Key Takeaways
- A management IP address is an IP address type.
- Network administrators can access, manage, and monitor these devices remotely.
- Management IP offers benefits like remote access and more security when implemented in growing server environments.
- Management IP operates through dedicated interfaces or ports on the device.
- It separates management traffic from regular network data for security and efficiency.
- Dedicated servers improve IP management through stability, scalability, security, etc.
Efficient management of IP addresses is a key goal that all businesses today aim to meet. Why does it matter so much? One of the main reasons behind this is that it helps businesses to maintain smooth network operations. Network downtime incidents can occur due to issues like IP address conflicts and mismanagement without efficient management of IP practices.
This blog will help readers understand the concept of a Management IP Address. It will also review its benefits in growing server environments and how it works through various interfaces.
Let’s Begin!
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is a Management IP Address?
- Benefits of Management IP in Growing Server Environments
- How does Management IP Work?
- Management Interface
- Configuring a Management IP Address
- Setting Proposed Management IP
- Changing Current Management IP
- Enable IP Access Management
- Disable IP Access Management
- Management IP and Dedicated Servers
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is a Management IP Address?
Credits: FreePik
A management IP address is a specific IP address assigned to network devices like switches, routers, servers, firewalls, and other network hardware. It allows network administrators to access, manage, and monitor these devices remotely.
This address is used exclusively for administrative purposes. It offers a dedicated pathway for tasks like configuration changes, software updates, troubleshooting, and network monitoring, distinct from the device’s normal operational data traffic.
The management IP address facilitates secure and convenient remote access to the device’s management interface. It often achieves this through various protocols. Examples include SSH (Secure Shell), Telnet, or SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) for monitoring.
It’s usually configured on a separate, dedicated VLAN or network segment to isolate management traffic from regular user traffic. This boosts security by reducing the risk of unauthorized access to critical network infrastructure.
Also Read: Learn About IP Addressing Schemes And Subnet Masks.
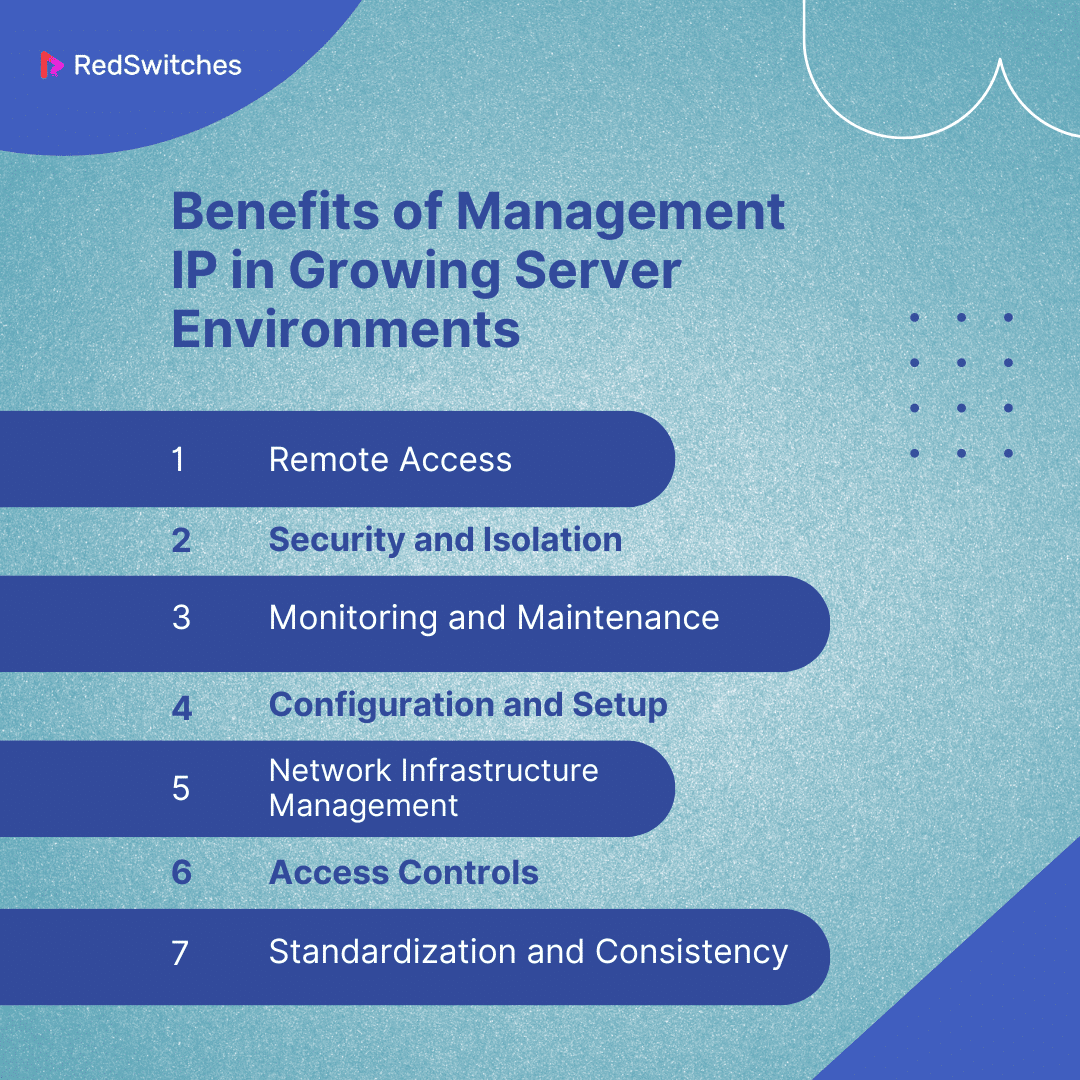
Benefits of Management IP in Growing Server Environments
Implementing management IP in growing server environments can offer numerous benefits to businesses. Here are a few of them:
Remote Access
The management IP address enables network administrators to perform remote operations effectively. Examples include firmware upgrades, system reboots, or modifying network configurations. This remote accessibility is even more important in large-scale or geographically dispersed networks, where physical access to devices can be impractical.
Security and Isolation
Organizations protect their critical network infrastructure from threats and vulnerabilities associated with regular internet traffic by isolating management traffic. This isolation also aids in the clear distinction of network traffic. It makes security monitoring and incident response easier. Using dedicated management VLANs or networks reduces the risk of management interfaces being exposed to unauthorized users on the public internet.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Advanced monitoring tools use the management IP address for real-time performance monitoring and alerting. This enables proactive identification and resolution of issues before they impact network users. This includes using threshold-based alerts for performance metrics, automated diagnostic tests, and detailed logging of all access and changes made through the management IP.
Configuration and Setup
The management IP address is also important during the initial bootstrapping process of network devices. It allows for zero-touch provisioning in some cases. This facilitates the deployment of standardized configurations across multiple devices. It also reduces manual configuration errors and ensures compliance with organizational policies.
Network Infrastructure Management
Credits: FreePik
Management IP addresses integrate with centralized network management systems (NMS). This offers a unified view of the network’s health, configuration status, and performance metrics. This integration also supports advanced features. Examples include configuration backups, batch updates, and network topology mapping. It enhances the efficiency of network operations.
Access Controls
Robust authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) mechanisms are often implemented with management IP access. It ensures that only authenticated users can perform authorized actions, with all activities logged for audit purposes. This may include integration with centralized identity management solutions, and multi-factor authentication to secure management access further.
Standardization and Consistency
A well-thought-out IP address management (IPAM) strategy includes policies for allocating, tracking, and documenting management IP addresses. This ensures that every device is reachable and manageable according to the organizational standards, simplifying operations and reducing the chances of IP conflicts or misconfigurations.
Following IP address lookup and allocation best practices can help ensure no downtime due to IP address allocation-related issues. Read our blog, ‘IP Address Lookup And Allocation Best Practices,’ to enhance your IP address lookup and allocation practices.
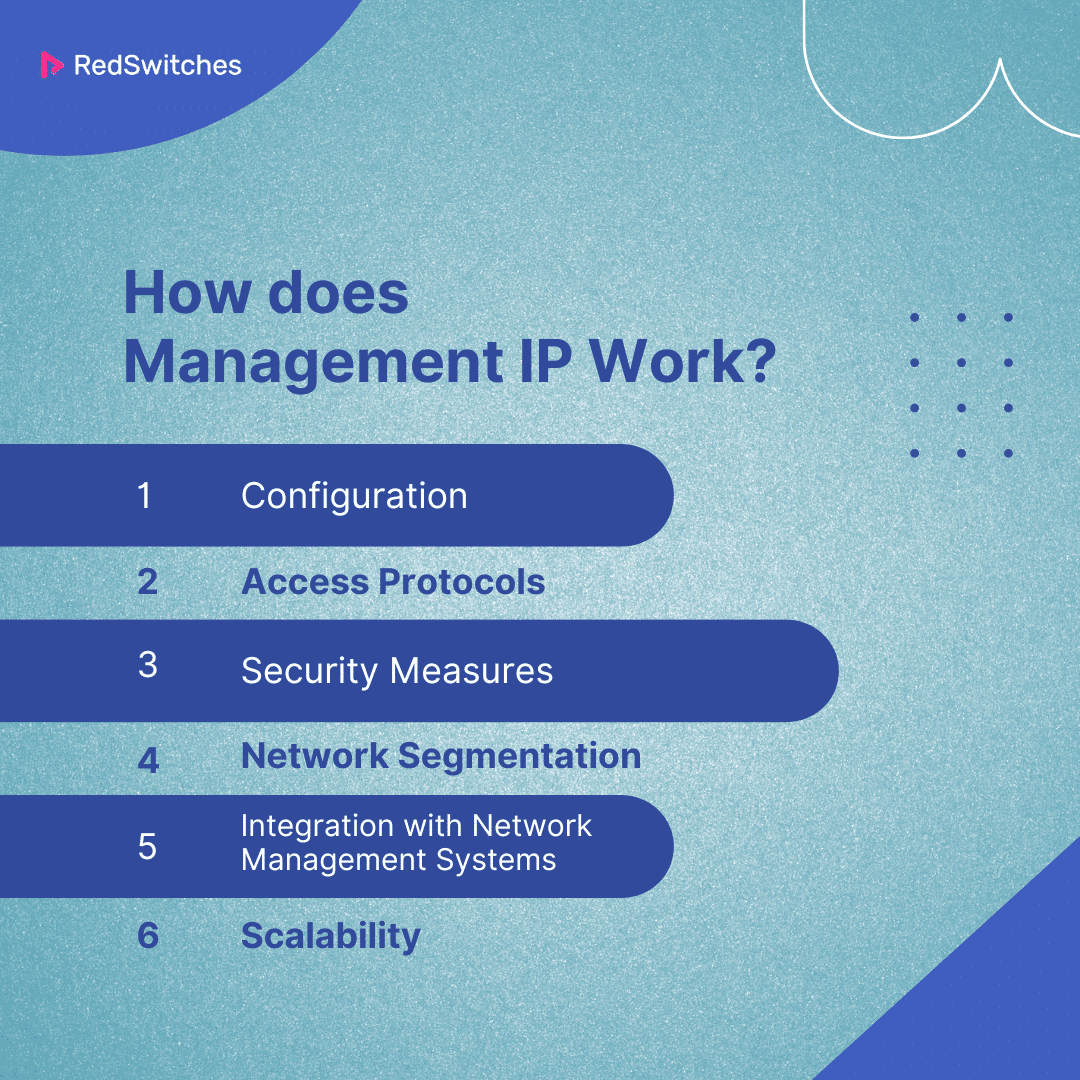
How does Management IP Work?
Understanding how management IP works involves exploring its operational framework, from configuration and access protocols to security measures and integration with network management systems.
Configuration
A management IP address is assigned to a network device’s management interface, a dedicated hardware or software interface used only for administration. A network administrator can do this assignment manually or automatically through the DHCP reserved for management interfaces. The management interface is configured to be accessible over the network, enabling remote connections to the device.
Access Protocols
Administrators use various network protocols that facilitate secure and efficient management tasks to access a device using its management IP address. The most common protocols include:
- SSH (Secure Shell)
Administrators can securely log into a device remotely and execute configuration commands, ensuring secure command-line access.
- HTTP/HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol/Secure)
Administrators can use a web browser to configure and manage the device through graphical user interfaces (GUIs) for web-based management interfaces.
- SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
For monitoring and managing network devices, SNMP helps gather detailed information about a device’s performance, utilization, and errors. It can also be used to make configuration changes.
Security Measures
Management IP addresses are secured through various measures to ensure that only authorized personnel can access the network management interfaces:
- Access Control Lists (ACLs)
Specify which IP addresses or networks can access the management interface. This effectively blocks unauthorized attempts.
- VPN (Virtual Private Network)
Ensures remote management connections are made over a secure, encrypted tunnel. This protects the data exchanged between the administrator and the device.
- Firewalls
Credits: FreePik
Can be configured to restrict access to management interfaces to specific ports and protocols. It reduces the surface area for potential attacks.
Network Segmentation
Management IP addresses are often placed on a separate, dedicated VLAN or network segment known as a management VLAN. This logical separation ensures that management traffic is isolated from regular user data traffic. It lowers the risk of interference or eavesdropping.
Integration with Network Management Systems
Management IP addresses are integral to network management systems (NMS). These systems use management IP addresses to communicate with devices for various purposes. Examples include:
- Configuration Management
Automating the deployment of configuration changes across multiple devices. This ensures consistency and compliance with policies.
- Performance Monitoring
Monitor device performance metrics (like bandwidth utilization, packet loss, and latency) to detect and resolve issues quickly.
- Inventory Management
Keeping an up-to-date inventory of all network devices. This includes their management IP addresses, hardware and software versions, and configuration status.
Scalability
Management IP addresses allow networks to scale efficiently. New devices are added to the network and assigned management IP addresses. This helps smoothly integrate them into the existing management framework. This scalability ensures that networks can grow in size and complexity without affecting performance.
Also Read: How To Assign Floating IP In Leaseweb With Your Subnet In New Ways.
Management Interface
Management interfaces on network devices provide different methods for administrators to access and manage these devices. Each interface type serves a unique purpose and is used in different scenarios. Here’s an overview of each:
Console Port
- Purpose
The console port is a physical interface providing out-of-band device access. It is mainly used for initial setup or troubleshooting when the device is inaccessible over the network.
- Connection
Usually uses an RJ-45 or RS-232 serial connection to a computer or terminal.
- Usage
