Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) - Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Most people can manage the discomfort of GERD with lifestyle changes and over-the-counter medications. But some people with GERD may need stronger medications or surgery to ease symptoms.
What is GERD (Gastroesophageal reflux disease or chronic acid reflux)?
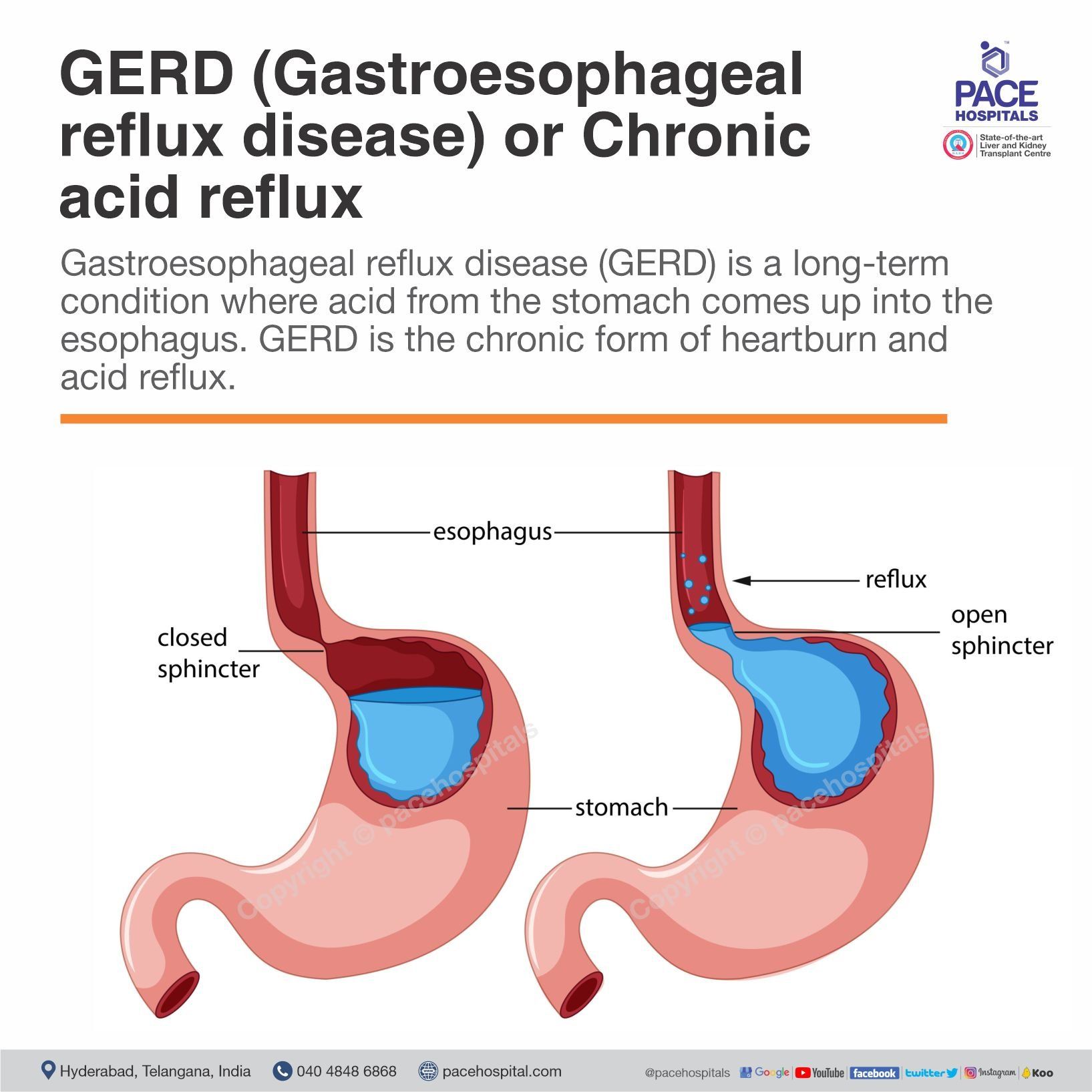
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or chronic acid reflux is a long-term condition where acid from the stomach comes up into the esophagus, a muscular tube connecting the stomach with the throat (pharynx). Flowing back up acid into the esophagus causes irritation to the esophagus lining.
GERD is the chronic form of heartburn and acid reflux. If you have symptoms of acid reflux more than twice a week, you might have a condition known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
What are the causes of GERD (Gastroesophageal reflux disease)?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or chronic acid reflux caused by frequently happening acid reflux.
Acid reflux happens when your LES doesn’t tighten or close properly. This allows digestive juices and other contents from your stomach to rise up into your esophagus.
The lower esophageal sphincter (LES) is a circular band of muscle at the end of your esophagus. When it’s working properly, it relaxes and opens when you swallow. Then it tightens and closes again afterwards.
What are the risk factors for GERD (Gastroesophageal reflux disease)?
These conditions that can increase risk of GERD:
- Bulging of the top of the stomach up into the diaphragm (hiatal hernia)
- Overweight or Obesity because of increased pressure on the abdomen
- Delayed gastric emptying
- Pregnancy
- Scleroderma or crest syndrome, a rare autoimmune disease
These risk factors can aggravate acid reflux and over the period of time it can cause GERD:
- Smoking
- Having large meals or eating late at night
- Consuming triggered food (fatty foods or fried foods)
- Going to sleep shortly after having meal
- Drinking alcohol or coffee or soda
- Taking medications without consulting doctor

