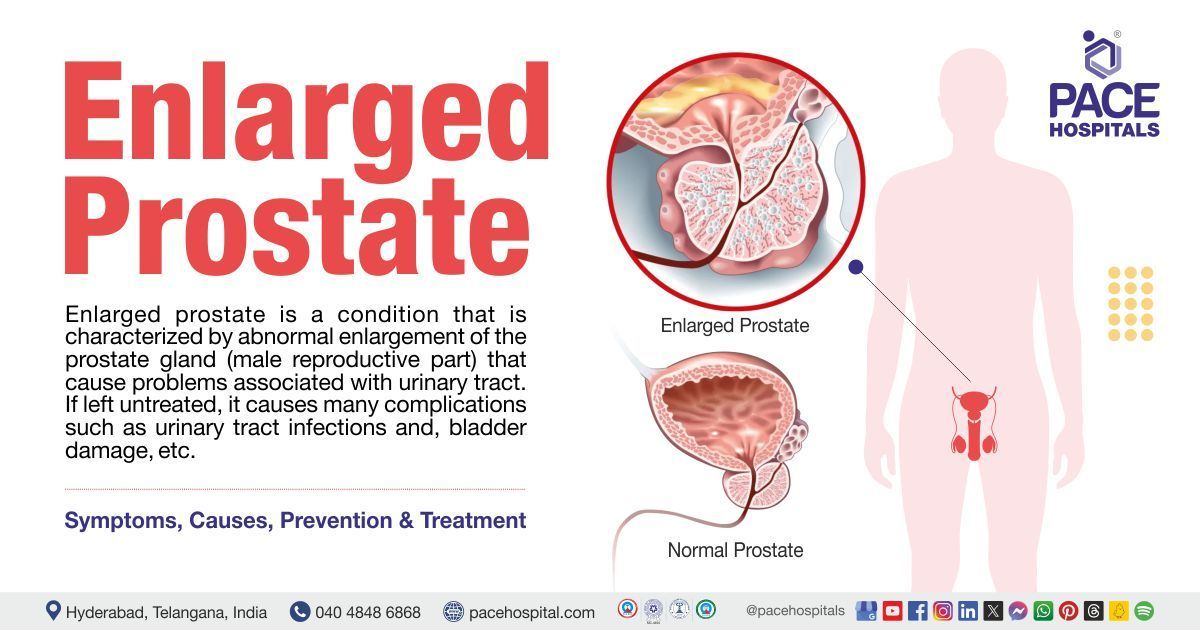
Appendicitis - Symptoms, Incidence, Types, Causes, Complications and Prevention
Appendicitis definition
Appendicitis is a condition characterised by painful swelling due to inflammation of the "vermiform appendix". The vermiform appendix is a small, thin, pouch-like structure ranging from 5 to 10 cm. It is situated at the end of the large intestine, usually at the tip of the caecum.
Appendicitis meaning
The word "Appendicitis" is a Latin word which stands for inflammation of the appendix; an appendix is a word that is used for "small outgrowth of an internal organ", whereas it stands for "diseases characterized by inflammation".
Incidence of appendicitis
According to the studies, appendicitis is the most common abdominal surgical emergency globally. With a mean age of 28, appendicitis most commonly affects people between the ages of 5 and 45. The incidence of appendicitis is 233 persons per one lakh population in a year, with a lifetime incidence risk of 6.7 and 8.6% in women and men, respectively.
