![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
77 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Phylum Porifera |
- Animals without tissues; sponges - Consist of loose aggregations of cells; little or no tissue organization - No organs - Contains sponges in Classes Calcarea, Hexactinellida, and Demospongiae - Body organization for sponges: Asconoid, Syconoid, or Leuconoid |
|
|
Basic body form for sponges |
- Sac-like structure consisting of three layers of tissue wrapped around a cavity (spongocoel) with one opening to the outside (osculum) 1) Outer epidermal layer 2) Middle layer of amoeboid cells for skeletal structure 3) Inner layer of flagellated choanocytes - All three layers perforated by pores |
|
|
Choanocytes |
- Flagellated cells present in the inner cell layer of sponge bodies Phylum Porifera |
|
|
Spongeocol |
- Cavity of the sponge body Phylum Porifera |
|
|
Osculum |
- Opening to the outside present somewhere on the sponge body Phylum Porifera |
|
|
Classes in Phylum Porifera (and how they are classified) |
- Sponges are classified based on skeletal materials produced - Calcareous spicules (calcium carbonate), siliceous spicules (silicon dioxide), or spongin fibers (protein-based/cellulose) - Class Calcarea, Class Hexactinellida (siliceous spicules), and Class Demispongiae (spongin fibers) |
|
|
Class Calcarea |
- Phylum Porifera - Calcium Carbonate spicules - All marine
|
|
|
Class Hexactinellida |
- Phylum Porifera - Siliceous spicules - All marine; usually cylindrical in form |
|
|
Class Demispongiae |
- Phylum Porifera - "Bath sponges" - Spongin fibers (cellulose/protein based) |
|
|
Phylum Porifera; body form classifications |

- Asconoid = body wall is not folded - Syconoid = body wall is folded into canals - Leuconoid = canals formed by body wall are extensively branched
|
|
|
Ostia |
- In asconoid sponges = Openings of pores - In syconoid/leuconoid sponges = Openings into the canals formed by the body wall |
|
|
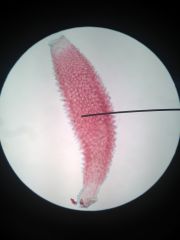
Asconoid sponges |
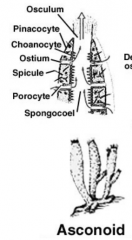
- Simplest sponges; body wall is not folded - Water enters through the ostia into the spongeocol due to the beating of flagellated choanocytes - Water is expelled through the osculum Ex: Leucosolenia |
|
Phylum: Body type: Class: Major structures listed |
- Phylum Porifera - Class Calcarea - Leucosolenia - Asconoid (body wall is not folded) • Spongeocol = body cavity • Osculum = Apical opening to outside • Ostia = Pores dotting epidermis • Choanocytes = Flagellated cells |
|
|
Syconoid Sponges |
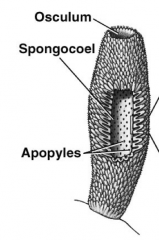
- Tubular design with folded body wall - "Folds" form radial canals, which are lined with choanocytes |
|
Phylum: Class: Body type: Major structures listed |
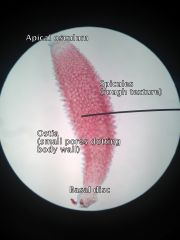
- Phylum Porifera - Class Calcarea - Scypha (aka Granita) - Syconoid (body wall is folded) • Spicules extend through the body wall • Dermal ostia dotting body • Basal disc at bottom, apical osculum at top |
|
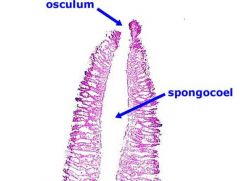
Phylum: Class: Body type:
|
- Phylum Porifera - Class Calcarea - Scypha (aka Granita) - Syconoid
|
|
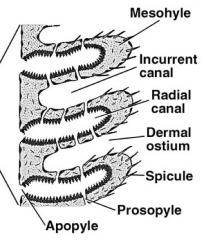
Definitions of labeled structures |
- Raidal canals = radiate from spongeocol - Apopyles = opening into radial canals - Ostia (pores) open into incurrent canals - Prosypyles connect radial canals and incurrent canals - Choanocytes (flagellated cells) line radial canals
Syconoid sponge (Scypha) |
|
Phylum: Class: Body type: Major structures listed
|
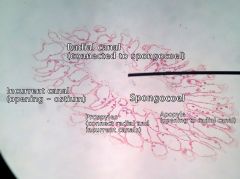
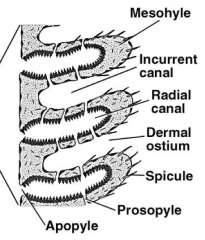
Phylum porifera Class Calcarea Syconoid
- Raidal canals = radiate from spongeocol - Apopyles = opening into radial canals - Ostia (pores) open into incurrent canals - Prosypyles connect radial canals and incurrent canals - Choanocytes (flagellated cells) line radial canals
|
|
Phylum: Class: Body type: Material? How many spines? |
Phylum Porifera Class Calcarea Syconoid sponge (Scypha spicules) Calcium carbonate Three spines |
|