What are signs and symptoms of GERD (Gastroesophageal reflux disease)?
GERD is curable disease, but most of the time people don't know they are suffering from Gastroesophageal reflux disease because its symptoms are associated with many other conditions. Common symptoms of GERD include:
- Heartburn, usually after eating, which might be worse at night
- Chest pain
- Nausea
- Bloating, gas and belching
- Certain food Intolerance
- Difficulty swallowing
- Regurgitation of food or sour liquid
- Sensation of a lump in your throat
If acid reflux occur during nighttime, one can experience:
- Disrupted sleep
- Chronic cough
- New or worsening asthma
- Laryngitis
Generally many people have acid reflux symptoms every now and then, especially after eating large meals or lying down right after a meal. If acid reflux occur at least twice per week then it can be classified as GERD (Gastroesophageal reflux disease) sometimes symptoms become moderate to severe. In case of the persistent symptoms, consult a gastroenterologist.

What are the Complications of GERD (Gastroesophageal reflux disease)?
In most people, GERD doesn’t cause serious complications. But in case of delayed diagnosis and treatment, GERD can can lead to serious or even life-threatening health problems.
- Esophageal stricture (Narrowing of the esophagus) - Damage to the lower esophagus from stomach acid causes scar tissue to form. The scar tissue narrows the food pathway, leading to problems with swallowing.
- Esophageal ulcer (An open sore in the esophagus) - Stomach acid can wear away tissue in the esophagus, causing an open sore to form. An esophageal ulcer can bleed, cause pain and make swallowing difficult.
- Barrett's esophagus (Precancerous changes to the esophagus) - Damage from acid can cause changes in the tissue lining the lower esophagus. These changes are associated with an increased risk of esophageal cancer.
- Esophageal cancer which affects a small portion of people with Barrett’s esophagus
- Asthma, chronic cough, or other breathing problems, which may develop if you breathe stomach acid into your lungs
- Dental problems - tooth enamel erosion, gum disease or other dental problems
GERD (Gastroesophageal reflux disease) Diagnosis
To confirm a diagnosis of GERD, or to check for complications gastroenterologist might use one or more of the following procedures-
- Upper GI Endoscopy: a flexible tube with a tiny camera is threaded into your esophagus to examine it and collect a sample of tissue (biopsy) if needed
- Esophageal Manometry: a flexible tube is threaded into your esophagus to measure the strength of your esophageal muscles
- Esophageal pH monitoring: a monitor is inserted into your esophagus to learn if and when stomach acid enters it
- Upper digestive system X-ray using barium swallow: after drinking a barium solution, X-ray imaging is used to examine your upper digestive tract
GERD (Gastroesophageal reflux disease) Treatment
Lifestyle changes may help reduce the frequency of acid reflux. If you've been experiencing frequent episodes of acid reflux, heartburn or any other symptoms of acid reflux, these steps will help in relieving acid reflux:
- Maintaining healthy weight. Excess weight put pressure on your abdomen, pushing up your stomach and causing acid to reflux into your esophagus.
- Quit smoking. Smoking decreases the lower esophageal sphincter's ability to function properly.
- Elevate the head of your bed. If you regularly experience heartburn while trying to sleep, place wood or cement blocks under the feet of your bed so that the head end is raised by 6 to 9 inches. If you can't elevate your bed, you can insert a wedge between your mattress and box spring to elevate your body from the waist up. Raising your head with additional pillows isn't effective.
