What is SAP HANA
SAP HANA (High-performance ANalytic Appliance) is a multi-model database that stores data in its memory instead of keeping it on a disk. The column-oriented in-memory database design allows you to run advanced analytics alongside high-speed transactions – in a single system. Why is this so important? Because it lets companies process massive amounts of data with near-zero latency, query data in an instant, and become truly data-driven. By storing data in column-based tables in main memory and bringing online analytical processing (OLAP) and online transactional processing (OLTP) together, SAP HANA is unique – and significantly faster than other database management systems (DBMS) on the market today.
Launched in 2010, SAP HANA is a modern and mature solution used by tens of thousands of customers around the world. But SAP HANA is much more than a database. In addition to acting as a database server, storing and retrieving data requested by applications, SAP HANA offers advanced search, analytics, and data integration capabilities for all types of data – structured and unstructured. It also functions as an application server and helps companies build smart, insight-driven applications based on real-time data, in-memory computing, and machine learning technology. These capabilities are available both in the cloud, and on-premise.
By combining multiple data management capabilities – and making all types of data instantly available from a single system – SAP HANA simplifies IT, helps businesses innovate, and knocks down barriers to digital transformation.
What is an in-memory database?
An in-memory database (IMDB) is a type of database that stores data in a computer’s main memory (RAM) instead of on traditional disks or solid-state drives (SSD). While most databases today have added more in-memory capabilities, they are still a disk-based storage database first. SAP HANA was built from the ground up to work with data in-memory first and leverage other storage mechanisms as necessary to balance performance and cost. Retrieval from memory is much faster than from a disk or SSD, resulting in split-second response times.
In-memory databases are often used for applications that require top speed and the ability to handle large spikes in traffic – such as telecommunications networks and banking systems. In the last 10 years or so, mainly due to advancements in multi-core processors and less expensive RAM, companies have started to use in-memory databases for a wider range of applications, including real-time analytics and predictive modeling, customer experience management, logistics, and much more.
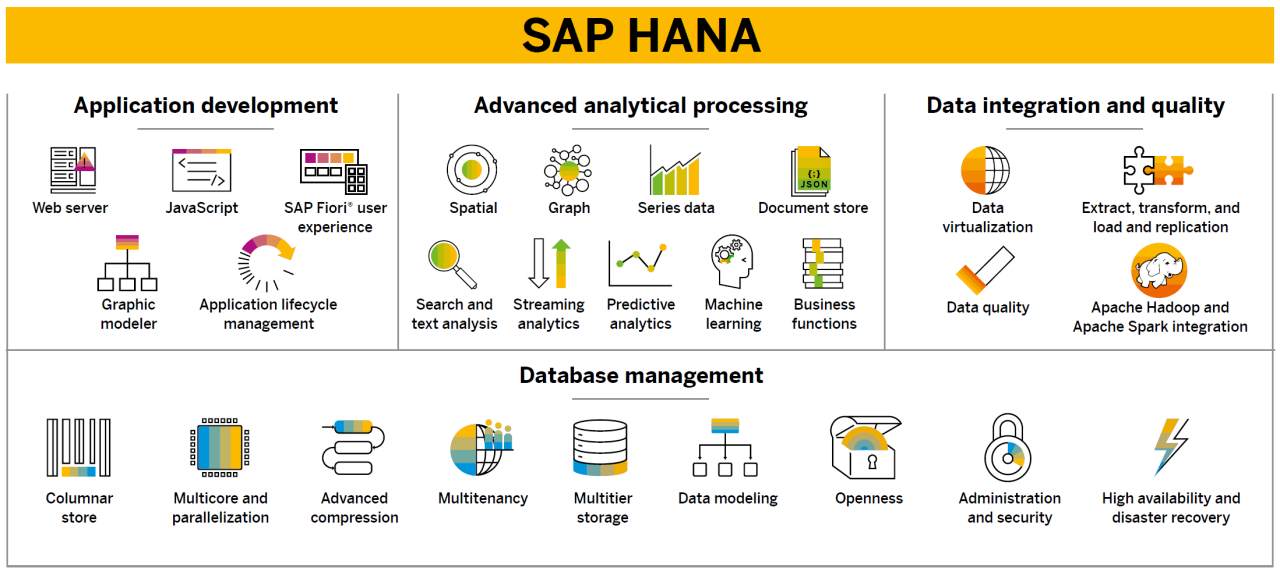
Top 10 benefits of SAP HANA
The SAP HANA database offers many more benefits than just storing data, serving it, and providing a single source of truth. The top 10 benefits of SAP HANA, both on-premises and with SAP HANA Cloud, are:
Complete: Includes database services, advanced analytical processing, application development, and data integration
Fast: Response to queries in less than a second in large production applications
Versatile: Supports hybrid transactional and analytical processing and many data types
Efficient: Provides a smaller data footprint with no data duplication, advanced compression, and reducing data silos
Powerful: Rapidly queries large datasets with a massively parallel processing (MPP) database
Scalable: Easily scales for data volume and concurrent users across a distributed environment
Flexible: Deploys in a public or private cloud, in multiple clouds, on-premise, or a hybrid scenario
Simple: Provides a single gateway to all your data with advanced data virtualization
Intelligent: Augments applications and analytics with built-in machine learning (ML)
Secure: Offers comprehensive data and application security, secure setup, and more