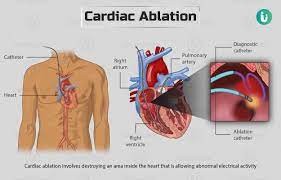
Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation Treatment: Managing Arrhythmias
Radiofrequency catheter ablation is an advanced medical procedure used to treat abnormal heart rhythms, known as arrhythmias. It is a minimally invasive technique that utilizes radiofrequency energy to selectively destroy abnormal heart tissue responsible for causing the arrhythmia. In this article, we will explore the radiofrequency catheter ablation treatment, including its principles, indications, procedure steps, potential benefits, and considerations.
Understanding Arrhythmias and their Impact:
Arrhythmias are abnormal heart rhythms that can disrupt the normal electrical activity of the heart. They can lead to symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness, shortness of breath, and even more severe complications like stroke or heart failure. Radiofrequency catheter ablation is primarily used to treat two types of arrhythmias:
a. Supraventricular Arrhythmias: These arrhythmias originate above the ventricles, such as atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, or supraventricular tachycardia.
b. Ventricular Arrhythmias: These arrhythmias arise from the ventricles, such as ventricular tachycardia or premature ventricular contractions.
Principles of Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation:
Radiofrequency catheter ablation works by delivering controlled heat energy to specific areas of the heart tissue responsible for generating or maintaining abnormal electrical signals. The aim is to create small scar tissue that interrupts the abnormal electrical pathways, restoring the heart's normal rhythm.
Procedure Steps:
a. Preoperative Evaluation:
Before the procedure, the patient undergoes a comprehensive evaluation, which includes a detailed medical history, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests such as electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, or electrophysiological studies. These tests help identify the specific arrhythmia and guide the treatment plan.
b. Anesthesia and Catheter Placement:
Radiofrequency catheter ablation is usually performed under local anesthesia with mild sedation. Long, flexible catheters are inserted through blood vessels, typically in the groin area, and advanced to the heart. These catheters have electrodes at their tips, which allow for precise mapping and delivery of radiofrequency energy.
c. Mapping the Abnormal Electrical Pathways:
During the procedure, the electrophysiologist uses the catheters to map the electrical activity of the heart and identify the precise location of the abnormal tissue responsible for the arrhythmia. Advanced mapping technologies, such as three-dimensional mapping systems, may be used to enhance accuracy.
d. Radiofrequency Ablation:
Once the abnormal tissue is identified, radiofrequency energy is delivered through the catheter to create controlled thermal lesions, effectively destroying the abnormal tissue. The energy is carefully targeted to minimize damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
e. Monitoring and Post-procedure Care:
Following the ablation, the patient is closely monitored for a period of time to ensure stable cardiac rhythm. Bed rest may be required initially, followed by a gradual return to normal activities. Medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms and prevent arrhythmia recurrence.
Potential Benefits and Considerations:
a. Restoration of Normal Rhythm:
Radiofrequency catheter ablation aims to restore the heart's normal rhythm, reducing or eliminating symptoms associated with arrhythmias and improving overall quality of life.
b. Reduction in Medication Dependency:
Successful ablation can potentially reduce or eliminate the need for long-term medication use, improving patient comfort and reducing the risk of medication-related side effects.
c. Individualized Approach:
Radiofrequency catheter ablation treatment is tailored to each patient's specific arrhythmia pattern and anatomy, allowing for a targeted and personalized approach.
d. Risks and Considerations:
While radiofrequency catheter ablation is generally safe, it does carry certain risks, including bleeding, infection, damage to blood vessels, and rare complications such as perforation of the heart. The healthcare provider thoroughly discusses the individualized risks and benefits with the patient before proceeding with the procedure.
Conclusion:
Radiofrequency catheter ablation treatment in India has seen significant advancements. Radiofrequency catheter ablation treatment is a highly effective and minimally invasive approach for managing arrhythmias. By selectively targeting and destroying abnormal heart tissue, this procedure aims to restore normal cardiac rhythm and improve the patient's quality of life. Proper patient selection, thorough preoperative evaluation, skilled procedural techniques, and comprehensive post-procedure care are essential for successful outcomes. If you are experiencing symptoms of an arrhythmia or have been diagnosed with an arrhythmia, consulting with a cardiac electrophysiologist can provide valuable insights into whether radiofrequency catheter ablation is a suitable treatment option for you.