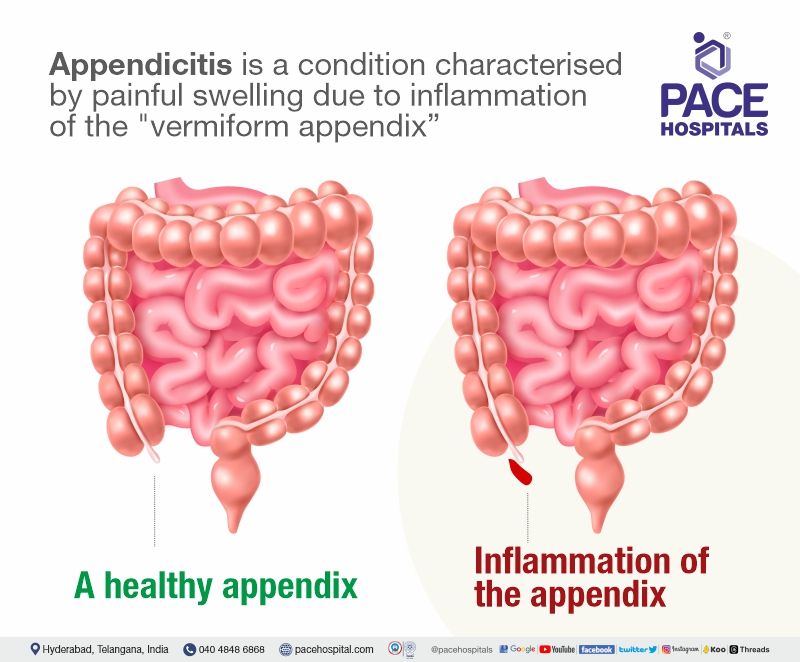
Types of appendicitis
Appendicitis is mainly categorised into two types based on the duration and severity of the inflammation:
- Acute appendicitis: Acute appendicitis is a condition with a severe and sudden onset of inflammation. Here, the symptoms and pain tend to develop quickly over a period of 24 hours. It is usually seen in children and younger adults within the ages of 10 and 30.
- Chronic appendicitis: Chronic appendicitis is a condition where the symptoms reappear over a period of weeks, months, or years. This condition tends to develop progressively, followed by acute appendicitis. It is a severe condition and a tough task to diagnose. This is an atypical condition when compared to acute appendicitis.
Stages of appendicitis
There are 4 stages of appendicitis, which include:
- Early appendicitis: In the majority of cases with acute appendicitis, luminal blockage is the main pathogenetic event. Appendiceal wall perfusion diminishes as intraluminal pressure rises because of arterial insufficiency, which results in mucosal ischaemia (early appendicitis).
- Suppurative appendicitis: When germs are able to penetrate the luminal wall and cause the transmural inflammation, this stage takes place. At this point, inflammation also affects other structures, including the parietal peritoneum (peri appendicitis).
- Gangrenous appendicitis: Moreover, intramural venous and arterial thromboses tend to develop gangrenous appendicitis.
- Perforated or complicated appendicitis: If the patient with gangrenous appendicitis does not undergo surgical intervention, it will lead to appendiceal infarction and perforation.
Appendicitis symptoms
Signs and symptoms of appendicitis include:
Generalised or peri umbilical abdominal pain in the right lower quadrant.
- This appendicitis pain begins at the belly button
- The onset is sudden and severe
- It worsens with deep breathing, coughing, or sneezing
Pain may or may not accompany by some common symptoms, such as:
- Anorexia (fear of gaining weight)
- Fever between 99°C to 102°C (experienced by 40% of patients)
- Rebound tenderness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhoea (watery or loose stools)
- Urinary frequency or urgency
- Generalised weakness
- Loss of appetite
Some patients might develop uncommon symptoms such as:
- Indigestion
- Abdominal swelling
- Constipation
- Inability to pass the gas
- Painful or difficult urination

Signs of appendicitis
Particularly in cases of early appendicitis, physical exam findings tend to be unnoticed. Signs of peritoneal inflammation appear as the inflammation worsens. Signs include:
- Rovsing's sign: pain in the right lower quadrant felt when the left lower quadrant is palpated.
- Dunphy's sign: worsening stomach pain accompanied by coughing.
- McBurney's point: Over McBurney's point, which is 1.5 to 2 inches from the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) and runs straight from the ASIS to the umbilicus, the patient experiences right lower quadrant guarding and rebound tenderness.
