- 979-485-9287
- office@bvallergy.com
-
 979-251-7804
979-251-7804
Getting to Know Angioedema (Allergic Swelling)

Everything You Need to Know About Allergic Rhinitis
March 15, 2019
Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)
April 11, 2019Defining Angioedema
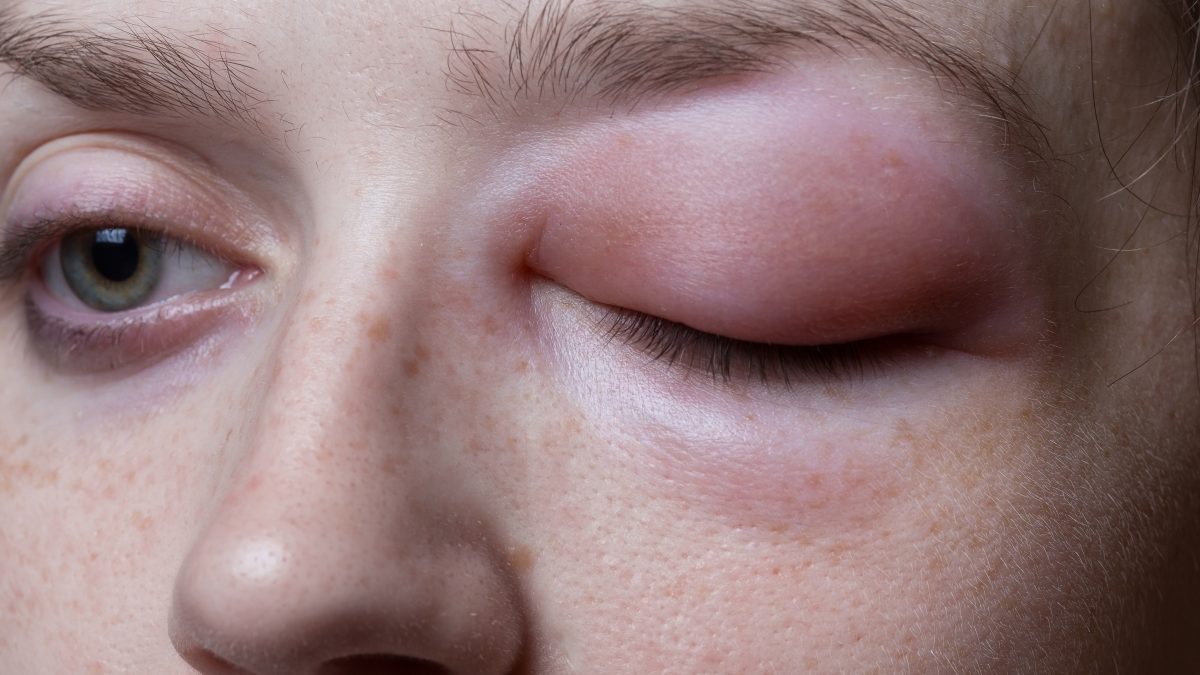
According to the American Academy of Allergy Asthma and Immunology (AAAAI), angioedema is the swelling in the deep layers of the skin, often seen with hives. It most often occurs in soft tissues such as the eyelids, mouth, or genitals. Angioedema may involve swelling in the face, airways, and throat. The swelling can begin within minutes or develop over the course of hours. Because of the rapid progression of this condition, it can lead to potential airway obstruction and suffocation. Angioedema happens when there is a reaction to a drug or other substance like an allergen–which acts as a trigger.
Types of Angioedema
There are many causes of angioedema but they all depend on the type of angioedema that you have. The 4 main types of angioedema are Allergic, idiopathic, drug-induced, and hereditary.
- Allergic Angioedema – This is actually the most common type of angioedema. The people who are affected by this are usually those with an allergy to a type of food, medication, pollen, animal dander, or venom. It sometimes occurs in combination with anaphylaxis, which is a life-threatening situation.
- Idiopathic Angioedema – There is no known cause for this type of angioedema. The doctor may not be able to identify the cause of this condition. Although there are factors that may trigger the symptoms such as stress.
- Drug-induced Angioedema – Swelling may occur because of a certain medication. Most often, it is caused by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, which is used to treat conditions such as high blood pressure.
- Hereditary Angioedema – This type of angioedema is inherited. The swelling may be caused by the genes inherited from a person’s parents. People with hereditary angioedema may have episodes that come and go over time.
Symptoms of Angioedema
As mentioned earlier, angioedema can affect a person’s hands, face, feet, and even the genitals. However, there are other symptoms that you should look out for which include:
- Redness of the skin
- Pain in the affected area
- Itchiness on the area
- Large and thick welts
- Trouble breathing
- Abdominal pain
- Throat tightness
- Voice changes
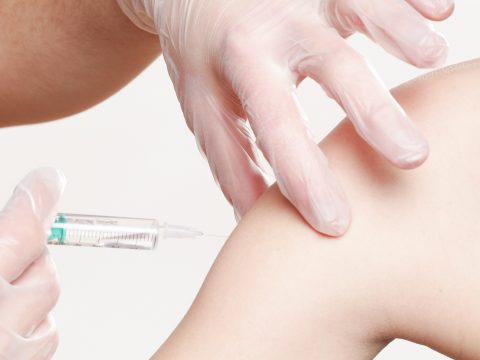
Severe angioedema can cause difficulty with breathing or swallowing. If this happens, emergency treatment is necessary. Most people who have severe reactions should always carry a syringe of self-injecting epinephrine to be used if a severe reaction occurs.
Diagnosing Angioedema
The doctor can diagnose angioedema by examining the affected skin or the appearance of the symptoms. They can also ask the patient for a description of what triggered the symptoms and by checking their family and medical history. Doctors may also check if the patient is taking any medications that have an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors.
The patient may take further tests to make sure or confirm the type of angioedema he or she has. These may include a skin prick test to confirm a link to possible allergies. A skin prick test is a blood test that confirms how the patient’s immune system reacts to an allergen.
Treatments and Medications for Angioedema
Most cases of angioedema get better without treatment after a few days, but some people prefer to use medication. For mild angioedema, taking antihistamines relieves the itching and reduces the swelling. Corticosteroids that are taken orally may also be used if other treatments are ineffective. Serious side effects may be experienced if corticosteroids are taken for a long time. For idiopathic angioedema, a high dose of antihistamine may help. Hereditary angioedema cannot be cured, however, regular drug treatment and specialized medications can prevent and manage the symptoms. If you also had symptoms of anaphylaxis during an episode of angioedema, you will probably be given an adrenaline auto-injector pen in case your symptoms return.
If you’re looking for an allergy clinic in college station, you can visit Brazos Valley Allergy and Asthma Clinic in College Station. They provide professional allergy, asthma, and immunology services to clients at numerous locations in the Brazos Valley region.
REFERENCE:
Medical News Today
NHS Inform
MSD Manuals