Uterine Prolapse: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Jun 27, 2023
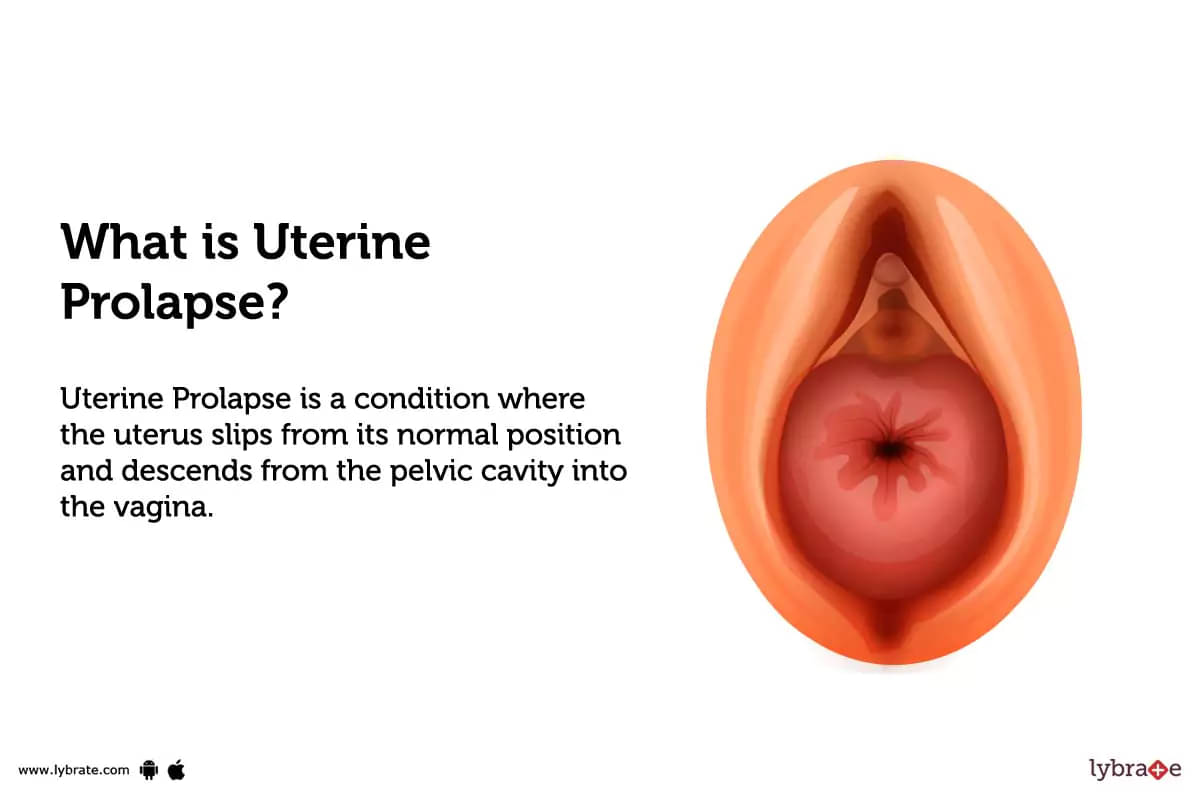
What is Uterine Prolapse?
Uterine Prolapse is a condition where the uterus slips from its normal position and descends from the pelvic cavity into the vagina. The degree of prolapse can range from mild to severe depending on how far down the uterus has descended. It is more common in postmenopausal women who have had multiple vaginal deliveries because childbirth stretches and weakens these muscles.
Types of Uterine Prolapse
- There are four types of Uterine Prolapse: cystocele, rectocele, enterocele and uterine descent.
- Cystocele: It is characterized by the bulging of our bladder into your vagina. It happens when your vaginal wall weakens and as a result your bladder drops from its normal location.
- Rectocele: It occurs when the muscular walls that separate the rectum from your vagina weaken or stretch, allowing part of your rectum to bulge through your vaginal wall.
- Enterocele: It is typically caused by repeated straining due to constipation, childbirth or the aging process. The descending parts of the intestines may press on one side of the cervix and force it against its surrounding support tissues, causing them to stretch downwards towards our lower abdomen before they start to protrude out of our vagina as an internal ballottement defect which we call an enterocele
- Uterine Descent: It is diagnosed if any uterine consistency drops down towards our vaginal opening without causing any bladder or bowel defects that cause changes in our pelvic floor muscles or contents like those seen with cystoceles, rectoceles or enteroceles.
What causes Uterine Prolapse?
