Learn About Actinomycosis
Actinomycosis is a long-term (chronic) bacterial infection that commonly affects the face and neck.
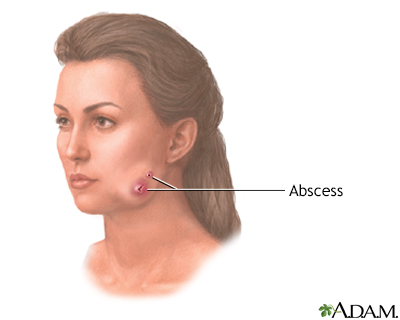
Lumpy jaw
Actinomycosis is usually caused by the bacterium called Actinomyces israelii. This is a common organism found in the nose and throat. It normally does not cause disease.
Because of the bacteria's normal location in the nose and throat, actinomycosis most commonly affects the face and neck. The infection can sometimes occur in the chest (pulmonary actinomycosis), abdomen, pelvis, or other areas of the body. The infection is not contagious. This means it does not spread to other people.
Symptoms occur when the bacteria enter the tissues of the face after trauma, surgery, or infection. Common triggers include dental abscess or oral surgery. The infection can also affect certain women who have had an intrauterine device (IUD) to prevent pregnancy.
Once in the tissue, the bacteria cause an abscess, producing a hard, red to reddish-purple lump, often on the jaw, from which comes the condition's common name, "lumpy jaw."
Eventually, the abscess breaks through the skin surface to produce a draining sinus tract.
Symptoms may include any of the following:
- Draining sores in the skin, especially on the chest wall from lung infection with Actinomyces
- Fever
- Mild or no pain
- Swelling or a hard, red to reddish-purple lump on the face or upper neck
- Weight loss
Treatment of actinomycosis usually requires antibiotics for several months to a year. Surgical drainage or removal of the affected area (lesion) may be needed. If the condition is related to an IUD, the device must be removed.
Campus Benjamin Franklin
Verena Moos practices in Berlin, Germany. Moos and is rated as an Elite expert by MediFind in the treatment of Actinomycosis. Her top areas of expertise are Whipple Disease, Actinomycosis, Malabsorption, and COVID-19.
Annette Moter practices in Berlin, Germany. Moter and is rated as an Elite expert by MediFind in the treatment of Actinomycosis. Her top areas of expertise are Whipple Disease, Actinomycosis, Endocarditis, and Malabsorption.
Alain Saraux practices in Brest, France. Saraux and is rated as an Elite expert by MediFind in the treatment of Actinomycosis. His top areas of expertise are Dry Mouth, Whipple Disease, Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), Hip Replacement, and Knee Replacement.
Full recovery can be expected with treatment.
In rare cases, meningitis can develop from actinomycosis. Meningitis is an infection if the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. This membrane is called the meninges.
Contact your provider if you develop symptoms of this infection. Starting treatment right away helps quicken the recovery.
Good oral hygiene and regular dentist visits may help prevent some forms of actinomycosis.
Published Date: November 23, 2021
Published By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Associate Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Associate in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Brook I. Actinomycosis. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 313.
Eckert LO, Lentz GM. Genital tract infections: vulva, vagina, cervix, toxic shock syndrome, endometritis, and salpingitis. In: Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 23.
Russo TA. Agents of actinomycosis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 254.