NAFLD and NASH - Symptoms, Causes, Differences and Treatment
About Liver
The liver is the largest full internal organ in the body. It is located under the rib cage in the upper right part of the abdomen. Although it varies in size with age, body size and shape, sex and disease state, it is roughly the size of a soccer ball in most adults. The liver has several important functions, such as:
- Works as a blood filter
- Metabolizes nutrients and other substances such as drugs
- Stores energy
- Synthesizes proteins essential for the function of our body, such as those which advise the blood to clot when we bleed.
Although the liver is a very resilient organ that has the ability to repair itself, it is susceptible to damage from many sources including viruses, toxins, inherited conditions, and even our own immune system.
NAFLD full form - Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
What is NAFLD?
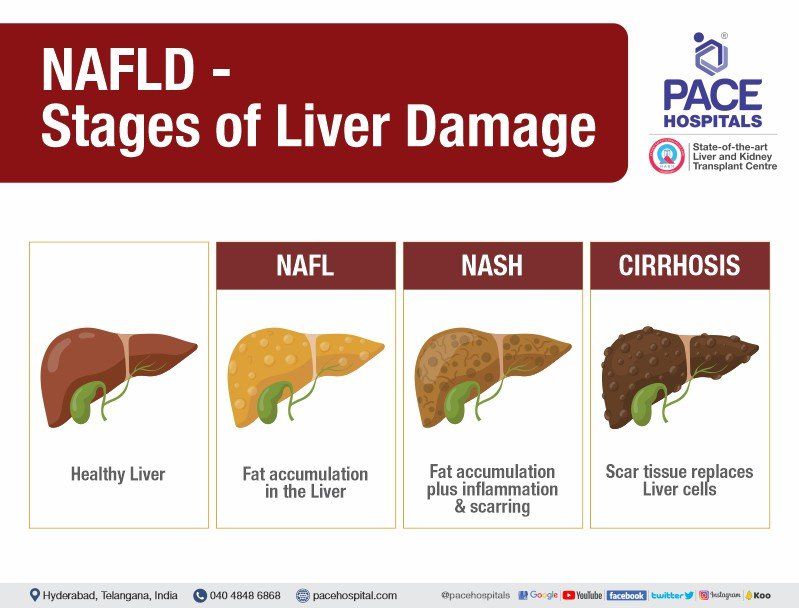
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a condition characterized by an accumulation of fat in liver cells (hepatocytes). Excess fat in the liver can lead to significant damage over the years. There are two types of NAFLD:
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL)
- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
NAFL (Non-alcoholic fatty liver) - It is a benign condition and in this fat is accumulated in the liver that can cause inflammation of liver but not a progressive damage or complications of the liver. This may result in abdominal discomfort or pain due to an enlarged liver (hepatomegaly).
NASH (Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis) – It is a malignant condition and in this fat is accumulated in the liver can cause scarring of liver, liver fibrosis and liver damage further it can cause cirrhosis of liver (also called as end-stage liver disease), further cirrhosis of the liver may lead to liver cancer.
Many people typically develop any type of NAFLD with having no symptoms; most of the time it is diagnosed by a healthcare professional or doctors by doing investigations for abnormal laboratory results or imaging test of the abdomen for unrelated problems.
In order to help people with this condition, doctor identify people those who all are at risk and offers advice on how to manage the condition before significant liver damage occurs. NAFLD is a condition that can be treated and often managed with lifestyle changes.
Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease - NAFLD causes
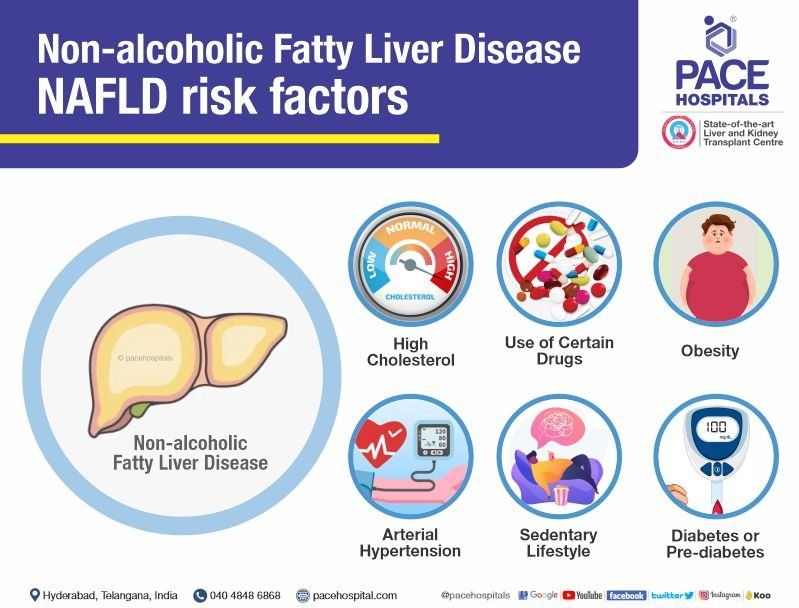
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is not a condition that can be passed on (i.e., it does not spread from person to person). In fact, it occurs most often in people who have one or more of the following risk factors:
- Obesity
- Diabetes or prediabetes
- High cholesterol
- Arterial hypertension
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Use of certain drugs
The medical researchers still do not know the exact reason why NAFLD affects some people with the conditions listed above, but not others.
