Intussusception: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Mar 09, 2023
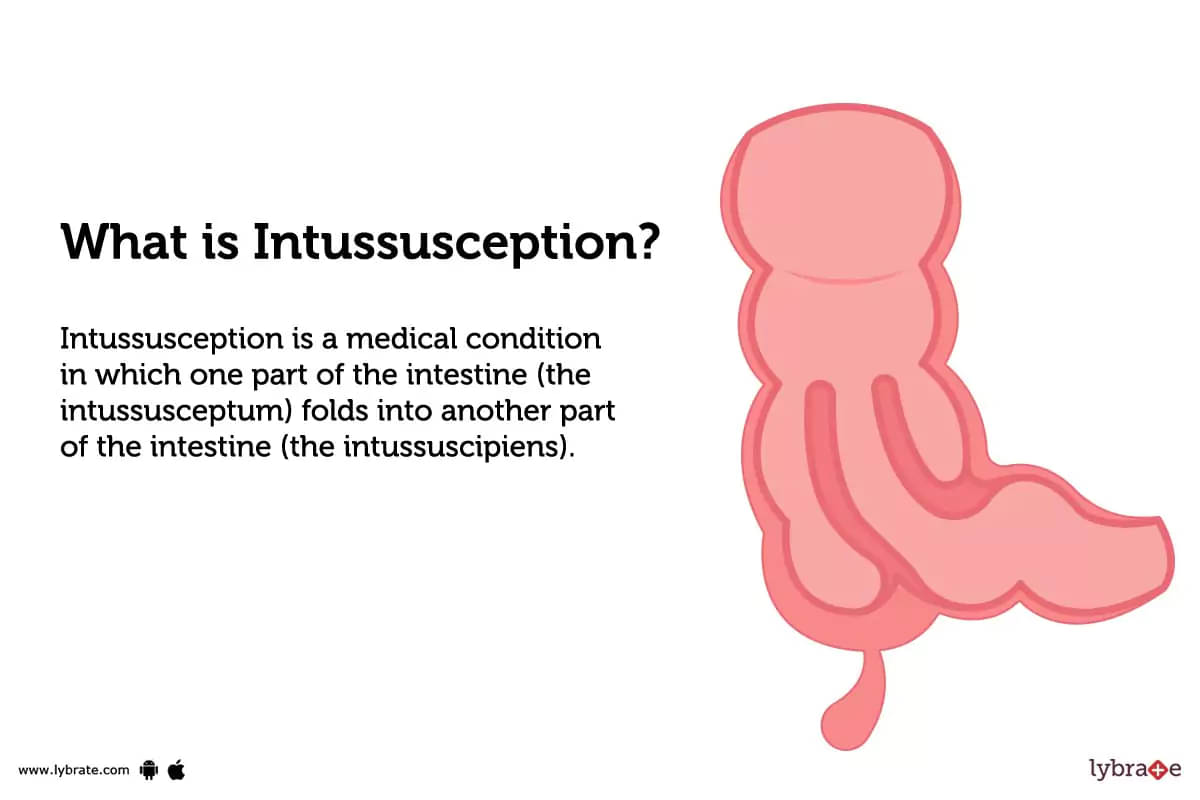
What is Intussusception?
Intussusception is a medical condition in which one part of the intestine (the intussusceptum) folds into another part of the intestine (the intussuscipiens). This can cause an obstruction in the intestinal tract. It is most common in infants and children, but can occur at any age.
Types of Intussusception
There are two types of intussusception:-
- Ileocolic Intussusception: This type involves the ileum (the end section of the small intestine) telescoping into the colon (the large intestine). It is most common in children ages 6 months to 3 years old, and accounts for more than 85% of intussusceptions in this age group.
- Colonic Intussusception: This type involves one part of the colon folding into another part of it, leading to an obstruction. It is less common than ileocolic intussusception, and mostly affects adults or older children who have had diseases that affect their gastrointestinal system (such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis).
What causes Intussusception?
- Intussusception is usually caused by excessive intestinal movement and can be associated with other causes such as blocks, tumours, or polyps in the intestines.
- Other possible causes include infections, stress, dietary changes and congenital disorders.
- In some cases, a cause may not be identified.
What are the symptoms of Intussusception?
- Abdominal pain, especially cramping and colicky in nature.
- Vomiting
- Alternating diarrhoea and constipation.
