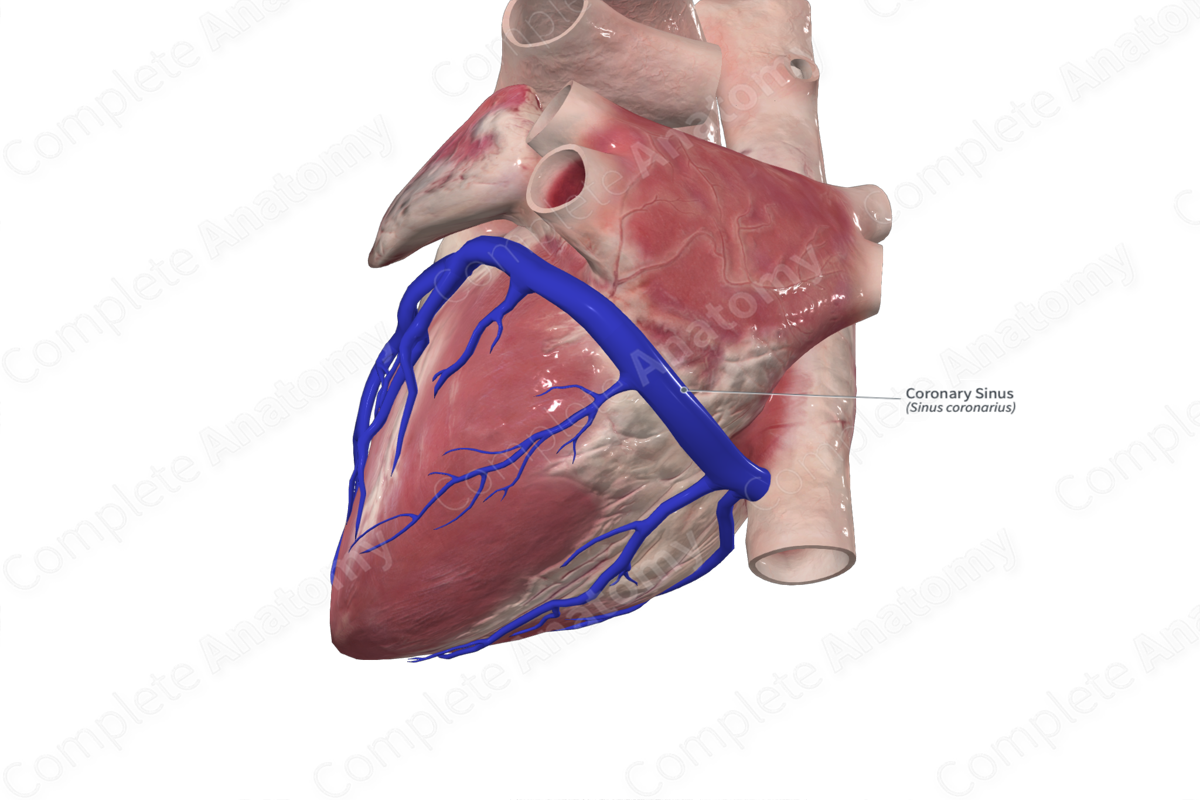
Quick Facts
Origin: Posterior interventricular region.