- Uterine Prolapse is caused by a weakening of the pelvic floor muscles and supporting ligaments, which can be due to childbirth, menopause, chronic constipation or straining due to coughing.
- Other risk factors include being overweight, having a history of hysterectomy or pelvic surgery and fractures of the pelvis.
What are the symptoms of Uterine Prolapse?
- Stress incontinence – Accidentally leaking urine when coughing, sneezing, laughing or exercising.
- Pelvic pressure or a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen.
- Low back discomfort
- Sensation of pulling in the groin area.
- Difficulty in having a bowel movement or urinating.
- Feeling of something pressing against the vaginal opening.
- Trouble comfortably wearing tampons.
How can you prevent Uterine Prolapse?
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Strengthen pelvic floor muscles with Kegel exercises.
- Avoid constipation and straining during bowel movements.
- Avoid heavy lifting or other activities that put strain on the pelvic floor muscles.
- Wear supportive underwear to help the muscles support the uterus.
- Change positions frequently when sitting, standing, and lying down.
- Talk to your doctor about hormone therapy or other treatments.
Uterine Prolapse - Diagnosis and Tests
Diagnosis of Uterine Prolapse includes:-
- Physical exam: The doctor will perform a physical examination to evaluate and determine the degree of Uterine Prolapse. This usually involves inspection of both the front and back walls of the vagina and measurement of how far down the uterus has descended into it.
- Imaging Tests: An imaging test such as ultrasound, MRI or CT scan may be used to view the internal structures to further confirm diagnosis as well as guide in treatment decisions if necessary.
- Urodynamic Testing: This type of testing measures bladder pressure and filling capacity to check for any associated bladder or urethral problems that may have caused or been caused by the Uterine Prolapse.
- Stress Test : This test assesses whether stress incontinence is present – Sudden urge to urinate due to sudden increase in abdominal pressure (e.g., during coughing, sneezing etc.). It will help in assessment and management, after prolapsed uterus has been treated surgically if necessary,to ensure any residual urinary issues are addressed too when treating this condition effectively.
What are possible complications of Uterine Prolapse?
- Urinary tract problems: This includes incontinence, frequent urinary tract infections, incomplete bladder emptying and difficulty controlling urine flow.
- Bowel problems: Difficulty having bowel movements and fecal incontinence.
- Pelvic pressure and pain, which may become severe with time leading to sexual dysfunction and discomfort during sexual activity.
- Organ damage: These long-term complications can affect nearby organs such as the bladder, lower intestine and rectum, possibly leading to more severe conditions such as fistulas or urethral stricture.
Home Remedies for Uterine Prolapse?
- Take ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) root powder- mix it with honey and ghee, and consume it regularly.
- To strengthen your reproductive organs, prepare fermented porridge with cow’s milk, turmeric and rock salt, and consume it daily.
- Massage the lower abdomen area with Ashwagandha oil or Dashamul oil to reduce pain and discomfort caused by prolapse of uterus.
- Prepare a decoction of Vidari Root (Pueraria tuberose), Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera), Gokshura (Tribulus terrestris) in equal parts and drink it twice daily for relief from symptoms of Uterine Prolapse.
- Yogasanas like Viparita Karani, Ushtrasana, PavanaMuktasana are beneficial to reduce heaviness in the abdomen region & improve strength of the ligaments & pelvic muscles.
What to eat in Uterine Prolapse?
- Eat an anti-inflammatory diet. Foods such as salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts are high in omega-3 fatty acids that help reduce inflammation in the body.
- Increase your intake of fiber to promote healthy digestion and make stools softer and easier to pass. Good sources of fiber include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds.
- Consume plenty of fluids throughout the day to prevent dehydration which can make constipation worse.
- Include probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, sauerkraut, kombucha and kimchi in your diet for increased digestive health.
What not to eat in Uterine Prolapse?
Here are some foods you should avoid while dealing with Uterine Prolapse:
- Caffeinated beverages: Caffeine can cause irritation and dehydration, which may worsen symptoms of Uterine Prolapse.
- Alcohol: Alcohol increases the risk for further weakening of the pelvic muscles which could cause the condition to worsen.
- Processed/Junk Foods: These types of highly-processed foods are rich in sugar, refined grains, unhealthy fats, and less nutritious than whole food options so should be avoided for a successful treatment plan.
- Salt: Eating too much salt can lead to water retention and bloating which could place added pressure on the bladder, urethra and pelvis area which could lead to more severe symptoms of Uterine Prolapse.