Phylum: Class: Body type: Skeletal material |
Phylum Porifera Class Demospongiae (spongin fibers) Leuconoid sponge Proteins/cellulose (spongin) |
|

Phylum: Class: Body type: Species name Skeletal material |
Phylum Porifera Class Hexactinellida (siliceous spicules) Leuconoid sponge Euplectella sp. (Venus Flower Basket) Silicon dioxide |
|
|
Leuconoid Sponges |
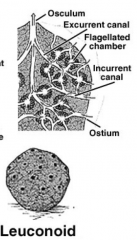
- Most complex body form; canal system formed by body wall folds is extensively branched - Many oscula present - Ex: "bath sponge" |
|

Phylum: Class: Body form: Common name: |
Phylum porifera Class Hexactinellida (siliceous spicules) Leuconoid Elephant ear sponge |
|
Phylum? |
Porifera |
|
Classes in phylum Porifera? |
Class Calcarea, Hexactinellida, Demispongiae |
|
Body types in phylum Porifera? |

Asconoid (body canal is not folded) Syconoid (body canal is folded into radial canals) Leuconoid (body canal is folded extensively)
|
|

Examples of each body type & their classes? |
Asconoid = Leucosolina (class Calcarea) Syconoid = Scypha (class Calcarea) Leuconoid = "Bath sponge" (class Demospongiae), Venus flower basket (class Hexactinellida)
|
|

Body types of examples from lab? |
Scypha = Syconoid Leucosolenia = Asconoid "Bath sponge", Venus flower basket = Leuconoid |
|
|
Phylum Cnidaria |
- Radially symmetrical animals - Tissue organization, no organs - Diploblastic = two distinct tissue layers (endoderm and ectoderm) - Polymorphic = alternates between polyp (asexual, sessile) and medusa (sexual, free-swimming) stage - Classes: Hydrozoa, Scyphozoa, Anthozoa |
|
|
Basic body plan of Cnidarians |
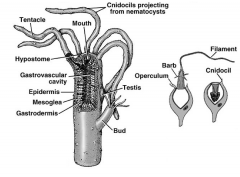
- Oral end = mouth; aboral end = opposite end - Sac-like structure with gastrovascular cavity - Opening from cavity (mouth/anus) is surrounded by tentacles - Body wall in layers = epidermis (outer), gastrodermis (internal), mesoglea (in-between) - Cnidocytes (specialized cells abundant on tentacles) contain nematocysts |
|
|
Orientation of Cnidarian body |
- Oral end = end with mouth - Aboral end = opposite end - Organism is radially symmetrical about the oral-aboral axis |
|
|
Gastrovascular cavity (Cnidarians) |
- Cavity within the sac-like main body of a Cnidarian |
|
|
Mouth (Cnidarians) |
- Single opening in the gastrovasuclar cavity of a Cnidarian which serves as mouth and anus - Often surrounded by tentacles |
|
|
Layers of the Cnidarian body wall |
- Epidermis (external) - Gastrodermis (internal, lines gastrovascular cavity) - Mesoglea (in-between other two layers) |
|
|
Nematocysts |
- Organelles, unique to Cnidarians, found in cells called cnidocytes which are abundant on tentacles |
|
|
Cnidocytes |
- Specialized cells, unique to Cnidarians, contain nematocysts, abundant on tentacles |
|
|
Polyp stage (Cnidarians) |
- One of the two phases of the Cnidarian life cycle - Sessile; attached at the aboral end to a substrate - Cylindrical - Asexual |
|
|
Medusa stage (Cnidarians) |
- One of the two phases of the Cnidarian life cycle - Free-swimming - Flattened; mouth oriented downwards - Sexual |
|

Phylum: Class: Body type: Skeletal material: |
Porifera Demospongiae Leuconoid Spongin (protein/cellulose)
"Commercial sponge" |
|

Phylum: Class: Body type: Skeletal material: |
Porifera Demospongiae Leuconoid Spongin (protein/cellulose)
"Yellow ball sponge" |
|

Phylum: Class: Body type: Skeletal material: |
Porifera Demospongiae Leuconoid Spongin (protein/cellulose)
Commercial sponge |
|

Phylum: Class: Body type: Skeletal material: |
Porifera Demospongiae Syconoid (note lack of multiple oscula) Spongin (protein/cellulose)
White Finger Sponge |
|

Phylum: Class: Body type: Skeletal material: |
Porifera Demospongiae Leuconoid Spongin (protein/cellulose)
Spongidae sp. |
|

Phylum: Class: Body type: Skeletal material: |
Porifera Demospongiae Leuconoid Spongin (protein/cellulose)
Spongia sp. (commercial sponge) |
|

Phylum: Class: Body type: Skeletal material: |
Porifera Demospongiae Leuconoid Spongin (protein/cellulose)
Orange puffball sponge |
|

Phylum: Class: Body type: Skeletal material: |
Porifera Demospongiae Leuconoid Spongin (protein/cellulose)
Cliona sp. (Commercial sponge) |
|

Phylum: Class: Body type: Skeletal material: |
Porifera Calcarea Syconoid Calcium carbonate
Urban sponge (sycon type) |
|

Phylum: Class: Body type: Skeletal material: |
Porifera Calcarea Asconoid Calcium carbonate
Leucosolenia |
|

Phylum: Class: Body type: Skeletal material: |
Porifera Calcarea Syconoid Calcium carbomate
Scypha (granita) |
|

Phylum: Class: Body type: Skeletal material: |
Porifera Calcarea Syconoid (??) Calcium carbonate
Leuconia sp. |
|

Phylum: Class: Body type: Skeletal material: |
Porifera Calcarea Syconoid (note single osculum, attachment to substrate) Calcium carbonate
White sponge (spongia sp.)
|
|

Phylum: Class: Body type: Skeletal material: |
Porifera Calcarea Leuconoid (multiple oscula) Calcium carbonate
Spongiidae sp. |
|

Phylum: Class: Body type: Skeletal material: |
Porifera Calcarea Leuconoid (multiple oscula) Calcium carbonate
Finger sponge (leucon type) |
|

Phylum: Class: Body type: Skeletal material: |
Porifera Hexactinellida Leuconoid Silicon dioxide
Glass sponge |
|
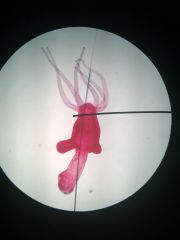
Phylum: Class: Species: Form:
Major structures listed |
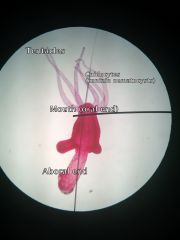
Cnidaria Hydrozoa Hydra Polyp
Tentacles Mouth (oral end) Aboral end Cnidocytes/nematocysts |
|
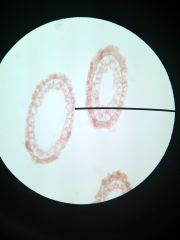
Phylum: Class: Species: Form:
Major structures listed |
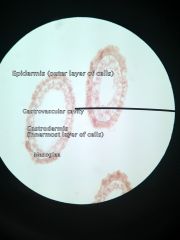
Cnidaria Hydrozoa Hydra Polyp (xs)
Epidermis Gastrovascular cavity Gastrodermis Mesoglea
|
|
|
Gonionemus anatomy |
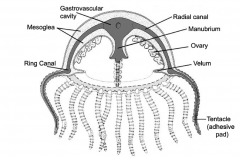
- Exumbrella = upper surface - Subumbrella = lower surface - Vellum = "rim" of umbrella - Manumbrium = hangs down from subumbrella cavity - Mouth = free end, below umbrella
|
|
|
Gonionemus anatomy 2 |
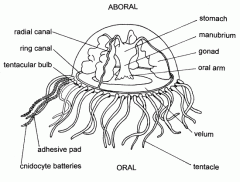
- Ring canal = runs around circumference of unbrella - Radial canals = extend to the margin of the umbrella - Tentacles - Statocysts = organs of balance, between tentacles - Gonads = ribbon-like structures beneath radial canals |
|
Phylum: Class: Species: Form: |
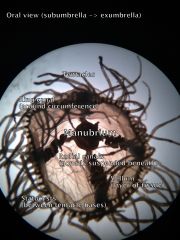
Cnidaria Hydrozoa Gonionemus Medusa |
|

Phylum: Class: Species:
Notable feature:
|
Cnidaria Hydrozoa Aurelia (moon jelly)
Vellum absent |
|

Phylum: Class: Species: |
Cnidaria Anthozoa Sea Pansy (Renilla) |
|

Phylum: Class: |
Cnidaria Hydrozoa
Ostrich-plumed hydroids |
|

Phylum: Class: |
Cnidaria Hydrozoa
Fire coral |
|

Phylum: Class: Species: |
Cnidaria Anthozoa Sea Pansy (Renilla) |
|

Phylum: Class: |
Cnidaria Anthozoa
Sea pen |
|

Phylum: Class: |
Cnidaria Anthozoa
Sea pen |
|

Phylum: Class: |
Cnidaria Anthozoa
Moon coral (Coral) |
|

Phylum: Class: |
Cnidaria Anthozoa |
|

Phylum: Class: |
Cnidaria Anthozoa |
|

Phylum: Class: |
Cnidaria Anthozoa |
|

Phylum: Class: |
Cnidaria Anthozoa |
|

Phylum: Class: |
Cnidaria Anthozoa |
|

Phylum: Class: Species:
Major parts labelled |

Cnidaria Anthozoa Metridium
Oral disc Tentacles Mouth Gastrovascular cavity Pedal disc
|
|
Classes of phylum Cnidaria |
Anthozoa ("flowering animals" - polyp only) Scyphozoa (medusa dominant; reduced/absent polyp) Hydrozoa |
|
Examples of Class Anthozoa |
Phylum Cnidaria
Metridium (sea anenome), corals, sea pansy (Renilla)
|
|
Examples of Class Hydrozoa |
Phylum Cnidaria
Hydra, Gonionemus |
|
Examples of Class Scyphozoa |
Phylum Cnidaria
Aurelia (moon jelly) |