It is also poorly understood why in some people fat accumulates in the liver without causing significant damage (benign steatosis), while in other people it causes significant damage (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis - NASH).
Since the prevalence of this condition is increasing in INDIA, if you have one or more of the risk factors for the disease, it may be reasonable to discuss with your Hepatologist (Liver Specialist Doctor) whether you need evaluation or not. However, there are no specific-accepted guidelines for who should be further investigated for this condition, other than those with unexplained abnormalities in liver enzymes.
Prevalence of NAFLD (Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease)
Only a few researchers took a part and studied the prevalence of NAFLD in urban-rural regions of India. From the very limited data, NAFLD prevalence in India ranges vary from 8% to 54%. As per the studies urban population reported higher prevalence than the rural population. Due to very limited data and different regions, it is very difficult to define prevalence of NAFLD in India.
Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease - NAFLD Symptoms
Many people with NAFLD do not have any symptoms, but in those who do, these are usually non-specific such as:
- Mild fatigue
- Discomfort or pain in upper right abdomen
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis – NASH Symptoms
Over the years, the presence of fat can trigger inflammation of the liver, which can lead to the formation of scar tissue. In an advanced state, the amount of scar tissue in the liver can reach a level called cirrhosis of the liver, which refers to the precise appearance of the scar tissue, liver fibrosis and its degree. In patients with NASH and cirrhosis of the liver can eventually lead to the appearance of signs and symptoms such as:
- Increased fatigue
- Buildup of fluid in the abdomen (ascites)
- Confusion (encephalopathy)
- A decreased or loss of appetite
- Bleeding easily or bruising (Ecchymosis)
- Nausea (an uneasiness of the stomach)
- Edema (Swelling in your feet, ankles or feet)
- Unexplained weight loss
- Yellow discoloration in the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Esophageal varices - enlarged or swollen veins in the esophagus that can cause vomiting of blood, bloody or black tar-like stool
The goal of screening for NAFLD is to ensure adequate surveillance, offer treatment advice and decrease the chances of complications such as cryptogenic cirrhosis, hepatic transaminases, and cryptogenic hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC - common type of primary liver cancer).
Difference between NAFLD and NASH | NAFLD vs NASH
Non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) and Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) are are types of Non alcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD, indicated by the deposition of fats in liver and can be differentiated based on the damage done to the liver.
| NAFL (Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver) | NASH (Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis) |
|---|---|
| Non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) is type of NAFLD, happens due to accumulation of fats in liver. | Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a severe form of NAFLD, associated with high level of fats accumulation in liver accompanied by Hepatitis infection. |
| Non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) is also known as simple fatty liver, and usually it is reversible. | Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) can be reversed but depends on its progression. |
| Non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) doesn't cause inflammation and liver cell damage. | Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) causes inflammation and liver cell damage due to hepatitis infection, which can lead to liver scarring (fibrosis). |
| Non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) is not progressive in nature, does not lead to any severe complication. | Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) can possibly lead to severe complications like Fibrosis, cirrhosis, liver cancer, liver failure. |
| Non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) can be treated by losing 3-5% of body weight. | Inflammations of liver due to Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) can be reduced by losing 7-10% of body weight. |
Risk Factors of NAFLD - Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
There are many health conditions that can increase risk of NAFLD / NASH that includes:
- Abdominal obesity (excessive fat around the abdomen & stomach)
- Sleep apnea (breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep)
- Metabolic syndrome (high blood sugar, high blood pressure, excess body fat around the waist and abnormal cholesterol levels)
- High levels of cholesterol or triglycerides in the blood
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Type 2 diabetes
- Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid)
- Hypopituitarism (deficiency of the pituitary hormones)
People those who are having any of the above-mentioned risk factors should go for liver function tests once in a year. To differentiate between NAFL and NASH, doctors may advise blood test, imaging tests and / or liver biopsy.
Complication of NAFLD - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
NAFLD complications depends upon its type of condition, such as:
- In NAFL (Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver) people don’t develop any complications of liver
- In NASH (Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis) people may develop complications of liver that includes end-stage liver disease (ESLD), cirrhosis of the liver, hepatic encephalopathy, liver fibrosis, ascites, esophageal varices and liver cancer.