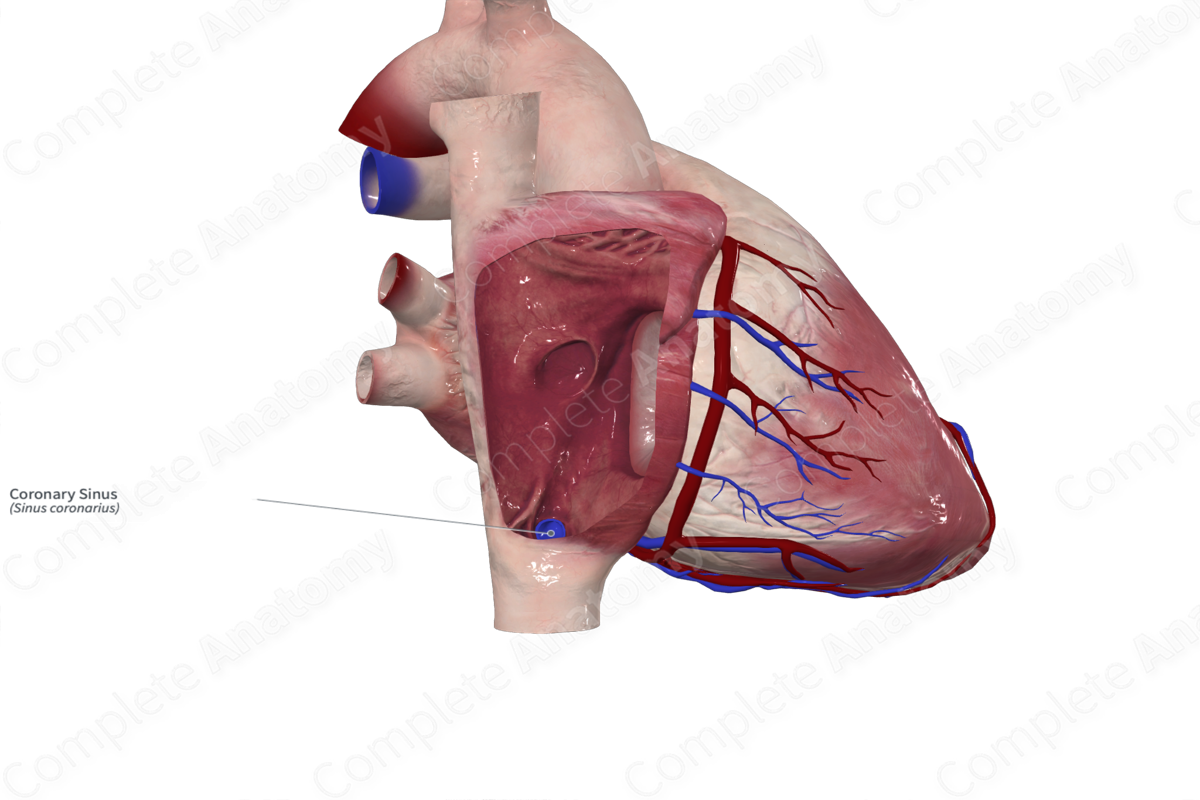
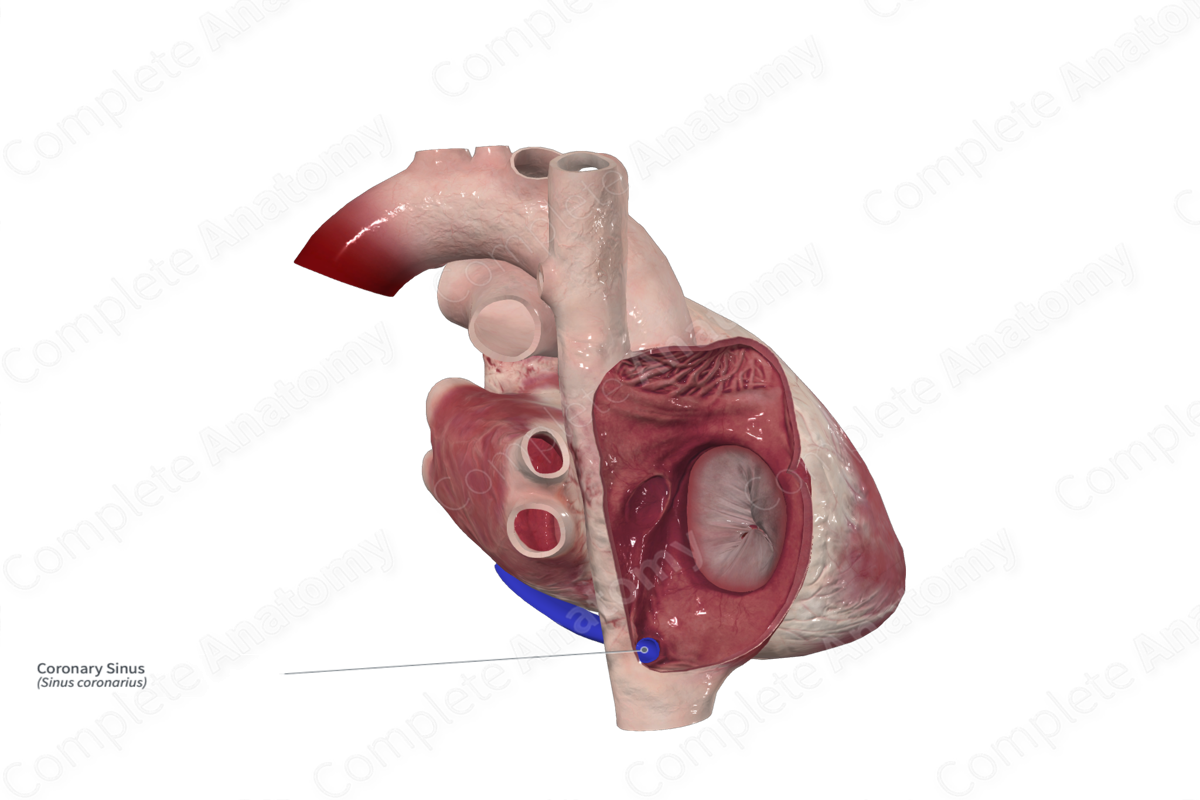
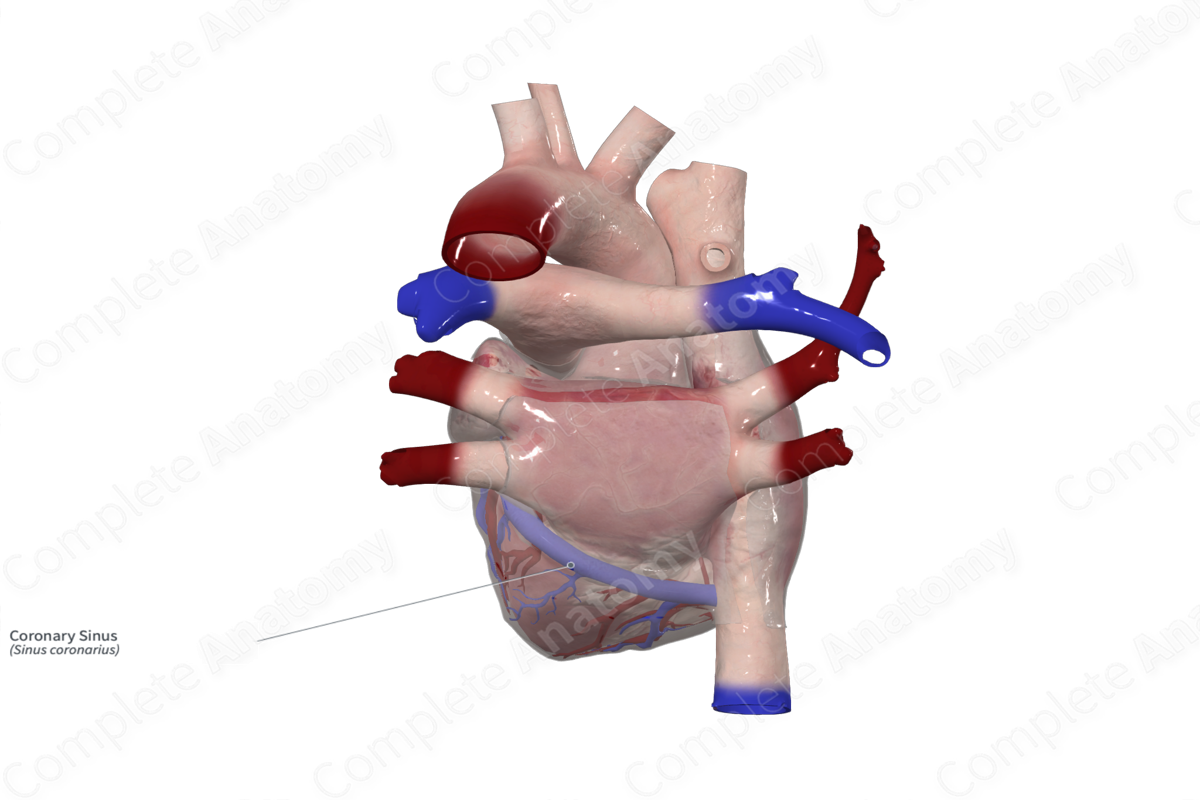
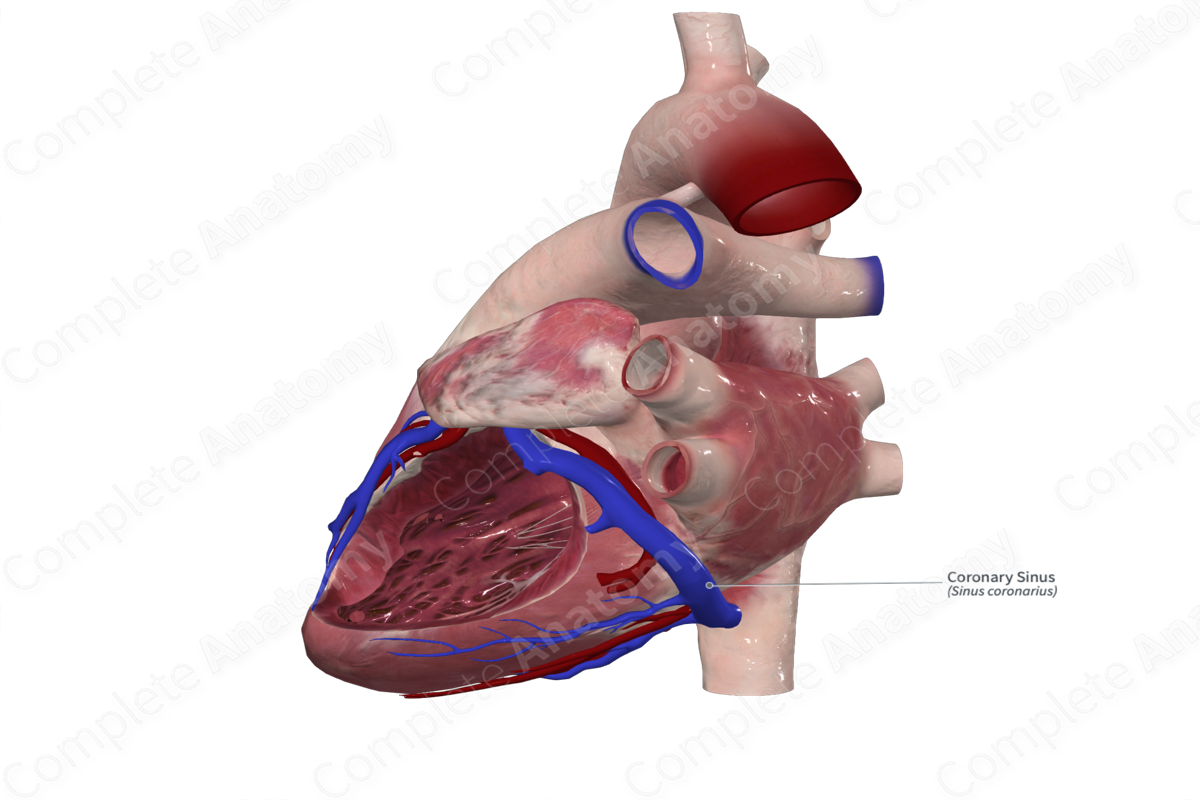
Course: Along the inferior (diaphragmatic) surface of the heart in the region of the coronary sulcus and runs through the myocardium to drain into the right atrium.
Tributaries: The great, middle, and small cardiac veins, the posterior vein of the left ventricle, the oblique vein of the left atrium, and the left marginal vein.
Drainage: External aspect of the myocardium of the heart.
Origin
The coronary sinus is approximately 2–3 cm long and sits at the junction of the atrioventricular sulcus and the posterior interventricular sulcus.
Course
The coronary sinus sits between the inferior vena cava and the atrioventricular opening between the right atrium and ventricle. The inner opening of the coronary sinus may be covered by the Thebesian valve (Standring, 2016).
Tributaries
The great, middle, and small cardiac veins drain into the coronary sinus. Additionally, it receives the posterior vein of the left ventricle, the oblique vein of the left atrium, and the left marginal vein (Tubbs, Shoja and Loukas, 2016; Standring, 2016). Occasionally, if the coronary sulcus is absent, venous drainage of the heart is completed by drainage into the pulmonary trunk (Standring, 2016).
Structures Drained
The coronary sinus delivers deoxygenated blood from the myocardium to the right atrium.
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41 edn.: Elsevier Limited.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Coronary Sinus

Coronary sinus ASD (i.e., unroofed coronary sinus) is a defect in the atrial wall that allows blood to flow from the left atrium to right atrium through the coronary sinus.