- Blood or mucus in the stool
- Abdominal swelling or distension.
- Lethargy/listlessness
- Dehydration from fluid loss.
How can you prevent Intussusception?
- Breastfeed: Breastfeeding babies exclusively can help reduce the incidence of intussusception.
- Vaccination: Vaccinating children against rotavirus can help reduce the risk of developing this condition.
- Proper Diet: Avoiding foods that are associated with intussusception, such as dairy products, eggs and nuts, can also help decrease risk.
- Proper Hygiene: Maintaining strict hygiene standards can reduce risk of infection and subsequent likelihood of developing intussusception.
Intussusception - Diagnosis and Tests
- Abdominal Exam:A physical exam of the abdomen can reveal signs of intussusception, including a “sausage-like” swelling in the abdomen, tenderness to touch, and/or fluctuation (air movement) when touched.
- X-ray:An x-ray may show an abnormal pattern of air due to distended small bowel loops, often referred to as the 'target sign'. This is indicative of intussusception and is seen in more than 85% of cases.
- Ultrasound:An ultrasound can be used if physical exam and x-rays don't provide enough evidence due to bowel obstruction. This test shows enlarged loops of the small bowel with an obvious target sign on display ('intraluminal hematoma'). It also allows for overall assessment for other abdominal conditions that may exist alongside intussusception or have been caused by it.
- Computed Tomography (CT):This scan has become a routine diagnostic tool for intussusception as it provides very detailed images which enables further assessment.
- Barium Enema:This involves introducing a liquid barium solution into the rectum after injections are given to make sure it doesn't just come out immediately (this prevents diarrhoea). The barium outlines any obstruction inside the intestine, allowing doctors to see if there is any sort of blockage present due to intussusception as well as provide useful information regarding its size and location which can help them decide on treatment options if necessary.
- Colonoscopy:It is often used to diagnose intussusception through visualisation of the intestine's inner lining. Colonoscopy involves inserting a long flexible tube with a camera on one end through the rectum and advancing it all the way up to the part of the intestine affected by intussusception.
What are possible complications of Intussusception?
- Shock:Intussusception can cause shock due to reduced blood flow in the section of intestine where it occurs.
- Perforation:There is a risk of the intestine tearing due to the pressure of the intussusception, leading to infection and other serious complications.
- Vascular compromise:Blood supply to the area where intussusception has occurred can be decreased, resulting in tissue death and potential organ failure.
- Necrosis (tissue death):Tissue death occurs when blood supply is restricted for an extended period of time, which can lead to further complications such as abscess formation or sepsis if not treated promptly.
- Bowel obstruction:Intussusceptions may form an obstruction in the intestine's passageway, resulting in severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and possibly constipation or diarrhoea depending on the location and severity of blockage.
Home Remedies for Intussusception
- Fomentation using warm water or medicated oils on the affected area, followed by gentle massage.
- Use of castor oil to obtain quick relief from the symptoms like pain and itching.
- Mixing a teaspoon each of aniseed, fennel seed, and ginger in 1 cup of water and boiling it for 5 minutes; straining it; adding sugar or jaggery; and drinking it twice a day for 7-8 days.
- An enema using warm sesame seed oil with garlic can help reduce inflammation and pain caused due to intussusception.
- Consuming fresh mint juice mixed with honey every day is also beneficial in treating intussusception.
What to eat in Intussusception?
Diet for intussusception should be composed of easy to digest foods that offer nutrition without irritating the bowel. Examples include:
- Clear soup or broth.
- Steamed vegetables, such as carrots or green beans.
- Plain cooked proteins, such as chicken or fish.
- Cooked grains, such as oatmeal and rice.
- Soft fruits, such as bananas and applesauce.
- Cooked potatoes and other starchy root vegetables.
- Yoghourt with probiotics to help boost gut health.
What not to eat in Intussusception?
- Spicy and fatty foods:Foods that are high in fat or contain spices such as hot pepper, chilli powder, and garlic powder can increase abdominal pain and pressure in those with intussusception.
- Fried foods:Fried or greasy foods may worsen symptoms of intussusception as they are harder for the body to digest and can also aggravate abdominal discomfort from gas and bloating in some individuals.
- High-fibre foods:High-fibre foods like whole grains and raw fruits and vegetables should be limited or avoided as they add bulk to the intestinal contents which may be too much for an inflamed intestine during a flare-up of symptoms caused by intussusception.