Appendicitis causes
Some of the common causes of the appendicitis might include:
- Obstruction of the appendiceal lumen due to an appendicolith (stone of the appendix) or some other mechanical causes or injuries
- Diseases of the intestines
- Infections due to viruses, bacteria, or intestinal parasites
- Hypertrophied lymphatic tissues
- Carcinoid tumours of the appendix, etc.
Appendicitis risk factors
Some of the risk factors for appendicitis include:
- Age: Appendicitis is commonly seen in young adults in their mid-20s. However, it might occur at any age.
- Gender: Appendicitis is more likely to be seen in men when compared to women.
- Family history: Family history and genetic conditions like cystic fibrosis increase the risk of appendicitis due to the genetic factors accompanying them.
- Trauma or injuries: Trauma causes mechanical injuries to the appendix that might cause inflammation.
- Tumours and cancers: Tumours such as carcinoid tumours and appendiceal adenocarcinomas increase the risk of developing appendicitis.
- Abdominal infections: Intestinal parasites and aerobic and anaerobic bacteria build up, increasing the risk of developing appendicitis.
- Blockage in the appendix: Obstruction due to the stone or a foreign object can lead to the infection.
Complications of appendicitis
If left untreated, appendicitis might cause some serious complications, such as:
- Peritonitis: An untreated appendix bursts and causes the bacteria to spill over the abdominal cavity lining or peritoneum, which leads to inflammation and infection.
- Abscess: If the appendix bursts and is localised, an abscess arises. An abscess is a pocket of pus associated with pain that forms near the burst appendix.
- Ischemia and necrosis: When there is a severe swelling in the appendix, the blood supply will be cut off (ischemia), which exacerbates inflammation and finally leads to necrosis, or the decomposition of the tissues.
- Sepsis: Sepsis is a severe and rare condition where bacteria travel to other body parts through the bloodstream. It requires a medical emergency, as the signs of sepsis include shortness of breath, confusion, and a high or low temperature.
Appendicitis diagnosis
Various diagnostic approaches are used to diagnose appendicitis, such as:
- Medical history and physical examination
- Blood tests - Complete blood count, CRP (C- Reactive protein)
- Imaging tests - Ultrasonography, Abdominal computed tomography scan (CT scan), Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Laparoscopy diagnosis
Appendicitis treatment
In mild cases, appendicitis can be treated with medications, whereas in severe cases, surgery is the golden standard treatment for treating appendicitis. Management includes both medical management and surgical management of appendicitis:
- Appendicitis medications
- Antibiotics (oral or intravenous)
- Pain relievers
- Appendicitis surgery
- Open appendectomy
- Laparoscopic appendectomy
Appendicitis prevention
There are no proven or definitive ways to prevent appendicitis. Appendicitis prevention can be done only in a few cases by following preventive measures, but in some cases, it cannot be prevented. Some of the preventive measures are as follows:
- Taking a fibre-rich diet such as fruits, vegetables, lentils, and grains
- Avoid processed and deep-fried foods
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Performing regular exercises
- Smoking and alcohol cessation
- Taking treatment for other digestive-associated diseases
- Managing other comorbid conditions
- Going for regular health check-ups or follow-ups
FAQs - Frequently asked questions on appendicitis
What are the 5 signs of appendicitis?
The typical signs of appendicitis include abdominal pain, loss of appetite, fever, vomiting, rebound tenderness, and changes in bowel habits.
Is appendicitis painful?
Yes, particularly in the lower right side of the abdomen, severe abdominal pain can often be related to appendicitis. Over time, the pain may get worse.
How to treat appendix problem?
An appendectomy, or surgical removal of the inflamed appendix, is the primary treatment for appendicitis. Antibiotics may be recommended in place of surgery in some cases where difficulties are not present.
Is appendicitis surgery safe?
The appendectomy, or surgical removal of the appendix, is a standard treatment for appendicitis and is generally regarded as safe. Although there are risks associated with any surgical operation, complications are rare.
How long is appendix recovery?
