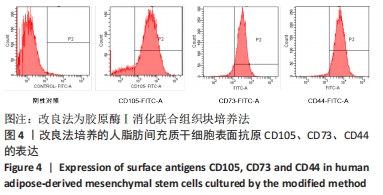
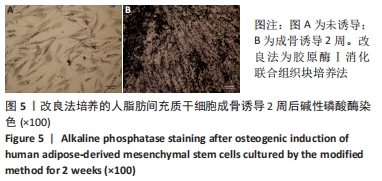
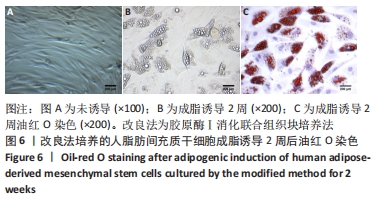
[1] MENG QS, LIU J, WEI L, et al. Senescent mesenchymal stem/stromal cells and restoring their cellular functions. World J Stem Cells. 2020; 12(9):966-985.
[2] ÁLVAREZ-VIEJO M. Mesenchymal stem cells from different sources and their derived exosomes: A pre-clinical perspective. World J Stem Cells. 2020;12(2):100-109.
[3] FRIEDENSTEIN AJ, CHAILAKHYAN RK, LATSINIK NV, et al. Stromal cells responsible for transferring the microenvironment of the hemopoietic tissues. Cloning in vitro and retransplantation in vivo. Transplantation. 1974;17(4):331-340.
[4] WEGMEYER H, BRÖSKE AM, LEDDIN M, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell characteristics vary depending on their origin. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(19):2606-2618.
[5] LU X, CUI J, CUI L, et al. The effects of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on endometrial receptivity are associated with Th1/Th2 balance change and uNK cell expression of uterine in autoimmune premature ovarian failure mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):214.
[6] DICKER A, LE BLANC K, ASTRÖM G, et al. Functional studies of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult human adipose tissue. Exp Cell Res. 2005;308(2):283-290.
[7] POULOS SP, HAUSMAN DB, HAUSMAN GJ. The development and endocrine functions of adipose tissue. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010; 323(1):20-34.
[8] ZUK PA, ZHU M, MIZUNO H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001; 7(2):211-228.
[9] BAJEK A, GURTOWSKA N, OLKOWSKA J, et al. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells as a Tool in Cell-Based Therapies. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2016;64(6):443-454.
[10] LÓPEZ JF, SARKANEN JR, HUTTALA O, et al. Adipose tissue extract shows potential for wound healing: in vitro proliferation and migration of cell types contributing to wound healing in the presence of adipose tissue preparation and platelet rich plasma. Cytotechnology. 2018;70(4): 1193-1204.
[11] ZUK PA. The adipose-derived stem cell: looking back and looking ahead. Mol Biol Cell. 2010;21(11):1783-1787.
[12] BAER PC. Adipose-Derived Stromal/Stem Cells. Cells. 2020;9(9):1997.
[13] KUNZE KN, BURNETT RA, WRIGHT-CHISEM J, et al. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Treatments and Available Formulations. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2020;13(3):264-280.
[14] GU X, LI C, YIN F, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells in articular cartilage regeneration: current concepts and optimization strategies. Histol Histopathol. 2018;33(7):639-653.
[15] HASSANSHAHI A, HASSANSHAHI M, KHABBAZI S, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells for wound healing. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(6):7903-7914.
[16] 陈睿,马骞,傅建芳,等.脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体对阿霉素所致心肌损伤的影响及其分子机制 [J].山东医药,2021,61(11):15-19,23.
[17] SHEBABY W, ABDALLA EK, SAAD F, et al. Data on isolating mesenchymal stromal cells from human adipose tissue using a collagenase-free method. Data Brief. 2016;6:974-979.
[18] 张若冰,谢惠明,张杰.自体脂肪干细胞的浓缩提取及在面部填充中的应用效果[J].中国美容医学,2019,28(8):22-25.
[19] VARGHESE J, GRIFFIN M, MOSAHEBI A, et al. Systematic review of patient factors affecting adipose stem cell viability and function: implications for regenerative therapy. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017; 8(1):45.
[20] 陈奕静,戴鹏秀,张露文,等.永生化犬骨髓间充质干细胞株的建立[J].中国兽医学报,2021,41(6):1140-1145.
[21] 杨旭芳.人脂肪干细胞的获取及其定向分化为内皮细胞差异蛋白筛选的实验研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2010.
[22] 李志然,马强,马利民.大鼠脂肪干细胞的提取与鉴定[J].南通大学学报(医学版),2019,39(1):14-18.
[23] 沈甜甜,方翼.间充质干细胞的研究进展[J].中国临床药理学杂志, 2019,35(22):2939-2942.
[24] 孙伟.自体脂肪干细胞治疗骨性关节炎临床运用[J].临床医药文献电子杂志,2000,7(25):38,42.
[25] NI X, SHAN X, XU L, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells combined with platelet-rich plasma enhance wound healing in a rat model of full-thickness skin defects. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):226.
[26] ROGERS CJ, HARMAN RJ, BUNNELL BA, et al. Rationale for the clinical use of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells for COVID-19 patients. J Transl Med. 2020;18(1):203.
[27] 黄成龙,黎庆,王雷,等.两种方法培养骨质疏松症小鼠脂肪干细胞的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(29):4654-4659.
[28] MAZINI L, ROCHETTE L, ADMOU B, et al. Hopes and Limits of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs) and Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) in Wound Healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(4):1306.
[29] 邓颖珊,杜晶春,徐霞,等.Toll样受体预活化的人脂肪间充质干细胞对人肺癌H460细胞生长的抑制作用[J].中国生物制品学杂志, 2021,34(6):657-665.
|