Just outside Syria’s capital, a battle still rages over one of the last rebel-held enclaves
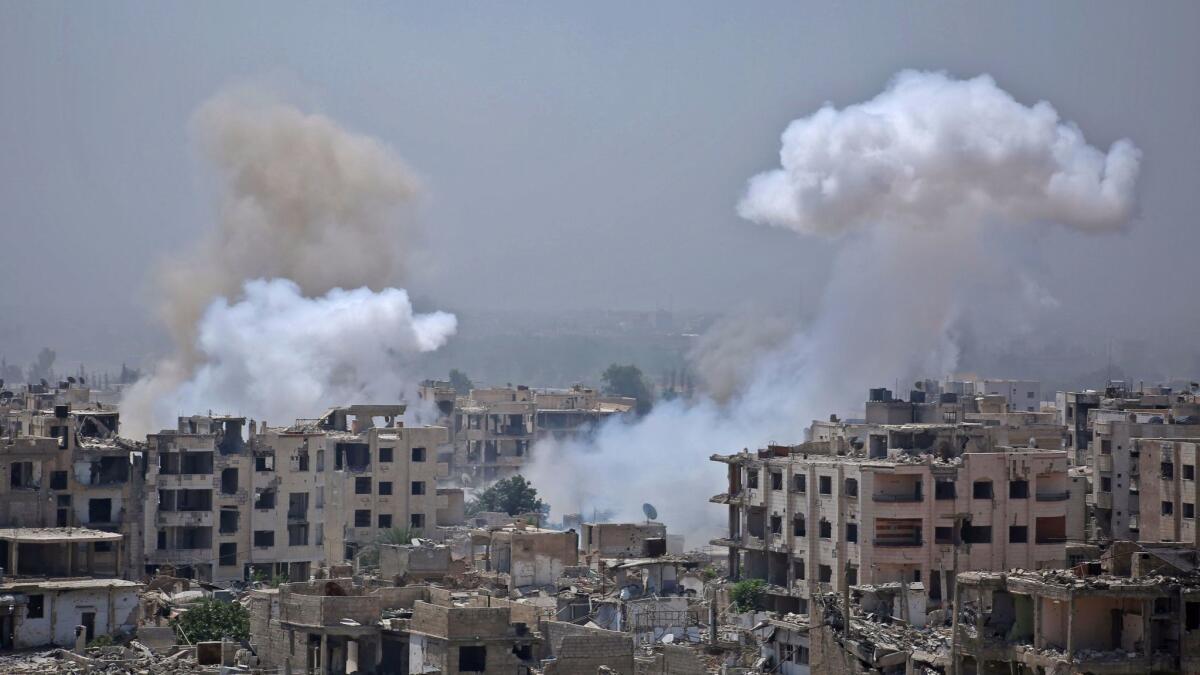

As international attention has shifted to the fight against Islamic State militants in eastern Syria, a little-noticed but bitter struggle continues on the outskirts of the capital, Damascus.
There, government forces are determined to reclaim one of the last remaining urban areas controlled by rebel factions committed to overthrowing President Bashar Assad.
With a population of about 450,000, the area east of Damascus known as eastern Ghouta has been under siege by the Syrian army since 2013. Its story is not unlike that of east Aleppo, where rebels stubbornly held ground for years in Syria’s second-largest city. The Aleppo siege ended in a government victory after a bruising offensive late last year.
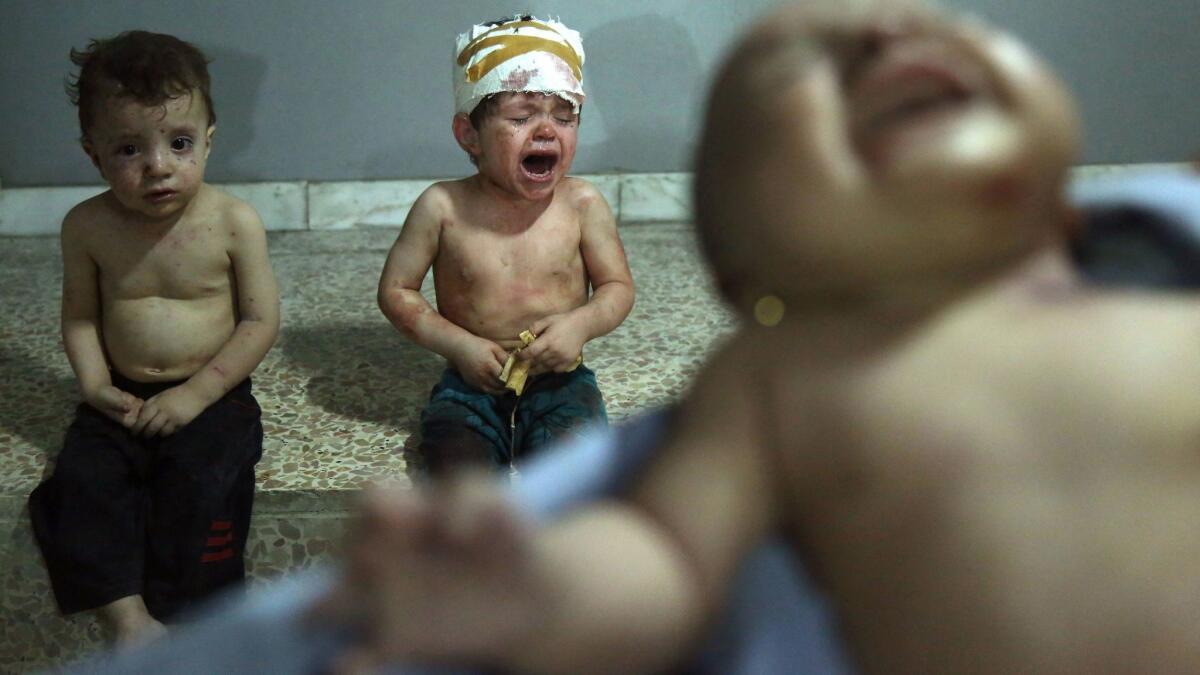
Ghouta was the site of a chemical weapons attack in August 2013 that killed hundreds of people. The United States and allies blamed Assad’s government for the attack, and the government blamed the rebels. Rights groups and rebels have accused the government of continuing to target the area with chemical weapons in smaller-scale attacks since.
Recent cease-fire agreements brokered by Russia — the Syrian government’s ally — and various rebel groups have abated but not halted the fighting in the Damascus suburbs, and experts said it’s a matter of time before the last rebel-held pocket near the capital falls to government control.
Sam Heller, a Syria expert and fellow with the Century Foundation, said bringing the east Damascus suburbs under control has been a “major long-standing priority” for the Syrian government.
“I think that there are a handful of sections of the country out of which it may be possible to exclude the regime or in which the regime’s local authority will only be incomplete,” Heller said, adding that those areas would probably be far from the capital, such as Dara in the southwest or the Kurdish areas of the northeast. “But when it comes to these opposition-held internal pockets … it’s very difficult to imagine any outcome other than complete regime victory.”
At most, he said, the government might permit “some factions and local structures to be integrated, mostly intact, into the regime-led state.”
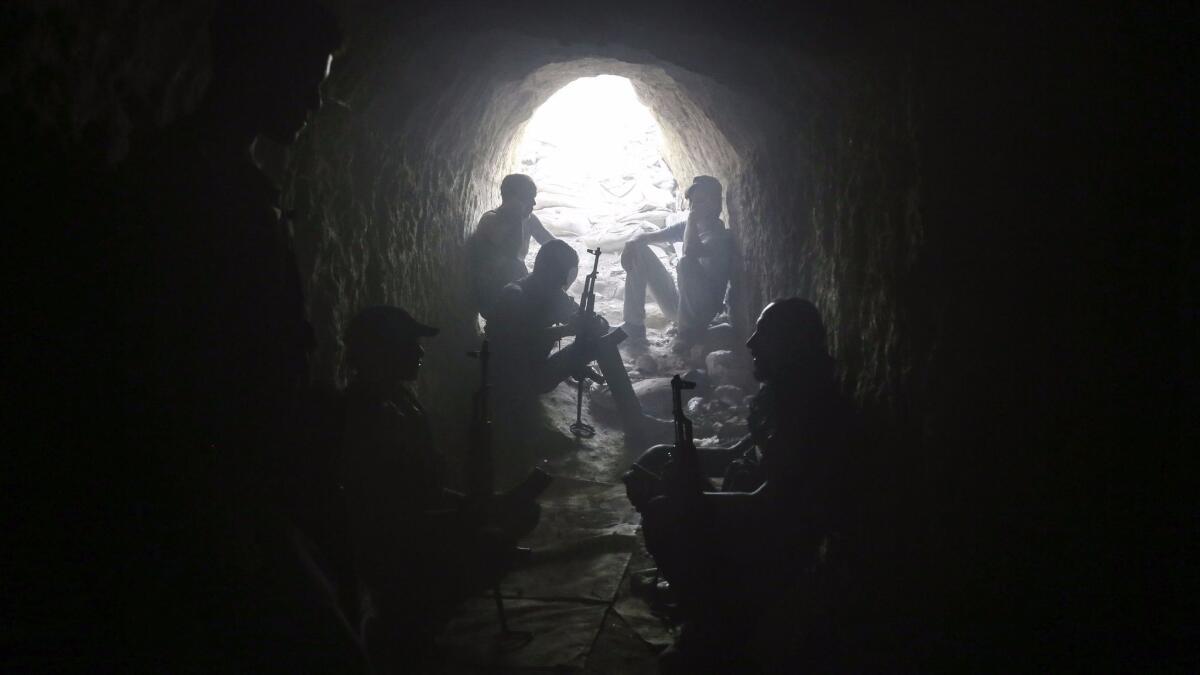

The town of Jobar has been the site of much of the most intense fighting in the Damascus outskirts. Before the war, it was an unremarkable middle-class suburb. In the more distant past, it had been a center of Syria’s now-departed Jewish population, with a centuries-old synagogue remaining as a reminder.