Used for direct, local access to the device’s command-line interface (CLI) without network connectivity. It’s essential for recovery procedures, firmware updates, or configuration changes when network access is unavailable.
Mini USB Port
Credits: FreePik
- Purpose
Similar to the traditional console port, the mini USB port provides out-of-band access through a USB interface. This offers a modern alternative for supporting devices.
- Connection
Uses a mini USB cable to connect to a computer’s USB port, emulating a serial connection.
- Usage
Allows direct device management via CLI, instrumental in environments where USB connections are more common than serial ports on modern laptops and computers.
Ethernet Management Port
Credits: FreePik
- Purpose
The Ethernet management port is a dedicated network interface for in-band management. It allows remote access to the device’s management functions.
- Connection
Connects to the management network using standard Ethernet cabling.
- Usage
Used for remote network access to the device for tasks like monitoring, configuration, and management. It is usually isolated in a separate VLAN for security.
Service Interface
- Purpose
Service interfaces are used for specific functions such as device stacking, inter-device communication, or maintenance services.
- Connection
This can vary widely depending on the device and specific function. It ranges from Ethernet to proprietary connectors.
- Usage
These interfaces are not typically used for general network management. They are reserved for specialized services. This includes:
- Connecting to a cluster of devices.
- Accessing a storage network.
- Connecting to a dedicated diagnostics system.
Configuring a Management IP Address
Configuring a management IP address involves assigning an IP address to a network device for management purposes. This configuration enables network administrators to access, manage, and monitor the device remotely. The process varies depending on whether the IP address is configured on an Ethernet management port or a service interface.
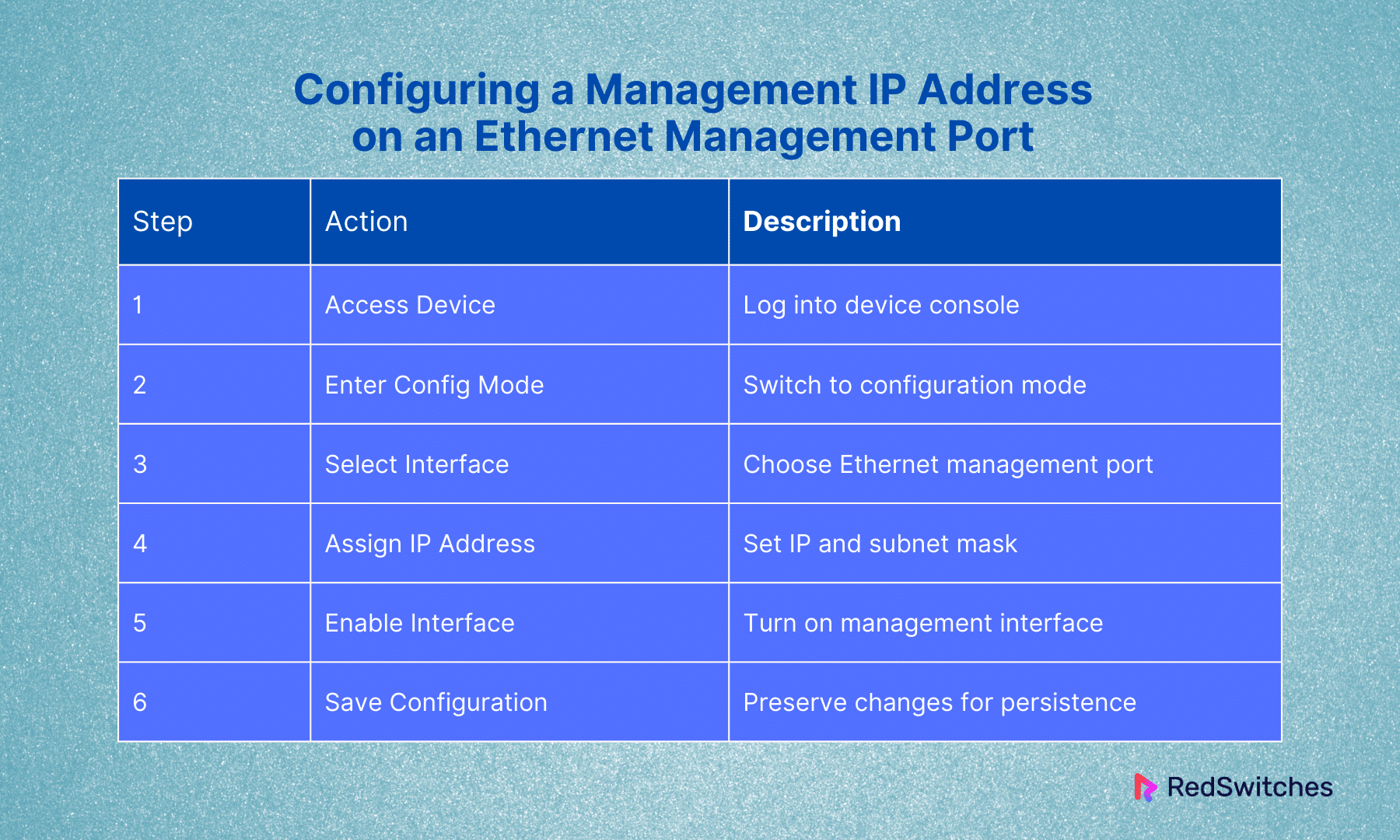
Configuring a Management IP Address on an Ethernet Management Port
Ethernet management ports are dedicated ports on a device intended only for management traffic. They are separate from the ports that handle regular network traffic. To configure a management IP on such a port:
- Access the Device: Log in to the device’s console through a direct console connection or remotely via SSH or Telnet. This variation depends on the device’s current setup and capabilities.
- Enter Configuration Mode: Access the device’s configuration mode. This often involves a command like configuring the terminal on Cisco devices.
- Select the Management Interface: Spot and choose the management interface. The command might look like interface management 0 or interface gigabitEthernet 0 depending on the device model.
- Assign the IP Address: Assign an IP address and subnet mask to the interface using a command similar to ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0.
- Enable the Interface: Ensure the management interface is activated, often with a command like no shutdown.
- Save Configuration: Save the changes to the device’s configuration to ensure they persist after a reboot. Use a command like write memory or copy running-config startup-config.
Also Read: Evolving Internet Protocols: IPV4 Vs IPV6 Compared.
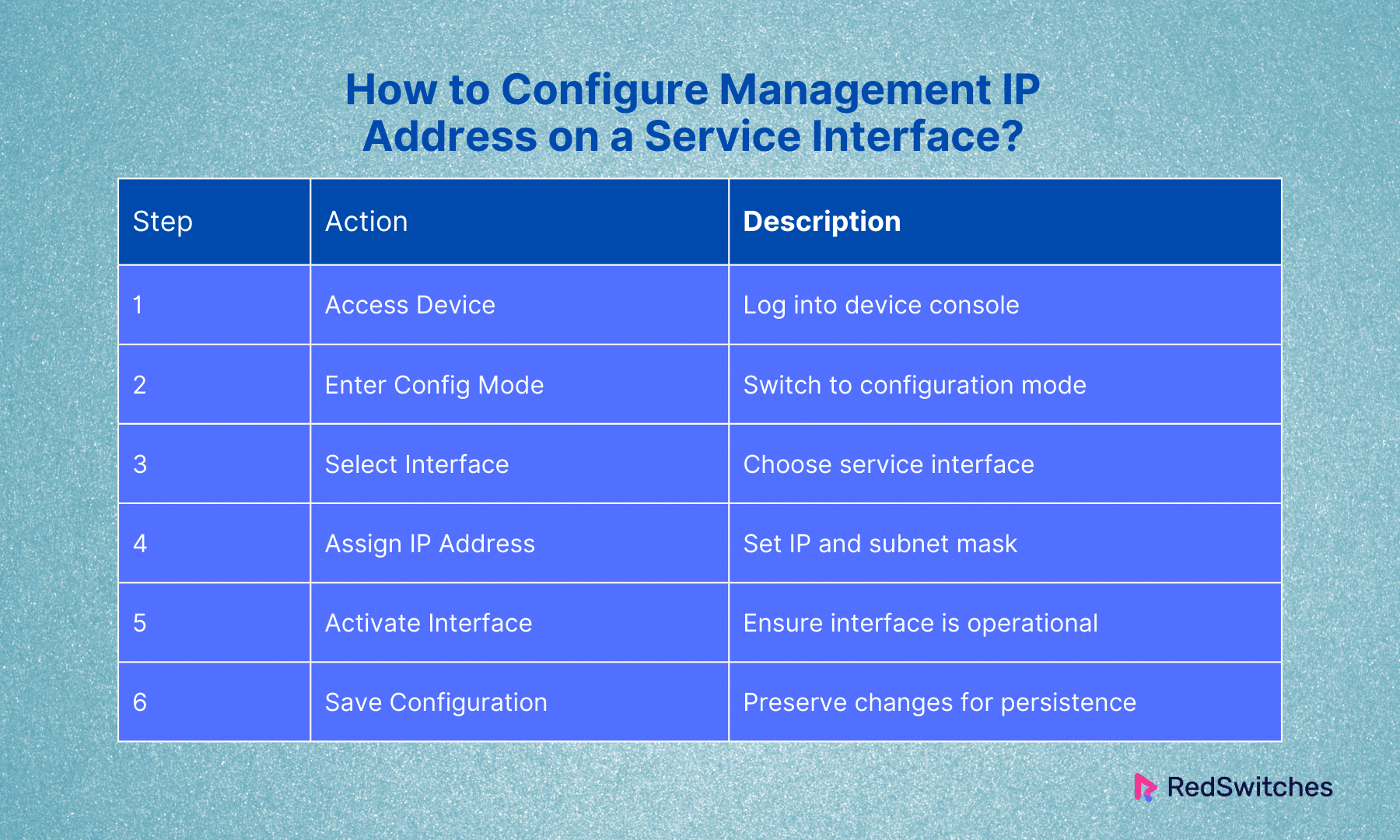
How to Configure Management IP Address on a Service Interface?