Intussusception Treatment
- Hydrostatic reduction:A non-surgical procedure used to reduce intussusception. The patient is given an enema with warm water and air, which helps push out the intestine, reducing the intussusception.
- Air or Bubble Reduction:A technique in which air is injected into the rectum followed by a release of pressure that can cause the intestine to return to its normal position.
- Open or Closed Reduction (Surgery):In this procedure, the surgeon makes an incision in the abdomen and manually reduces the intussusception by pushing it back into place and securing it with stitches or tucking techniques.
Which doctor to consult for Intussusception?
A doctor specialised in treating gastrointestinal problems such as gastroenterologists should be consulted for Intussusception.
Gastroenterologists are doctors trained to diagnose and treat a wide range of diseases and disorders related to the digestive system, including conditions such as Intussusception.
Which are the best medicines for Intussusception?
- Laxatives:An example of a laxative used to treat intussusception is polyethylene glycol, which helps soften the impacted stool in the intestine and aids in passing it more easily.
- Prokinetics:Prokinetics are medications that stimulate the digestive tract and can help push food and gas through intestines, thus reducing the risk of intussusception recurrence. An example of a prokinetic medication is erythromycin, which can be given orally or intravenously.
- Narcotic analgesics:Narcotic analgesics are used to help manage severe pain associated with intussusception surgery or diagnostic procedures such as barium enemas. Examples include morphine, fentanyl, and hydrocodone/APAP (Vicodin).
- Corticosteroids:Corticosteroids may be prescribed in certain situations such as when there is evidence of an underlying inflammatory condition thought to be contributing to the intussusception risk or if an infant or child has developed significant peritonitis or sepsis following reduction (manual procedure for resolving obstruction). Examples include prednisone and solumedrol (methylprednisolone).
How long does it take to recover from Intussusception?
The duration of time it takes to recover from intussusception can vary depending on the severity of the case and the treatments used.
Generally, most cases are resolved with nonsurgical treatments such as using air or barium contrast to reduce obstruction, or manual reduction with a scope under anaesthesia. If surgery is required, recovery times will be longer. Recovery usually takes 2-4 weeks unless complications occur after treatment or surgery.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
The results of treatment for intussusception are usually permanent, with over 90% of patients not requiring further intervention after initial treatment. However, recurrent intussusceptions can occur in some cases and additional treatments may be needed.
What are post-treatment guidelines?
- Post-treatment care for intussusception usually begins with supportive measures such as intravenous fluid administration to replace lost fluids and electrolytes as well as intake of pain relievers to reduce discomfort.
- In addition to the above measures, patients may also be advised changes in diet such as switching from solid foods to semi-solid or liquid diet, avoiding gas forming foods and increasing intake of dietary fibres like fruits and vegetables that help in easy passage of stools.
- Regular monitoring for any signs of complications such as reappearance of obstruction needs to be done; this includes follow up visits with ultrasound imaging and X-rays to assess the healing condition.
- In rare cases when the surgery is not successful, the patient may require additional surgery or other medical interventions including medication after proper assessment by a doctor.
What is the cost of Intussusception treatments in India?
The cost of treating intussusception in India varies, depending on the severity and complexity of the condition. Generally, the average cost of diagnosis and treatment for a mild case is approximately 5,000-10,000 INR. However, more severe cases may require surgery with associated costs ranging from 15,000 to 25,000 INR.
What are side-effects of Intussusception treatments?
- Primary side effects of intussusception treatments include abdominal pain and discomfort, which can last for several days to weeks.
- Abdominal cramping, nausea, vomiting and fever may occur in some cases from the forceps used during treatment.
- Less common side effects may include negative reactions to the anaesthesia used for surgery, as well as infections of incision sites or wound breakdowns due to tissue trauma from the procedure itself.
- Complications from certain treatments like barium enema can also include problems with bowel obstruction or perforation and infection of the inner lining of the intestine, leading to sepsis or peritonitis inflammation and overwhelming infection in some cases.
Intussusception - Outlook/ Prognosis
If you are suffering from any complications relating to intussusception then you should consult a doctor nearby as they can cause complications like 'perforation, necrosis, bowel obstruction' in which treatment course can range from a few months to years depending on the severity of the situation.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Gastroenterologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors