![]()
Silicon is the second most abundant element on Earth, and it plays a crucial role in the electrical industry. It is a versatile material with unique properties that make it suitable for various applications, from solar panels and microelectronics to insulators and more.
Table of Contents
Silicon as a Semiconductor
![]()
Semiconductors are materials that have electrical conductivity properties between those of conductors (e.g., metals) and insulators (e.g., glass). Silicon is an excellent semiconductor material due to its unique properties.
Intrinsic Silicon
In its pure form, silicon has a crystalline structure with four valence electrons, which allows it to form covalent bonds with other silicon atoms. Intrinsic silicon has a moderate level of electrical conductivity that can be significantly increased by introducing impurities.
Doped Silicon
Doping is the process of adding impurities to intrinsic silicon to enhance its electrical conductivity. There are two types of doped silicon: n-type and p-type. N-type silicon is doped with elements that have five valence electrons, while p-type silicon is doped with elements with three valence electrons. The combination of these two types of silicon creates a p-n junction, which is the basis of many semiconductor devices, such as diodes and transistors.
Silicon Wafers
![]()
Silicon wafers are thin slices of crystalline silicon used in the fabrication of integrated circuits, solar cells, and other electronic devices. The manufacturing process of silicon wafers includes growing a single-crystal silicon ingot, slicing it into thin wafers, and polishing them to achieve a smooth surface.
Applications
Silicon wafers are used in various applications, such as:
- Integrated circuits
- Solar cells
- Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS)
- Power electronics
Composite Insulators
![]()
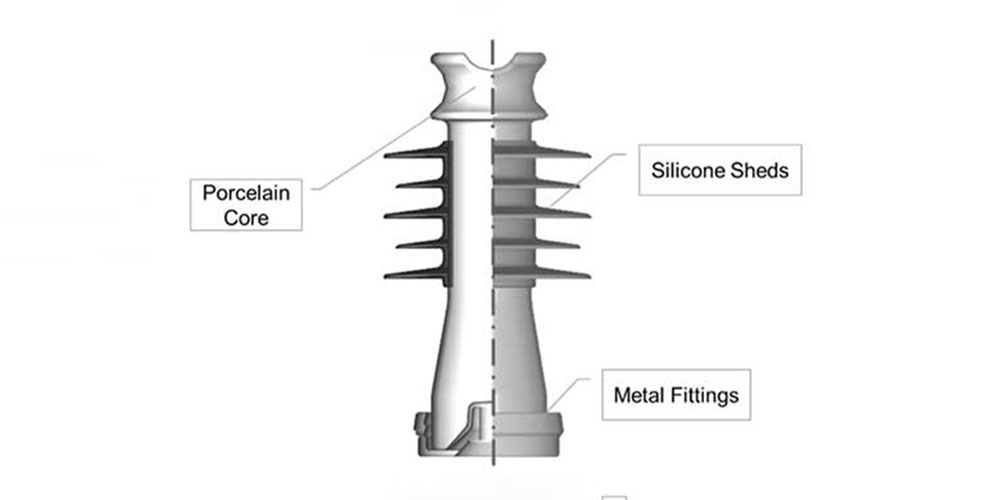
Insulators are essential components in electrical systems, as they prevent electrical current from flowing where it’s not desired. Traditional insulators, such as porcelain or glass, have certain limitations in terms of weight, durability, and maintenance.
Silicone Rubber Insulators
Composite insulators are a modern alternative to traditional insulators, offering several advantages. These insulators consist of a fiberglass core, silicone rubber housing, and end fittings. Silicone rubber provides excellent electrical insulation and resistance to environmental factors, such as UV radiation and pollution.
Advantages of Composite Insulators
Composite insulators offer numerous benefits over traditional insulators, including:
Durability and Reliability
- Long service life
- Resistance to environmental factors, such as pollution and UV radiation
- Excellent hydrophobic properties
Lightweight and Easy Installation
- Reduced weight compared to traditional insulators
- Easier handling and installation
- Lower transportation costs
Cost-effectiveness
- Lower maintenance requirements
- Reduced replacement costs
- Enhanced performance and efficiency
Powertelcom: A Leading Manufacturer of Composite Insulators
Powertelcom is a professional manufacturer of composite insulators, offering high-quality products that meet stringent industry standards. By choosing Powertelcom as your wholesale supplier, you can enjoy the following benefits:
- Premium quality composite insulators with proven performance
- Competitive pricing for cost-effective solutions
- Expert technical support and customer service
- Customizable product offerings to meet specific requirements
Trust Powertelcom for your composite insulator needs and experience the advantages of partnering with a leading manufacturer in the industry.
FAQs
Is silicon a conductor or an insulator?
Silicon is neither a conductor nor an insulator; it is a semiconductor. This means that its electrical conductivity lies between that of conductors and insulators, and can be modified by adding impurities through a process called doping.
How does temperature affect the electrical conductivity of silicon?
As the temperature increases, the electrical conductivity of silicon also increases. This is because the increased thermal energy causes more electrons to be excited from the valence band to the conduction band, resulting in a higher number of charge carriers available for conduction.
Why is silicon preferred over other semiconductors in the electronics industry?
Silicon is preferred due to its abundance, stability, and unique electrical properties. It forms a native oxide layer (silicon dioxide) on its surface, which provides excellent insulation and protection against contamination, making it ideal for manufacturing integrated circuits and other electronic devices.
What are some common applications of silicon in the electronics industry?
Silicon is used in various applications, such as the manufacturing of integrated circuits, transistors, diodes, solar cells, and power electronics.
How are silicon wafers used in the electrical industry?
Silicon wafers are thin slices of crystalline silicon used in the fabrication of integrated circuits, solar cells, microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), and power electronics.
What are the advantages of composite insulators over traditional insulators?
Composite insulators offer numerous benefits, including enhanced durability and reliability, lightweight construction for easier handling and installation, and cost-effectiveness due to reduced maintenance and replacement costs.