- Don't lie down shortly after a meal. Wait at least three hours after eating before lying down or going to bed.
- Slowly Eat food and chew thoroughly. Put down your fork after every bite and pick it up again once you have chewed and swallowed that bite.
- Avoid trigger foods and drinks that cause reflux. Common triggers include fatty or fried foods, tomato sauce, alcohol, chocolate, mint, garlic, onion, and caffeine.
- Avoid tight-fit clothing. Clothes that fit tightly around your waist put pressure on your abdomen and the lower esophageal sphincter.

The gastroenterologist is likely to recommend that you first try lifestyle modifications and over-the-counter medications. If you don't experience relief within a few weeks, the Gastroenterologist might recommend prescription medication or surgery.
FAQs - Frequently Asked Questions
Is GERD a lifetime disease?
Yes, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic, usually lifelong disease that often may return if the treatment is stopped or discontinued and can progress to major complications.
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Oops, there was an error sending your message. Please try again later. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.

Our Locations
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated with the latest health information.
By clicking on subscribe now, you accept to receive communications from PACE Hospitals on email, SMS and Whatsapp.
Subscribe to PACE Hospitals News
Thank you for subscribing. Stay updated with the latest health information.
Oops, there was an error. Please try again submitting your details.
-

Payment in advance for treatment (Pay in Indian Rupees)
For Bank Transfer:-
Bank Name: HDFC
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.50200028705218
IFSC Code: HDFC0000545
Bank Name: STATE BANK OF INDIA
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.62206858997
IFSC Code: SBIN0020299
Scan QR Code by Any Payment App (GPay, Paytm, Phonepe, BHIM, Bank Apps, Amazon, Airtel, Truecaller, Idea, Whatsapp etc)
Call us at 04048486868
ADDRESS
PACE Hospitals
Hitech City : Beside Avasa Hotel, Pillar No. 18, Hyderabad - 500081
Madinaguda: Mythri Nagar, Beside South India Shopping, Madinaguda, Hyderabad - 500050
QUICK LINKS
Disclaimer
General information on healthcare issues is made available by PACE Hospitals through this website (www.pacehospital.com), as well as its other websites and branded social media pages. The text, videos, illustrations, photographs, quoted information, and other materials found on these websites (here by collectively referred to as "Content") are offered for informational purposes only and is neither exhaustive nor complete. Prior to forming a decision in regard to your health, consult your doctor or any another healthcare professional. PACE Hospitals does not have an obligation to update or modify the "Content" or to explain or resolve any inconsistencies therein.
The "Content" from the website of PACE Hospitals or from its branded social media pages might include any adult explicit "Content" which is deemed exclusively medical or health-related and not otherwise. Publishing material or making references to specific sources, such as to any particular therapies, goods, drugs, practises, doctors, nurses, other healthcare professionals, diagnoses or procedures is done purely for informational purposes and does not reflect any endorsement by PACE Hospitals as such.