When was the Ancient Sumer civilisation?
Ancient Sumer civilisation began in around 5300BC and ended around 1940BC.
Ancient Sumer lasted from the late Neolithic period to the early Bronze Age.
The civilisation weakened when city rulers began fighting with each other.
Flooding meant that crops weren't growing as well. Cities began to struggle.
In the end, Sumer was invaded by the Elamites who came from modern-day Iran.
Watch: An introduction to Ancient Sumer
Narrator: Hello, future people of the UK.
Would you like to visit me at the dawn of civilisation in ancient Sumer?
Well, to do that, you’ve got to travel back in time.
Back before the Vikings, before the Romans, and keep going back, back, back, before Stonehenge was even built.
Right… Now aim between those two rivers that run through modern-day Iraq.
YAWNS
Good morning. I am Uri and…I’m afraid I’ve only just got up. And yes, I sleep on the roof. It’s cooler. Hmm… I wonder what time it is? Oh no! Look at the sundial.
I’ve slept in again. I’m going to be late for school. We invented 60-minute clocks, though I wish they came with alarms like your ones. Actually, invention is our big thing.
Come on, I’ll show you what else we’ve come up with. First up is city living because this Uruk, the first city ever. We’ve got streets, shops and houses. We even use the grid system for our roads and buildings, just like you still do.
We invented all this well before the ancient Egyptians. It all started when we stopped hunter-gathering food and began growing it instead. With the abundance of water and good soil, we found we could grow almost anything here. That’s why they call it ‘the fertile crescent.’
Soon, we had more crops than we could possibly eat. This meant we had time to do other stuff instead. That’s when the inventing began! We thought of lots of stuff to make our lives easier.
Better ways of farming…sailboats, games, and even skyscrapers ten storeys high which have lasted into your time.
We also invented the first schools, and our teachers are very strict. Yikes! That reminds me, I’m late!
Luckily, we’ve invented wheels, too. They’re great for carrying goods for long distances and faster than walking. Giddy-up!
With so much going on, this fast-paced city life can get really confusing, so we started keeping records and became one of the first people to start writing.
Paper doesn’t exist yet, but we use clay tablets, like this, which we mark with…um…Oh bother. I’ve left it at home. Quick, down to the river.
We don’t have pens, we use sharpened reeds instead. Just one more perk of living near the water.
Phew, I made it just in time! This is my school. Well, it’s just a bench. But I’m lucky to be here because most people in our city don’t ever get to learn the secret of writing.
I can show you though. We push the reed into the clay and the different combinations of marks make words. Our written records will last into your time. They’ll tell you what life was like here and how, eventually our crops will dry out and the population will shrink, spelling the end of the Sumerian Empire. And all this? Well, it’ll be history.
Where was Ancient Sumer?
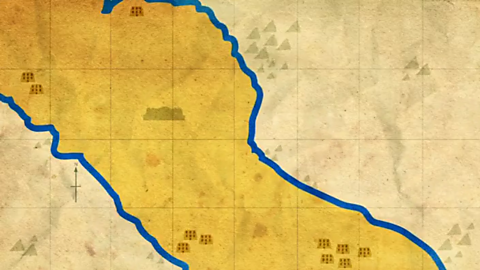
Ancient Sumer was in the southern part of a place called Mesopotamia. Most of the area now falls in modern-day Iraq.
Cities were built along the rivers Tigris and Euphrates. Being close to the rivers allowed people to grow crops, travel and transport goods easily.
The civilisation was famous for its cities. Ur, Uruk, Eridu, and Larsa were some of the largest.

What was Mesopotamia like?
Each city-state had its own ruler. Cities were surrounded by walls to protect them from attack.
Each city had a temple in its centre called a Ziggurat. They were tall so that people could be closer to the gods in the sky.

Mud-brick houses were built around a central courtyard where children could play. People sometimes slept on the flat roofs of their houses to keep cool.
Sumerian people were some of the first to have schools. Teachers could be very strict and only boys were allowed to attend.
The wheel, writing, and the 60 minute clock are all thought to have been invented by the Sumerians.
What can we learn from relics?

Archaeologists have found artefacts that tell us about Ancient Sumer life, rulers and beliefs.
The Epic of Gilgamesh is a collection of stories written about a superhuman king called Gilgamesh.
They were written thousands of years ago on clay tablets.


The Sumerian King List is a group of clay prisms with names of Sumerian cities and rulers on them.
The prisms are an important record of the Sumerian language.
They are believed to be from around 1800BC.
They are now part of the Ashmolean museum's collection in Oxford.
In the 1920s Sir Leonard Woolley excavated at the site of Ur. He found artefacts in graves from around 2,600BC.
One of these was the Royal Standard of Ur buried in a royal grave. It shows the king of Ur as a warrior on one side and him enjoying a banquet on the other.
Woolley’s discoveries are important because they tell us about ancient Sumerian life.

How did Ancient Sumer end?
Eventually, city-state rulers began fighting with each other and flooding meant that crops weren't growing as well. This weakened the civilisation and Sumer was invaded by the Elamites who came from modern-day Iran.
Activity: Quiz – Ancient Sumer
Get ready for the SATs with videos, activities and games
Refresh your knowledge and practise your skills for the maths and English SATs.

More on Ancient Sumer
Find out more by working through a topic
- count2 of 2