People with NAFLD are at higher risk of developing certain health condition, such as:
- Type 2 diabetes
- Cardiovascular disease (CVD) - affecting the blood vessels or heart
- Metabolic syndrome (high blood sugar, high blood pressure, excess body fat around the waist and abnormal cholesterol levels)
Diagnosis of NAFLD and NASH
Initial stage it’s difficult to find out the NAFLD and NASH because of no symptoms. Usually, many patients fortuitously reported with liver problem while doing medical tests for other disease, medical ailments or conditions.
Doctors may advise some of these tests to identify severity of NAFLD / NASH.
Blood Tests: Doctors may advise these blood tests to identify NAFLD / NASH:
- CBP (Complete blood picture)
- Liver function tests
- Viral load tests and Genotype test for chronic viral hepatitis
- Genetic & Serology testing for celiac disease
- Hemoglobin A1C (HbA1c) test
- Lipid profile (for cholesterol and triglycerides levels)
- FibroTest and APRI (AST-to-Platelet Ratio Index)
Diagnostic imaging procedures:
- Abdominal Ultrasound
- Computerized tomography (CT) scan or Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Transient elastography (FibroScan)
Liver biopsy: It’s a type of liver tissue examination procedure in which a needle is used to remove a small piece of liver tissue for examination under a microscope, is the gold standard for diagnosing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Although currently the only way to confirm a diagnosis, in practice a combination of blood tests and imaging is usually sufficient to make the diagnosis in more than one patient.
The role of liver biopsy in the diagnosis of NAFLD, mainly NASH remains important in some circumstances, especially if the diagnosis is questionable. In addition, the biopsy can determine if there is scar tissue in the liver and its extent, if so.
Quantification is the process of determining the amount of scar tissue (fibrosis) in the liver; in the past, a liver biopsy was the only technique used. Normal tissue without scarring is found at stage 0. An increasing amount of scar tissue in the liver in combination with a change in its appearance increases the classification at a higher stage.
- Stage 1 is represented by a minimal amount of scar tissue
- Stage 4 refers to cirrhosis.
Although a biopsy is a safe procedure, it is invasive and therefore carries risks, including bleeding and pain after the procedure. Other than its invasive nature, one of the disadvantages of this procedure is that it only takes a sample from a very small section of a large organ and is therefore susceptible to sampling error.
Investigations
When a person is diagnosed with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, it is important that they see a hepatologist doctor who has specialized knowledge in this area. It could be a nurse, a family doctor or a specialist (hepatologist or gastroenterologist doctor) who will undertake the initial investigations to ensure that the diagnosis is certain and to rule out other liver diseases that may coexist. Much of this information can be obtained from a physical examination, blood test, imaging of the abdomen and Liver tissue examination.
Non-invasive procedures for liver fibrosis
- Liver biopsy remains the gold standard for quantifying liver disease and is still a good option for many patients. However, health care providers are increasingly using other effective tools to determine the degree of fibrosis in the liver.
- FibroScan is a non-invasive technique used to assess the degree of fibrosis in the liver. This is a technique used to measure liver elasticity which is closely related to the degree of fibrosis in the liver. A probe is placed on the surface of the skin without causing pain, all of which is completed in a few minutes. The section sampled is approximately 100 times larger than that of a typical liver biopsy. This procedure gives a reliable reading in most people.
- FibroTest and APRI (AST-to-Platelet Ratio Index) are non-invasive technique that use calculations based on blood tests to measure the degree of fibrosis in the liver. FibroTest is likely not covered by health insurance plans and will therefore incur personal expenses. APRI is derived from the calculation of a simple equation based on common blood tests.
Regardless of the technique used to estimate the degree of fibrosis, expert interpretation is essential to ensure that the information obtained is useful in making treatment decisions. In addition, a liver biopsy can still provide valuable information regarding disease activity, which non-invasive tools could not.
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease - NAFLD treatment
Doctors may advise patients with NAFLD to lose weight by following healthy diet, regular exercise and lifestyle as a 1st line of NAFLD treatment. People who are successful in losing weight equivalent to 3-10% of their total body weight by increasing their activity level and improving their diet are also successful in improving their liver enzymes and reducing the amount of fat accumulated in the liver.
Not all people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) will be at risk for developing active liver disease. However, since the management of this condition emphasizes a healthy lifestyle, it may also reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
- Alcohol: Heavy alcohol consumption is a known risk factor for the accumulation of fat in the liver. More than two drinks per day are generally considered heavy consumption. For a person with established NAFLD, limit ingestion to a maximum of two drinks per day (one drink is 148 mL of wine, 44 mL of spirits or 355 mL of beer) without consuming alcohol every day is a reasonable goal. In fact, complete abstinence from alcohol would be preferable.
- Other medical conditions: As already mentioned, other medical conditions such as high cholesterol, diabetes and high blood pressure increase the risk of developing NAFLD and may make it worse if it is already present. Optimal control of these risk factors is therefore essential for the management of NAFLD. Medicines typically used to treat these risk factors can usually be used safely by people with liver disease; patients should discuss this further with their health care provider.
- Medicines: As per the studies, many drugs, vitamins and supplements for beneficial effects that would be helpful in the management of NAFLD. Unfortunately, to date, no evidence has been found to support their universal and widespread use in people with this condition.
- Diet and lifestyle changes: Although research continues to find drugs that are suitable for widespread use in the management of NAFLD, many well-designed trials have shown that lifestyle changes (exercise and diet) that lead to weight loss are effective in the management of this disease.
The current Medical Society recommend that adults 18 to 64 years of age get at least 150 minutes of moderate to vigorous aerobic physical activity per week in sessions of at least 10 minutes, to achieve health benefits. This is also a reasonable goal for people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease who are not already physically active at this level.
Limiting the consumption of foods high in fat and sugar, limiting portion sizes, and eating regular, balanced meals. Following the advice of a personal trainer or dietitian can also help you reach your goals.
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis - NASH treatment
Although nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is mild, if left untreated it can lead to a much more serious disease state, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which involves inflammation of the liver, scarring of the liver, liver fibrosis, cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer.
Liver fibrosis can cause advanced scarring (cirrhosis) or cancer of the liver. About 20% of people diagnosed with NASH will develop cirrhosis, a serious problem that can cause many complications. In this condition, patients may require liver transplantations.
The future of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) lies in raising awareness; it will allow hepatologist to determine which people have this condition in order to treat them.
Lifestyle modifications to reverse NAFLD
People with Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) can these steps to control and reverse it that includes:
- Healthy diet – Follow a healthy diet consist of whole grains, fruits, and leafy vegetables, especially rich in vitamin E.
- Weight loss
- Regular exercise and staying active
- Controlling diabetes
- Lower down the cholesterol
- Preventing liver damage
Request an appointment, in case of having any symptoms of NAFLD or Fatty Liver Disease
NAFLD / Fatty Liver Appointment
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 7842171717
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Oops, there was an error sending your message.
Please try again later. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 7842171717
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to reduce NAFLD?
NAFLD can be reducded by knowing the reason of NAFLD like diabetes, obesity, dislipidimia, thyroid dysfunction or patients with hepatitis c, any cause which is found out if treated the NAFLD can be reduced.
Can NAFLD be reversed?
Yes, NAFLD can be reversed.
Is NAFLD curable?
NAFLD is curable with proper evaluation and treatment in time.
Is NAFLD fatal?
NAFLD is not fatal but if we don't diagnose and treat in time can lead to NASH and ultimately Cirrhosis of the liver and complication of it can lead to liver cancer.
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Oops, there was an error sending your message. Please try again later. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.

Our Locations
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated with the latest health information.
By clicking on subscribe now, you accept to receive communications from PACE Hospitals on email, SMS and Whatsapp.
Subscribe to PACE Hospitals News
Thank you for subscribing. Stay updated with the latest health information.
Oops, there was an error. Please try again submitting your details.
-

Payment in advance for treatment (Pay in Indian Rupees)
For Bank Transfer:-
Bank Name: HDFC
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.50200028705218
IFSC Code: HDFC0000545
Bank Name: STATE BANK OF INDIA
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.62206858997
IFSC Code: SBIN0020299
Scan QR Code by Any Payment App (GPay, Paytm, Phonepe, BHIM, Bank Apps, Amazon, Airtel, Truecaller, Idea, Whatsapp etc)
Call us at 04048486868
ADDRESS
PACE Hospitals
Hitech City : Beside Avasa Hotel, Pillar No. 18, Hyderabad - 500081
Madinaguda: Mythri Nagar, Beside South India Shopping, Madinaguda, Hyderabad - 500050
QUICK LINKS
Disclaimer
General information on healthcare issues is made available by PACE Hospitals through this website (www.pacehospital.com), as well as its other websites and branded social media pages. The text, videos, illustrations, photographs, quoted information, and other materials found on these websites (here by collectively referred to as "Content") are offered for informational purposes only and is neither exhaustive nor complete. Prior to forming a decision in regard to your health, consult your doctor or any another healthcare professional. PACE Hospitals does not have an obligation to update or modify the "Content" or to explain or resolve any inconsistencies therein.
The "Content" from the website of PACE Hospitals or from its branded social media pages might include any adult explicit "Content" which is deemed exclusively medical or health-related and not otherwise. Publishing material or making references to specific sources, such as to any particular therapies, goods, drugs, practises, doctors, nurses, other healthcare professionals, diagnoses or procedures is done purely for informational purposes and does not reflect any endorsement by PACE Hospitals as such.