- Spicy Foods: Spicy foods can irritate already weak pelvic muscles causing discomfort and worsening existing symptoms such as incontinence or back pain due to nerve compression or pressure placed on organs near the damaged muscles.
Uterine Prolapse Treatment
Treatment for Uterine Prolapse includes:-
- Lifestyle modifications: Lifestyle modifications are essential in managing Uterine Prolapse. Some of the modifications include avoiding heavy lifting, avoiding straining during bowel movements, adjusting dietary habits such as high fiber diets and drinking lots of water, quitting smoking and avoiding birth control pills.
- Pelvic floor exercises: Pelvic floor exercises, or Kegels, are a form of exercise that help strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. Regularly performing pelvic floor exercises can help increase support of the pelvic organs and relieve pressure from the uterus in cases of Uterine Prolapse.
- Pessary insertion: A pessary is a device that can be inserted into the vagina to provide support to the uterus and other pelvic organs in cases of Uterine Prolapse. It is generally made of silicone or plastic and helps to reduce or eliminate the symptoms associated with this condition. A doctor will first assess a woman's individual situation before determining if a pessary is an appropriate treatment option.
- Abdominal/vaginal surgery: This type of surgical repair involves placing a graft and sutures between the vaginal walls to hold the prolapsed tissue in place.
- Sacrohysteropexy: A reconstructive surgery occurs through laparoscopy where surgeon attaches abdominal muscles and tissues to hold up uterus normally in position by using threads or wires.
- Hysterectomy: In case when other treatments fail, this is recommended which involves removal of entire uterus either by abdominal or vaginal route.
Which doctor to consult for Uterine Prolapse?
A doctor specializing in female reproductive health, such as a gynecologist or urogynecologist can help diagnose and treat Uterine Prolapse.
Which are the best medicines for Uterine Prolapse?
- Hormone therapy: This class of drugs includes estrogen and progestin, which are used to reduce tissue laxity that might be contributing to Uterine Prolapse. It is thought that these hormones help support the pelvic floor muscles and connective tissue, making them stronger and less likely to stretch out or collapse.
- Muscle Relaxants: Muscle relaxants may also be used to treat Uterine Prolapse by helping to relieve some pressure from the pelvic floor muscles, allowing them to regain their strength and structural integrity more quickly. Commonly used muscle relaxants for this purpose include diazepam (Valium) and tizanidine (Zanaflex).
- Anti-inflammatory medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often prescribed for Uterine Prolapse, as they help reduce inflammation in the pelvic area that can be caused by excess pressure on the organs in the region. Common NSAIDS include ibuprofen (Motrin), naproxen sodium (Aleve), and celecoxib (Celebrex).
- Antidepressants: Certain types of antidepressants such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) may be helpful in treating symptoms associated with Uterine Prolapse, such as depression and anxiety which can accompany it due to its effects on physical well-being and lifestyle changes required for treatment. Popular SSRIs include fluoxetine (Prozac) and sertraline (Zoloft).
How long does it take to recover from Uterine Prolapse?
Recovery time will depend on the severity of the prolapse, and the type of treatment used. Generally, recovery can take anywhere from several weeks to several months, depending on how complicated the prolapse is and what type of treatments are necessary. Following medical advice on rest, diet and exercise can help expedite the healing process.
What is the cost of Uterine Prolapse treatments in India?
The cost of Uterine Prolapse treatments in India will vary depending on the type of treatment and medical facility chosen. Generally, conservative treatment such as medications, pelvic floor physiotherapy, or vaginal pessaries, would cost anywhere from Rs 5–20K; whereas, surgical procedures like laparoscopic colposuspension or sacrospinous fixation could be up to Rs 50K- 1 Lac. Aftercare and follow-up consultations will incur additional costs.
What are side-effects of Uterine Prolapse treatments?
- The most common side effect of Uterine Prolapse treatments is increased pain and discomfort in the pelvic area following the procedure.
- Other side effects may include nausea, fever, bleeding, infection, and blood clots.
- Long term side effects may include bladder or bowel problems and difficulty walking or carrying out daily activities due to reduced mobility in the pelvic area.
- In some cases, complications from surgeries used to treat Uterine Prolapse can lead to damage to other organs in the pelvic cavity such as the bladder, rectum or intestines.
Uterine Prolapse - Outlook/ Prognosis
If you are suffering from any complications relating to Uterine Prolapse then you should consult a doctor nearby as they can cause complications like 'Urinary tract problems, bowel problems, organ damage' in which treatment course can range from a few months to years depending on the severity of the situation.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Urologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors