The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development OECD is an international, intergovernmental organization comprising 38 member countries that works towards building socio-economic policies designed ‘to foster prosperity, equality, opportunity, and well-being for all’. It was established on December 14, 1960, by 18 European nations, joined by the United States and Canada, to reform the previous Organization for European Economic Co-operation (OEEC) which was responsible for administering American and Canadian aid allocated for the reconstruction of Europe following World War II.
The OECD works to address a broad range of international and local policy issues related to tax, economy, trade, innovation, and governance. It regularly publishes a series of geographically and thematic focused economic reports, statistical analyses, working papers, and forecasts that are available to the public and can be accessed via the OECD iLibrary.
Member countries, OECD candidates and key partners
The OECD brings together 38 member countries from the European, North American, Latin American, and Pacific regions. The collective weight of the OCED member countries accounts for 62% of the world’s economy, 61% of global merchandise imports, and 17% of the world’s population.
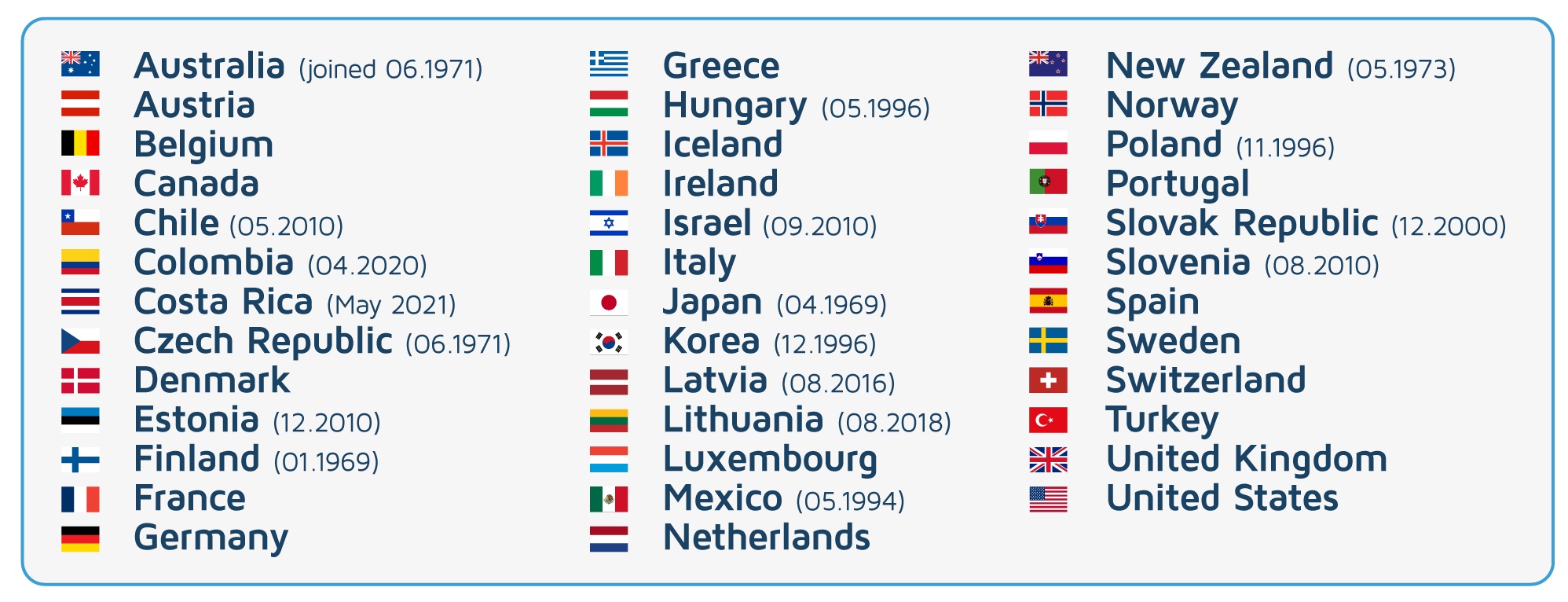
OECD members
For a country to become a member of the OECD, it must undergo a rigorous review process that focuses on the efficiency of its domestic policy reforms and the rate of implementation of pre-established standards. The latest country to receive OECD candidate status is Costa Rica which was invited to become a member on May 15th, 2020 after the OECD countries voted unanimously for this decision. One year later, in May 2021, after taking all the necessary legal and technical steps, Costa Rica joined the organization as a member.
The OECD lists Brazil, China, India, Indonesia, and South Africa as Key Partners. These countries are directly involved in the OECD’s day-to-day operations, participate in policy discussions, take part in various thematic surveys, and are included in OECD’s internal statistical databases.
Regional Initiatives
The OECD promotes collaboration with non-member countries at the regional level via several regional initiatives that are designed to help to facilitate policy benchmarking and the efficient exchange of good practices. These initiatives span across Africa, Eurasia, the Middle East, and North Africa, Latin American and the Caribbean, Southeast Asia, and South East Europe. Here are some of the OECD’s focus areas for each region:
🔹 Africa
At the core of the OECD’s agenda for the African continent is sustainable economic transformation. The organization follows a multi-stakeholder approach in designing and implementing innovative policies that are intended to improve the socio-economic wellbeing of the African people.
🔹 Eurasia
The OECD currently provides country-specific support to countries such as Ukraine and Kazakhstan but also works with actors at the regional level to encourage sustainable and inclusive economic growth. Moreover, at the core of the OECD’s agenda for the Eurasian region is the advancement of structural reforms, capacity building, and efficient policy dialogue.
🔹 Latin America and the Caribbean
Over the last 20 years, the OECD has worked with local actors to facilitate an effective policy dialogue in the region with a strong focus on the dissemination of good practices in education, investment, inclusiveness, and anti-corruption policy.
🔹 Middle East and North Africa
At the foundation of OECD activity in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) is the acknowledgment of innate regional diversity, high socio-economic potential, and advantageous geographical positioning. The MENA-OECD Initiative on Governance and Competitiveness for Development aims to advance sustainable economic growth and improve governmental structures via innovative policy dialogue and a multi-actor approach.
🔹 Southeast Asia
Since 2007, South East Asia has been identified as a region of strategic priority for the OECD. The Southeast Asia Regional Programme (SEARP), launched in 2014, is designed to promote a systematic exchange of good practices and mutual learning in various socio-economic spheres such as education, inclusiveness, sustainable growth, good governance, and fiscal policies.
🔹 South East Europe
For the last two decades, the OECD has been actively collaborating with actors from the South East Europe (SEE) region to ensure peace, stability, and prosperity. The OECD assists governments, business leaders, and civil society to elaborate upon and implement efficient reforms intended to foster private sector development, regional competitiveness and prepare the region for future accession to the European Union.
DevelopmentAid is the leading provider of business intelligence and recruitment tools for those active in the development sector. Join today and gain access to exclusive data on funding opportunities (tenders/grants), awarded projects, and past contractors from over 180 international donors.


