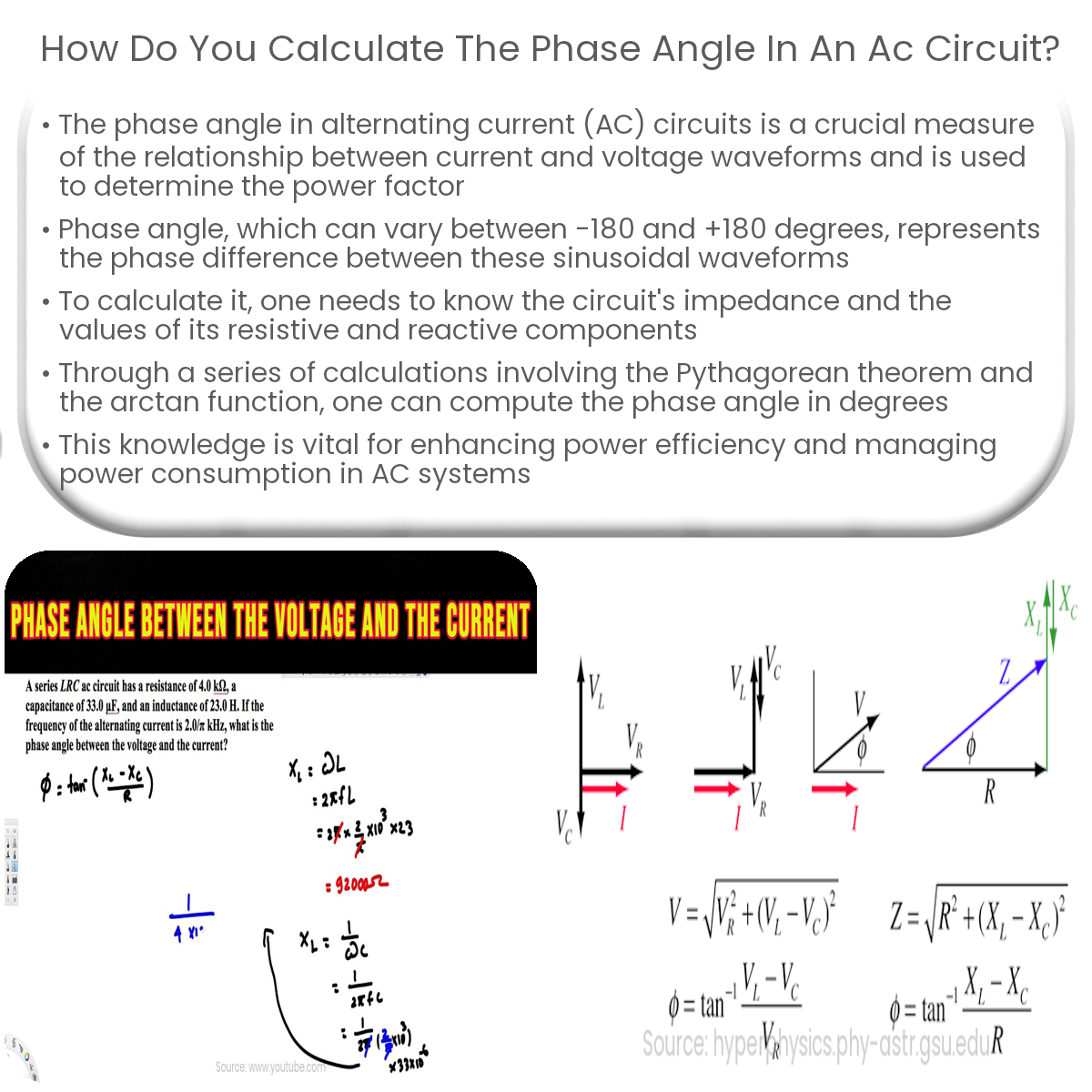
To calculate the phase angle in an AC circuit, find the impedance (Z), then use θ = arctan((Xₗ – Xc) / R) and convert to degrees.
Calculating Phase Angle in AC Circuits
In alternating current (AC) circuits, the phase angle is an important parameter that describes the relationship between the current and voltage waveforms. A phase angle can be used to determine the power factor, which is essential for efficient operation and power management. In this article, we will discuss how to calculate the phase angle in an AC circuit.
Understanding Phase Angle
In AC circuits, the voltage and current waveforms are sinusoidal in nature, and their values change continuously with time. The phase angle (θ) represents the difference in the phase between these waveforms. If the waveforms are in phase, the angle is 0 degrees, and if they are out of phase, the angle can vary between -180 and +180 degrees.
Calculating Phase Angle
To calculate the phase angle in an AC circuit, one needs to know the circuit’s impedance (Z) and the values of its resistive (R) and reactive (Xc or XL) components. The impedance is a complex quantity, and its real part represents resistance, while the imaginary part represents reactance. The phase angle can be determined using the following formula:
- Calculate the impedance (Z) using the Pythagorean theorem:
Z = √(R² + (XL – Xc)²)
- Find the angle in radians:
θ = arctan((XL – Xc) / R)
- Convert the angle to degrees:
θ = θ × (180 / π)
Example
Let’s consider an AC circuit with a resistance of 50 ohms, an inductive reactance of 30 ohms, and a capacitive reactance of 20 ohms.
- First, calculate the impedance (Z):
Z = √(50² + (30 – 20)²) = √(50² + 10²) = √2600 = 51 ohms
- Next, find the angle in radians:
θ = arctan((30 – 20) / 50) = arctan(10 / 50) = 0.197 radians
- Finally, convert the angle to degrees:
θ = 0.197 × (180 / π) ≈ 11.31°
In this example, the phase angle between the current and voltage waveforms is approximately 11.31°, indicating that the current lags the voltage by this angle.
In summary, calculating the phase angle in an AC circuit involves determining the circuit’s impedance and using the arctan function to find the angle between the current and voltage waveforms. This information is crucial for optimizing power efficiency and managing power consumption in AC systems.