Service interfaces are logical interfaces on a device that can be used for various services, including management. These might share physical hardware with regular traffic interfaces but are logically distinct.
Access the Device
Start by accessing the device.
Enter Configuration Mode
Access the configuration mode of the device.
Select the Service Interface
Choose the logical service interface you want for management. Examples include a VLAN interface or another virtual interface.
Assign the IP Address
Provide the interface with an IP address and subnet mask.
Activate the Interface
Ensure the interface is up and running.
Save Configuration
Save your changes to make sure they are applied.
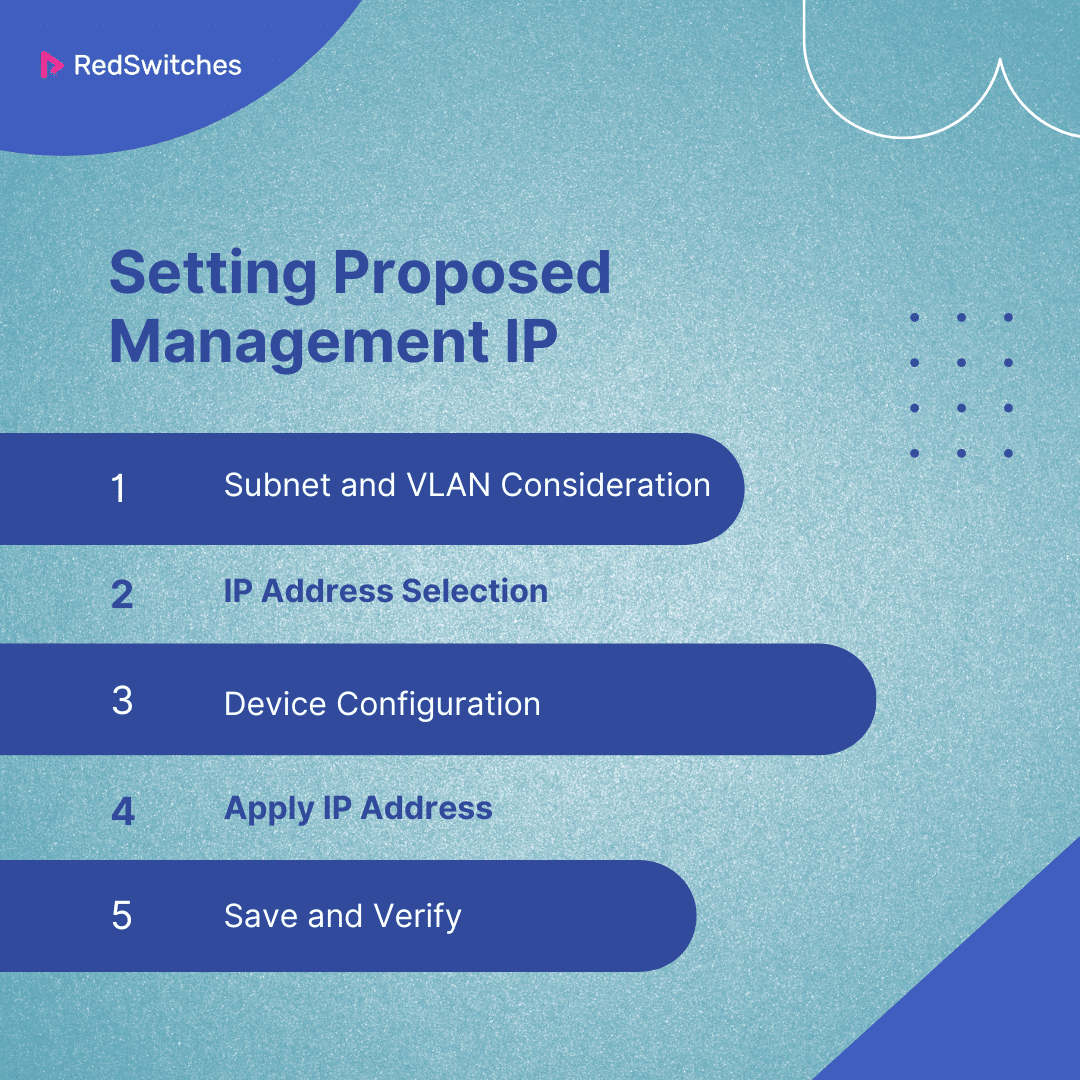
Setting Proposed Management IP
Setting a proposed management IP address for a device involves selecting an IP address within the designated management subnet or VLAN and ensuring it does not conflict with existing IP addresses within the network. This task usually includes:
Subnet and VLAN Consideration
Identify the management VLAN or subnet to which the device will be connected. This subnet is often isolated from the operational network to enhance security.
IP Address Selection
Choose an available IP address within the management subnet. It’s essential to avoid IP addresses already in use or reserved for other purposes.
Device Configuration
Access the device’s management interface, a command-line interface (CLI), or a web-based GUI, and navigate to the network settings.
Apply IP Address
Enter the chosen IP address and other necessary network information, such as subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS settings, into the device’s network configuration.
Save and Verify
Save the configuration changes and verify the device is accessible via the new management IP address. This might involve pinging the device from another system on the management network.