Although recovery times following appendiceal resections vary, most patients return to their regular routines in a few weeks. Compared to open surgery, the laparoscopic method often results in faster recovery.
Can you eat after removing appendix?
Yes, after removing the appendix, one can eat normally. Following surgery, there are usually no dietary restrictions.
What happens if appendix bursts?
A condition known as peritonitis results from the appendix rupturing and releasing contaminated material into the abdominal cavity. This is a medical emergency requiring rapid surgical intervention.
Can you survive a burst appendix without surgery?
Without surgery, the likelihood of someone surviving an appendicitis burst is quite low. If left untreated, peritonitis can be lethal. Antibiotics and surgical excision of the contaminated tissue are necessary for healing.
How can I check my appendicitis at home?
Attempting to diagnose appendicitis at home is not advised. The appropriate diagnosis and treatment of appendicitis are subject to qualified healthcare professionals. It is considered a medical emergency. Seek prompt medical assistance if it looks like one may have appendicitis.
Can stress cause appendicitis?
Appendicitis does not directly induce stress. Stress, however, might cause bowel patterns to alter, which could make appendicitis symptoms worse for a person who already has them. An obstruction in the appendix is the main cause of appendicitis.
Is it gas or appendicitis?
The symptoms of gas and appendicitis can sometimes overlap, making it challenging to distinguish between the two. However, appendicitis typically involves more severe and persistent pain, whereas gas pain is often cramp-like and may be relieved by passing gas. If you suspect appendicitis, it's crucial to seek medical evaluation to rule it out.
Can food habits cause appendicitis?
While dietary habits can influence gastrointestinal health, there is no direct evidence to suggest that specific foods or dietary habits directly cause appendicitis. Appendicitis is primarily caused by a blockage in the appendix.
What foods make appendicitis worse?
There are no specific foods known to make appendicitis worse. However, a diet low in fibre may contribute to gastrointestinal issues, which could potentially lead to problems like constipation or blockages. Maintaining a balanced and healthy diet is generally advisable for overall well-being.
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Oops, there was an error sending your message. Please try again later. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.

Our Locations
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated with the latest health information.
By clicking on subscribe now, you accept to receive communications from PACE Hospitals on email, SMS and Whatsapp.
Subscribe to PACE Hospitals News
Thank you for subscribing. Stay updated with the latest health information.
Oops, there was an error. Please try again submitting your details.
-

Payment in advance for treatment (Pay in Indian Rupees)
For Bank Transfer:-
Bank Name: HDFC
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.50200028705218
IFSC Code: HDFC0000545
Bank Name: STATE BANK OF INDIA
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.62206858997
IFSC Code: SBIN0020299
Scan QR Code by Any Payment App (GPay, Paytm, Phonepe, BHIM, Bank Apps, Amazon, Airtel, Truecaller, Idea, Whatsapp etc)
Call us at 04048486868
ADDRESS
PACE Hospitals
Hitech City : Beside Avasa Hotel, Pillar No. 18, Hyderabad - 500081
Madinaguda: Mythri Nagar, Beside South India Shopping, Madinaguda, Hyderabad - 500050
QUICK LINKS
Disclaimer
General information on healthcare issues is made available by PACE Hospitals through this website (www.pacehospital.com), as well as its other websites and branded social media pages. The text, videos, illustrations, photographs, quoted information, and other materials found on these websites (here by collectively referred to as "Content") are offered for informational purposes only and is neither exhaustive nor complete. Prior to forming a decision in regard to your health, consult your doctor or any another healthcare professional. PACE Hospitals does not have an obligation to update or modify the "Content" or to explain or resolve any inconsistencies therein.
The "Content" from the website of PACE Hospitals or from its branded social media pages might include any adult explicit "Content" which is deemed exclusively medical or health-related and not otherwise. Publishing material or making references to specific sources, such as to any particular therapies, goods, drugs, practises, doctors, nurses, other healthcare professionals, diagnoses or procedures is done purely for informational purposes and does not reflect any endorsement by PACE Hospitals as such.