmation parameters
Tcode: OPK4
Copy Plant 1000 and Order type PP01 as Plant IST5 and Order type IST5
Define Checking control
Path: Production- Shop Floor control – operations – availability check – define checking control
Tcode: OPJK
Copy Plant 1000 and Order type PP01 as Plant 01M1 and Order type 19PO for business functions 1 and 2
Define Material Type assignment
Path: Production – Basic Data – Routing – General Data – Define Material Type assignment
Tcode: OP50
Material Type defined in FI-MM
Maintain Overall Plant Parameters
Path: Production – MRP – Plant Parameters – carry out overall maintenance of plant parameters
Tcode: OPPQ
Copy Plant 1000 to Plant IST5
Click on Maintain – Enter plant IST5 – Click on MRP Controllers. Click on MRP controller – New entries – Enter Plant IST5 and save
Click on Conversion under maintain planned orders.
Click Planned Order and update Production Order to 19PO
Define Goods Received Valuation for Order Delivery
Path : Controlling – Product Cost Controlling – Cost Object Controlling – Product Cost by Order – Define Goods Received Valuation for Order delivery
Integration between CO and PP
Check Order Type
Path: Controlling – Product Cost Controlling – Cost Object Controlling – Product Cost by Order – Manufacturing Orders – Check Order Types
Tcode: KOT2
Update your order type 19PO as below:
Update Settlement Profile
Update Object Class: Production
Residence Time: 6
Define Cost Accounting relevant default values for order type
Path: Controlling – Product Cost Controlling – Cost Object Controlling – Product Cost by Order – Manufacturing Orders
Update as below:
RA Key: IST5
Costing Variant Plan: ISTP
Costing Variant Actual: ISTA
End User Steps
Create Finished Goods Material Master
Tcode: MM01
Basic Data 1 and 2 view
- Required for all material types
- Fields: Base Unit of Measure, Material Group, X-Plant Status, Prod Hierarchy
MRP 1 View (Material Requirement Planning)
- MRP Type: ND (No Planning)
- Procurement Type: X (Both Internal and External)
- Storage Location: FG
- Availability Check: KP (No Check)
MRP 2 View
Back flush:
- 1: Always Back flush
- 2: Work Center decides
Accounting 1
- Valuation Class: Determine GL account posted
- Price Control
- S: Standard cost. Used for FG
- V: Moving average price. Used for Raw Material
- Price Unit: Cost per Unit ( Units specified here)
Costing 1
- With Qty Structure: Selected for material costed with BOM + Routing
- Material Origin: Select to display Material Number in controlling reports
- Variance Key: Specify the one created earlier.
- Costing Lot size
Costing 2
- Future Price: Current market price
- Current Price: Current Release Price
FG Created : IST5FGX
Create Raw Material Master
Tcode: MM01
| Finished Goods | Raw material |
| IST5FGX | IST5RMX |
| IST5RMY |
Create BOM
Tcode: CS01 / CS02 / CS03
Create Finished Goods BOM (Bill of Material)
Above BOM => need 2 kg and 3 Kg of Raw material X and Y to manufacture 1 Kg of FG
Routing
| Routing | Setup Activity | Machine Activity | Labor Activity | Work Center |
| Operation 10 | 1 | 2 | 3 | WC 1 |
| Operation 20 | 1 | 2 | WC 2 |
Routing is a list of Operations performed on Raw material to convert it into FG. These operations are performed at locations called work centers.
Create Work Center
Tcode: CR01
To hide Person responsible field, go to OPFA – Basic Data – P3000-VERAN – Hide
Below screen appears when press enter on earlier screen
Cost center to which operational costs would be booked.
Similarly create work center IST5WC3
Create Routing
Tcode: CA01
Click Operations tab and enter below data.
- Control Key PP01: SAP standard for In House Production. Populated from work center
- Base Unit 1: Quantity of finished goods (IST5FGX) that will be produced by applying these operations in the work center.
- IST5WC2: Work Center 1. Will perform 1 hour of Setup activity, 2 hour of Machine activity and 3 hours of labor to produce one unit of FG
Routing was saved with group 50136545 material MK14POFGX.
Standard Cost Estimate
Tcode: CK11N
Reconciliation Excel
| BOM: CS01 | Standard Cost | ||
| FGX | 1 Kg | ||
| RMX | 2 | ||
| RMY | 3 | ||
| Routing: CA01 | Setup Activity | M/C Activity | Labor Activity |
| Operation 10 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Operation 20 | 1 | 2 | |
| Std Cost Estimation | |||
| Raw Material Cost | Kg | Avg Price | Total |
| RMX | 2 | 300 | 600 |
| RMY | 3 | 200 | 600 |
| Total Price RMX +RMY | 1200 | ||
| Operation 10 (Price from KSBT) | Hours | Rate/Hr/USD | Total |
| Setup | 1 | 20 | 20 |
| Machine | 2 | 15 | 30 |
| Labor | 3 | 20 | 60 |
| Total Price OP 10 | 110 | ||
| Operation 20 | |||
| Setup | – | ||
| Machine | 1 | 15 | 15 |
| Labor | 2 | 20 | 40 |
| Total Price OP 20 | 55 | ||
| OH Cost (Valuation variant : OKKN) | |||
| MOH | 10% | 1200 | 120 |
| AOH | 15% | 165 | 25 |
| Total OH Price / Kg | 145 | ||
| Standard Cost Estimation for 1 Kg | 1510 | ||
Raw Material Prices: MM02
Planned Activity Prices: KSBT
Mark and Release Standard Cost Estimation
Transaction code: CK24
Tcode : MM03
| Mark | Standard cost updated as future price in costing tab 2 in MM03 |
| Release | Future price now becomes current price in costing tab 2 in MM03 |
| Standard cost updated as standard cost in accounting tab 1 in MM02 |
May have to close MM period in MMPV
Release Standard Cost : CK24
Standard Cost in FG material master: MM03
Transaction Code: CK13N
Standard Cost Report Transaction Code : S_P99_41000111
Product Costing Tables
| s.no. | Tables | Description |
| 1 | KEKO | Product Costing – Header Data |
| 2 | CKIS | Items Unit Costing/Itemization Product Costing |
For detailed, step-by-step instructions on SAP Product Costing Advance, follow along with my video tutorial below SAP Product Costing Advance















































































































































































Pingback: SAP Tutorials | AUMTECH Solutions-SAP Training
Pingback: SAP Controlling Questions & Answers | AUMTECH Solutions-SAP Training