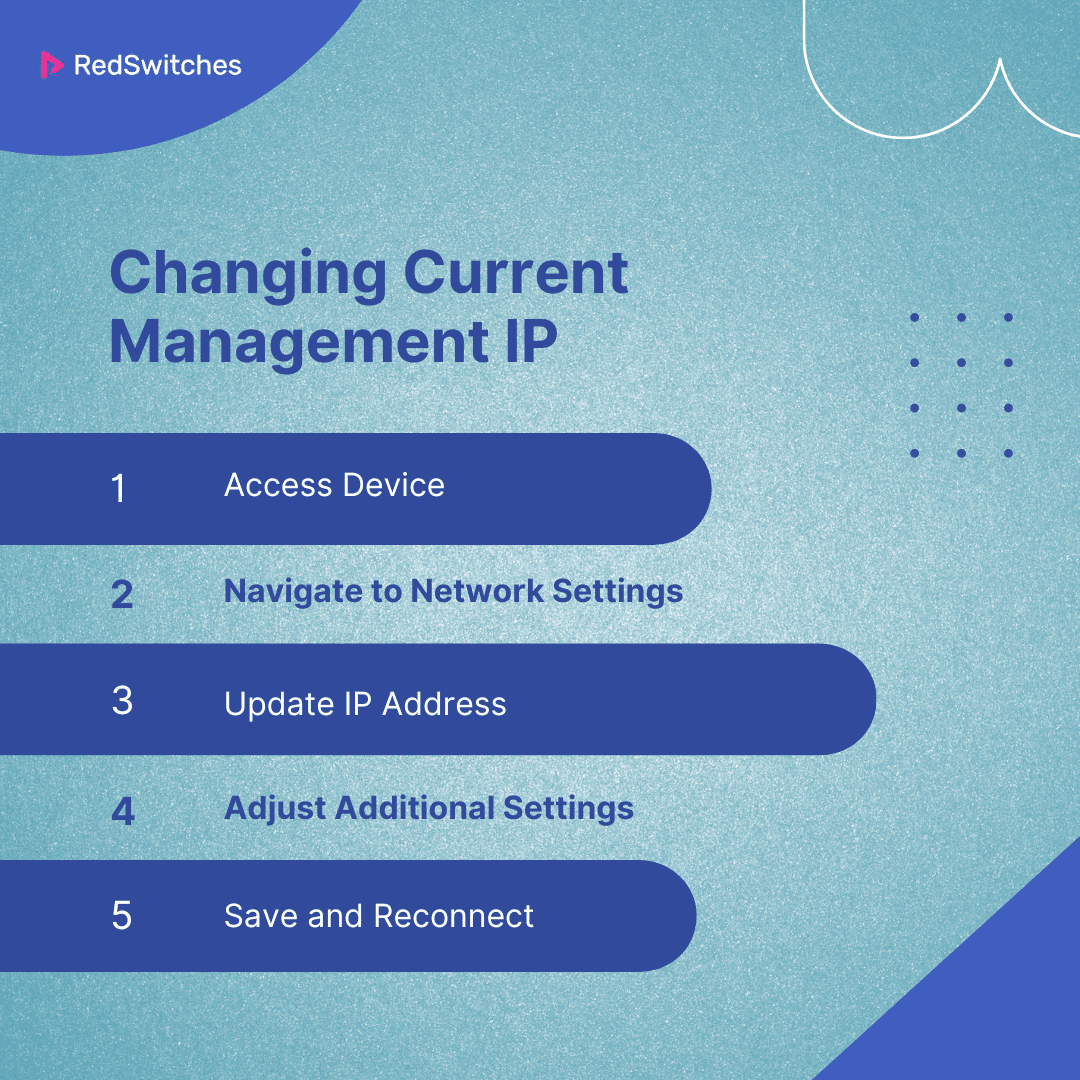
Changing Current Management IP
Changing a device’s current management IP address involves changing the existing network settings to replace the old IP address with a new one. This process is generally required when network reconfigurations occur or to resolve IP conflicts. Steps include:
Access Device
Log into the device using the current management IP address through a secure method like SSH for CLI access or a web browser for GUI access.
Navigate to Network Settings
Find the network configuration section where the current management IP address is set.
Update IP Address
Input the new management IP address, ensuring it is within the correct subnet and not in use by another device.
Adjust Additional Settings
Update related settings, like subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS servers, to match the new IP configuration.
Save and Reconnect
Save the changes and reconnect to the device using the new management IP address to ensure the update was successful.
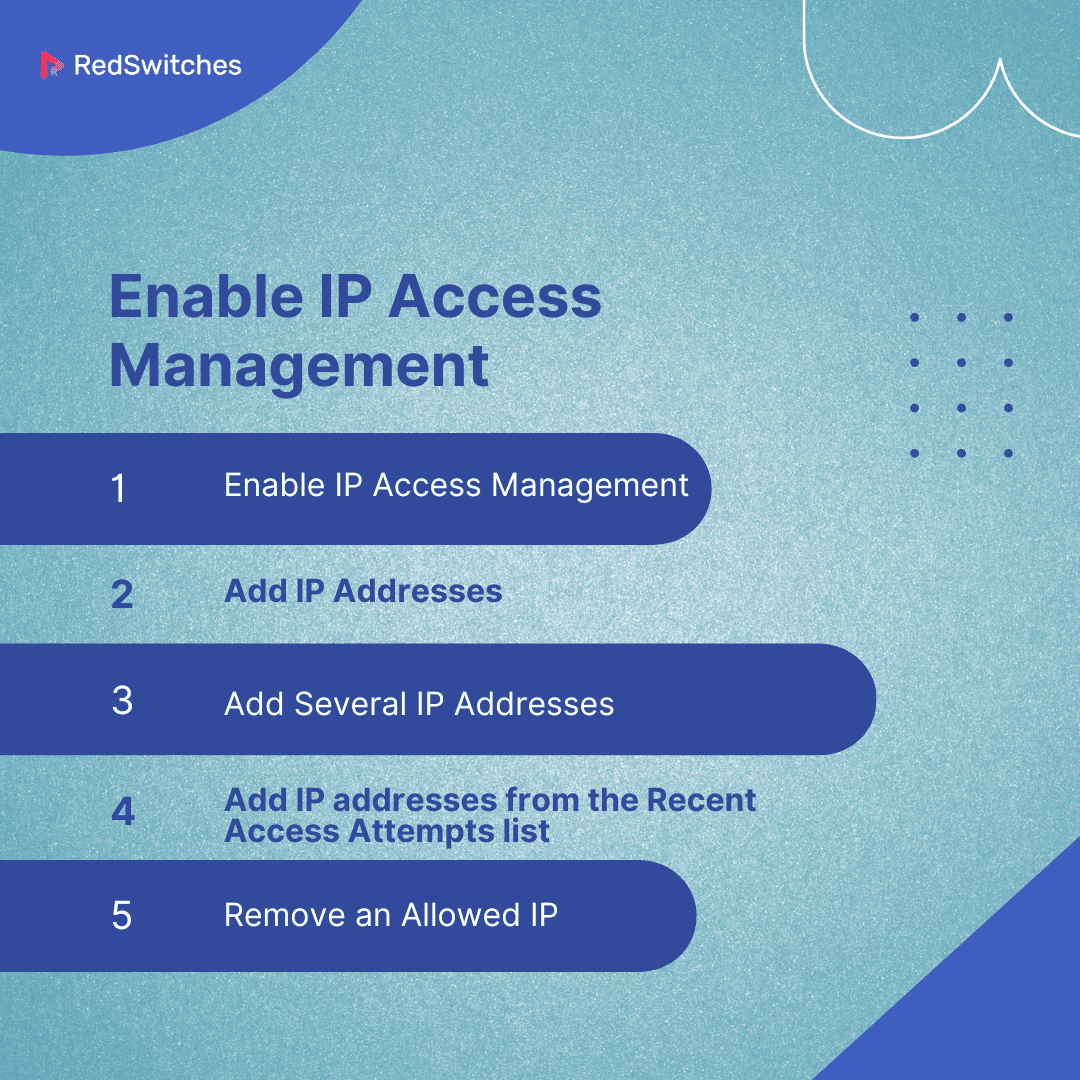
Enable IP Access Management
Enabling IP access management, adding individual IP addresses, and adding multiple IP addresses are crucial tasks for network administrators to ensure secure and efficient network operation. Here’s how these processes works:
Enable IP Access Management
Enabling IP access management involves configuring your network devices to recognize and enforce access controls based on IP addresses. This is important for managing which devices can communicate with your network infrastructure, especially for devices assigned specific management IP addresses.
Access Device Interface
Use the management IP address to log into the network device’s administrative interface securely.
Locate Security Settings
Navigate through the device’s settings to find the security or access control section.
Activate IP Access Control
Enable the feature that allows IP-based access management, often found under firewall settings, IP filtering, or access control lists (ACLs).
Also Read: Dedicated IP Vs Shared IP: Differences, Benefits & Their Impact.
Add IP Addresses
Adding an IP address usually involves specifying an IP address allowing access to the network device for management purposes.
Enter IP Management Section
Through the device’s management interface, go to the section where IP access control is configured.
Specify IP Address
Add a new rule or IP address and input the IP address you wish to allow.
Configure Access
Set parameters like rule name description and specify whether the IP is allowed or denied.
Apply Changes
Save the configuration to enforce the new access rule.
Add Several IP Addresses
When adding multiple IP addresses, the approach can vary depending on the device’s capabilities:
- Bulk Addition
Some devices allow you to add multiple IP addresses simultaneously by specifying a range or uploading a list.
- Specify Range: You may be able to specify a start and end IP address or use CIDR notation if adding consecutive IP addresses.
- Upload IP List: Prepare a list in a supported format (like CSV) for non-consecutive IP addresses. Use the device’s import function to add them simultaneously.
- Individual Addition
If the device does not support bulk addition, you will need to repeat the process of adding an individual IP address for each new address you wish to allow.