The synagogue was destroyed in an airstrike in 2014, and many of the former residential and business districts have also been reduced to rubble.
The area is strategically important to the rebels and the Syrian government because it serves as a link between the capital and suburbs to the east.
In March, rebels launched a surprise assault on Damascus from the enclave, using car bombs, suicide attacks and a network of tunnels running under the area. The tunnels are also used to smuggle food and supplies into the siege area, providing profits for government-linked businesses and for rebel groups.
In the latest round of fighting over the summer, the area has been pounded by so-called elephant rockets, improvised munitions known for their increased destructive power and inaccuracy.
“Even the shelters are no longer safe,” said Maher Abu Alkhair, 27, a former engineering student turned media activist in Jobar, speaking over a social media voice app this month before a new cease-fire deal was enacted. “The missiles and the reconnaissance aircraft don’t leave the skies. We try to rest at night, but before I spoke to you about an hour ago, the rockets were falling on us, causing fires.”
During the recent bombing, many of Abu Alkhair’s remaining neighbors loaded sleeping pads and blankets onto decrepit pickup trucks and bicycle-drawn carts amid the rubble in the streets and fled to nearby suburbs.
Many headed to other areas in eastern Ghouta covered by a cease-fire brokered last month between Russia and some of the rebel factions, including the dominant Army of Islam group. During the cease-fire, United Nations officials said, aid convoys were able to bring food and supplies into some areas that had been unreachable for as long as five years.
Jobar was not initially part of the cease-fire, but this month the Russian Defense Ministry and the main rebel group controlling the area, the Free Syrian Army-affiliated Rahman Corps, announced that the group had joined the deal. Russian officials said that under the deal, the rebels had agreed to help expel extremists from Islamic State and the group formerly known as Al Nusra Front, which had been affiliated with Al Qaeda.
Experts said that as the United States has turned its attention to fighting Islamic State rather than displacing the Assad government, Russia is likely to remain the major international player in east Damascus.
“The U.S. interest is mainly the Islamic State at this point,” said Aron Lund, another Syria expert with the Century Foundation. “And this has nothing to do with the Islamic State, so that’s that.”
Lund said the Syrian government sees Jobar in particular as a threat because of its proximity to the capital, which has been relatively sheltered from the violence unfolding elsewhere in the country in recent years.
But Lund said it’s unclear how quickly the government will move to retake the rebel-held areas of east Damascus.
“They have to use a lot of troops to keep the siege in place, but as long as they do, they can kind of work that area on their own timeline,” he said.
After the latest cease-fire was announced, the rebels promptly accused government forces of breaking it, saying in a statement that Assad’s forces “have been committing dozens of violations since the first hours of the agreement.” But they also acknowledged that fighting had eased since the deal was signed.
Abu Alkhair, the Jobar activist, said that the number of rockets falling on the area had abated but not stopped since the deal was put in place. So far, the displaced residents are not returning, he said. Estimates vary of how many people remain, but Siege Watch, an initiative of two humanitarian watchdog groups, put the number at just 225 people.
“No one is coming back to Jobar; you can count the people here on your fingers,” Abu Alkhair said. “One rocket can bring down a building.”
Sewell is a special correspondent.
ALSO
Depleted and on the run, Islamic State loses Tall Afar without much of a fight
Lebanese town looks for relief after three tough years tied to Syrian civil war
A small town in Italy was losing population. Now Syrian refugees are key to its survival
More to Read
Start your day right
Sign up for Essential California for news, features and recommendations from the L.A. Times and beyond in your inbox six days a week.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.