Advancements and Challenges in the Myasthenia Gravis Treatment Market
Introduction:
The myasthenia gravis treatment market was valued at $1.7 billion in 2022, and is estimated to reach $3.1 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 6.5% from 2023 to 2032.
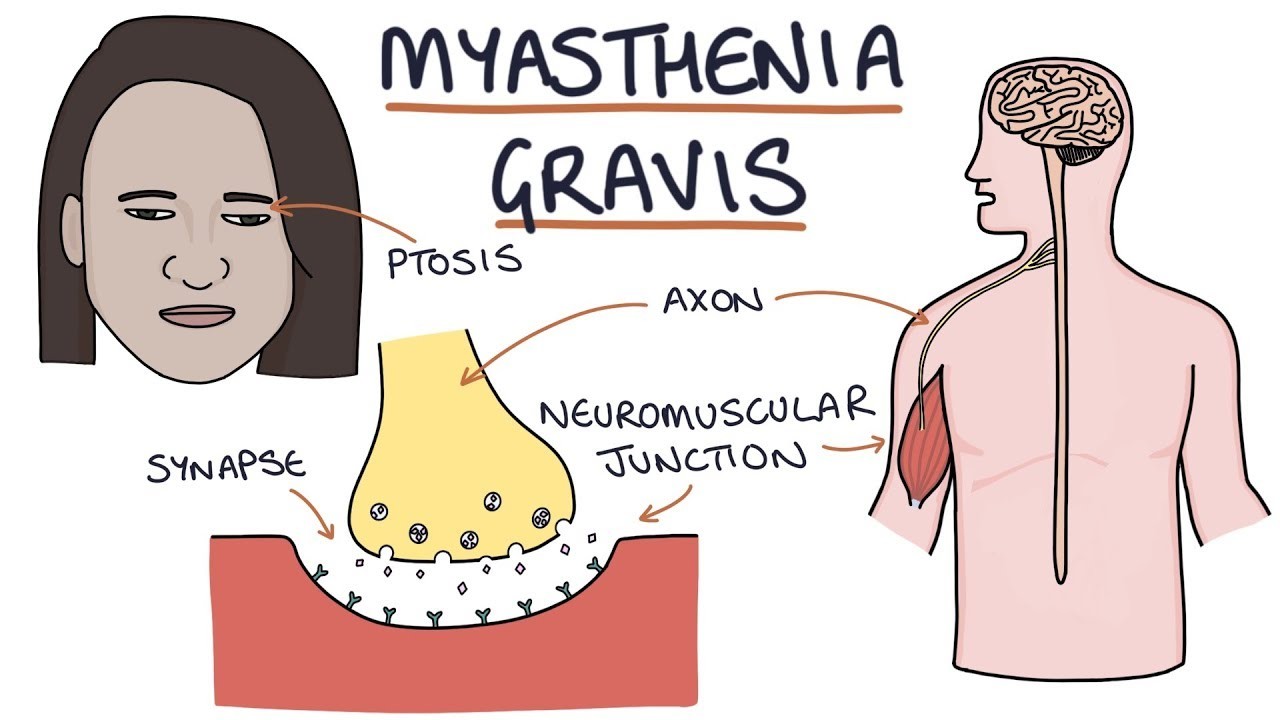
Myasthenia Gravis (MG) is a chronic autoimmune neuromuscular disorder characterized by muscle weakness and fatigue. While the exact cause remains unclear, it is known to involve antibodies that attack receptors on muscle cells, impairing the communication between nerves and muscles. Over the years, significant progress has been made in the treatment of MG, offering patients improved quality of life and better disease management. This article explores the evolving landscape of the Myasthenia Gravis Treatment Market, highlighting advancements, challenges, and future prospects.
📌 𝐑𝐞𝐪𝐮𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐒𝐚𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞 𝐂𝐨𝐩𝐲 𝐨𝐟 𝐑𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭👉 https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/request-sample/A11194
Advancements in Treatment:
Immunomodulatory Therapies: One of the cornerstones of MG treatment involves immunomodulatory therapies aimed at suppressing the abnormal immune response. These include corticosteroids, such as prednisone, which help reduce inflammation and antibody production. Additionally, immunosuppressants like azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, and methotrexate are used to dampen the immune system's activity, thereby alleviating symptoms.
Cholinesterase Inhibitors: Medications like pyridostigmine are commonly prescribed to enhance communication between nerves and muscles by inhibiting the breakdown of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter essential for muscle contractions. While these drugs can improve muscle strength and function, they do not address the underlying autoimmune process.
Monoclonal Antibodies: In recent years, the advent of monoclonal antibody therapy has revolutionized MG treatment. Drugs like rituximab target B cells responsible for producing the autoantibodies implicated in MG pathogenesis. By depleting these cells, rituximab helps alleviate symptoms and reduce disease severity, offering a promising option for patients refractory to conventional therapies.
Plasma Exchange and Intravenous Immunoglobulin: In severe cases or during MG exacerbations, plasma exchange (plasmapheresis) and intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) therapy are employed to rapidly remove pathogenic antibodies from the bloodstream or provide temporary immune modulation, respectively. These interventions can provide rapid symptomatic relief and are particularly beneficial in MG crises.
𝐈𝐧𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐝 𝐭𝐨 𝐏𝐫𝐨𝐜𝐮𝐫𝐞 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐑𝐞𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐜𝐡 𝐑𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭? 𝐈𝐧𝐪𝐮𝐢𝐫𝐞 𝐁𝐞𝐟𝐨𝐫𝐞 𝐁𝐮𝐲𝐢𝐧𝐠 : https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/purchase-enquiry/102653
Challenges in Treatment:
Treatment Response Variability: MG is a heterogeneous disorder, with patients exhibiting varying degrees of disease severity and treatment responsiveness. Identifying the most effective therapy for individual patients remains a clinical challenge, often requiring a trial-and-error approach and close monitoring of disease progression.
Side Effects and Complications: Many MG treatments carry the risk of adverse effects, ranging from mild to severe. Common side effects of immunosuppressive medications include increased susceptibility to infections, gastrointestinal disturbances, and bone marrow suppression. Additionally, long-term corticosteroid use can lead to metabolic disturbances, osteoporosis, and mood changes, necessitating careful risk-benefit assessment.
Cost and Access: The cost of MG treatment can be prohibitive for some patients, especially considering the need for lifelong therapy and potential hospitalizations. Access to novel biologic agents like rituximab may be limited by factors such as insurance coverage, healthcare disparities, and geographical barriers, posing challenges to equitable care delivery.
Future Directions:
Despite the challenges, ongoing research holds promise for further advancements in MG treatment. Targeted therapies directed against specific components of the immune system, such as complement inhibitors and selective B cell modulators, are under investigation and may offer improved efficacy and safety profiles. Moreover, efforts to identify biomarkers predictive of treatment response and disease progression are underway, facilitating personalized therapeutic approaches tailored to individual patient needs.
Conclusion:
The Myasthenia Gravis Treatment Market has witnessed significant progress in recent years, driven by advancements in immunomodulatory therapies, monoclonal antibodies, and supportive interventions. While challenges such as treatment response variability, side effects, and access barriers persist, ongoing research efforts offer hope for continued innovation and improved outcomes for patients living with MG. Collaborative efforts among healthcare providers, researchers, and pharmaceutical companies are essential to address unmet needs and optimize the management of this complex autoimmune disorder.