Add IP addresses from the Recent Access Attempts list
Network devices and security systems often log recent access attempts. This includes authorized and unauthorized access to network resources. Administrators can use these logs to find IP addresses that should be granted access. The steps involved include:
Review Access Logs
Access the device or security system logs to review recent access attempts. These logs typically include the IP address, timestamp, and access status (success or failure).
Identify Legitimate IPs
Find the IP addresses associated with legitimate access attempts that were possibly blocked or not yet allowed in the system.
Access IP Management Interface
Log into the device’s management interface or the network security system where IP access control lists or firewall rules are configured.
Add IP to Allow List
Navigate to the section where IP allow lists or ACLs are managed. Add the identified IP addresses to the list. This may involve specifying the IP address, setting a rule name, and defining the access level.
Apply and Verify Changes
Save the changes and, if necessary, apply the updated configuration. Verify that the added IP addresses now have the appropriate level of access by attempting a connection or monitoring log entries for successful access.
Remove an Allowed IP
Removing an IP address from the allowed list is a common administrative task. This is often required when an IP address no longer needs access or a security risk arises. The process involves:
Access IP Management Interface
Log into the management interface where IP access control is configured. This could be a firewall, router, or dedicated network security system.
Locate Allowed IPs List
Navigate to the section that lists all currently allowed IP addresses. This could be under firewall rules, ACLs, or a specific IP allow list.
Identify IP to Remove
Find the IP address that needs to be removed from the list. This could involve searching or filtering the list based on the IP address.
Remove the IP Address
Select the IP address and choose the option to remove or delete it from the list. Confirm the action if prompted.
Save and Apply Changes
Ensure the changes are saved and applied to the system. It might be necessary to update the configuration for the changes to take effect immediately.
Verify Removal
Confirm that the IP address has been successfully removed by checking the allow list and monitoring access logs for any attempts from the removed IP address.
Disable IP Access Management
Disabling IP Access Management involves turning off the capability to manage the device remotely via its management IP address. This action might be taken for various reasons. Examples include security concerns or transitioning to a different management platform. The process involves:
Secure Login
Access the device management interface securely using the current management IP address.
Navigate to Management Settings
Locate the device’s configuration interface section that controls remote management features. This could be under general settings, management settings, or network services.
Disable Management Access
Find the option to disable or turn off remote management access and select it. This might involve unchecking a box, changing the status to ‘disabled,’ or executing a specific command in a CLI environment.
Confirm Action
You might be prompted to confirm your decision to restrict remote management access. Confirm the action, understanding that this will prevent remote access to the device via the management IP address.
Apply and Save Changes
Save the configuration changes to ensure the remote management feature is disabled. This might involve clicking a ‘save’ button, executing a ‘commit’ command, or following a specific procedure to ensure changes are applied.
Physical Verification
Since remote management is now disabled, physical access to the device may be required for future management. Verify that the management IP address is no longer accessible remotely.
Documentation
Update network documentation to reflect the change in management access capabilities for the device, noting that remote management via the management IP has been disabled.
Also Read: Your Ultimate Cheat Sheet To IP Transit.
Management IP and Dedicated Servers
From the perspective of management IP, dedicated servers play an important part in ensuring efficient, secure, and scalable network operations. This is especially true in environments with extensive server resources and complex networking requirements. Here’s how dedicated servers contribute to effectively using management IPs:
Centralized Management
Dedicated servers can host centralized management tools and software, including IP Address Management (IPAM) systems, network monitoring tools, and configuration management databases (CMDBs). These tools use management IPs to communicate with various network devices. They allow administrators to manage the entire network from a single point. This centralization simplifies updates, configuration changes, and monitoring tasks, making network management more efficient and less prone to errors.
Security
Management IPs can be a target for unauthorized access because they provide control over network devices. Dedicated servers can enhance the security of management IPs through advanced security measures like firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and secure access protocols (SSH, HTTPS). You can isolate these critical services from the rest of the network by hosting management applications on dedicated servers. This lowers the attack surface and protects management IPs from unauthorized use.
Reliable Connectivity
Dedicated servers ensure reliable connectivity to management IPs by providing stable and high-performance hardware resources exclusively for network management tasks. This reliability is important for maintaining uninterrupted access to network devices. The dedicated nature of these servers means that management tasks do not compete with other network traffic. It ensures that management commands and responses are not delayed by congestion.
Scalability
The number of devices and, consequently, the number of management IPs increase as networks expand. Dedicated servers offer scalable solutions to handle this growth. They can manage the increased load from more devices being managed and more data being collected and processed. This scalability ensures that the management infrastructure can grow with the network it supports without impacting performance.
High Availability
Dedicated servers can be configured for networks that require 24/7 uptime in high-availability clusters. This ensures that management services are always accessible, even during hardware failure. This setup can be critical for maintaining access to management IPs. It allows network administrators to manage and troubleshoot devices without interruption.
Specialized Access Control
Credits: FreePik
Dedicated servers allow for implementing specialized access controls to management IPs. This ensures that only authorized personnel can change network devices. This can include multi-factor authentication, role-based access controls, and detailed logging of all access to management IPs. These measures are important for maintaining the security of the network.
Conclusion
The above exploration proves that the foundation of robust management IP is in the infrastructure that supports it. Dedicated servers, with their ability to offer dedicated resources, enhanced security, and superior control, stand out as the backbone for effective IP management strategies.
RedSwitches recognizes this critical need and offers dedicated server solutions. We aim to provide the reliability and performance necessary for complex IP management tasks and ensure businesses can scale their operations with growing network demands. By partnering with us, organizations can leverage the power of dedicated servers to optimize their IP management practices. Contact us today to learn more.
FAQs
Q. What is the purpose of management IP?
The purpose of a management IP is to provide a dedicated interface for managing network devices like routers, switches, and servers. This allows administrators to access, configure, and monitor the device remotely, separate from its normal data traffic. This helps improve security and management efficiency.
Q. What is the difference between management IP and production IP?
The management IP is used exclusively for device administration. It provides a secure path for configuration and monitoring. The production IP handles the device’s regular operational traffic, like user data or application traffic. This ensures that management activities don’t interfere with the device’s primary functions.
Q. What is server management IP?
A server management IP is a specific IP address assigned to a server for administrative tasks. It’s used for remote management access to the server. It allows administrators to perform updates, troubleshooting, and configuration changes. It does so without impacting the server’s main operational functions handled by its production IP addresses.
Q. What is a management IP address?
A management IP address is a specific IP address assigned to a device, like a server, switch, or router, that allows it to be remotely accessed and managed over a network.
Q. Why is the management IP address important in server environments?
The management IP address is critical in server environments as it allows administrators to remotely configure, monitor, and troubleshoot server hardware and software without needing direct physical access to the servers.
Q. How do I configure a management IP address for a server?
You can configure a management IP address for a server by accessing the server’s network settings and assigning a specific IPv4 or IPv6 address to the management interface.
Q. What is the default gateway’s management IP used for?
The default gateway’s management IP is used as the default route for outgoing network traffic from the server, allowing it to communicate with other devices on the network or the internet.
Q. Can I use the management IP address to manage cluster members?
Yes, the management IP address can remotely manage and monitor cluster members, allowing for centralized administration of the entire cluster from a single location.
Q. How do I change the management IP address of a server?
You can change the management IP address of a server by accessing the network settings, modifying the existing management address, and assigning a new IPv4 or IPv6 address to the server’s management interface.
Q. What is the importance of assigning an IPv4 or IPv6 management address to a server?
Assigning an IPv4 or IPv6 management address to a server is crucial for remote administration, as it allows administrators to securely access and manage the server using management software, telnet, or SSH protocols.
Q. How does the management IP address enable remote management of servers?
The management IP address enables remote management of servers by providing a dedicated interface through which administrators can access, configure, monitor, and administer the server without physically being present at the server location.
Q. What is lights out management, and how does it relate to the management IP address?
Lights-out management refers to remotely managing and controlling server hardware, even when the server is powered off or unresponsive. The management IP address is essential for establishing the remote connection required for lights-out management.
Q. Why is it important to configure an IPv6 management address for servers in modern server environments?
It is important to configure an IPv6 management address for servers in modern environments to ensure future compatibility with IPv6-based networks and to meet the growing demand for IPv6 addresses as IPv4 addresses become more scarce.
Q. What is open source IP management?
Open source IP management uses freely available software solutions to organize, track, and manage IP addresses within a network. These tools help automate the allocation, administration, and monitoring of IP spaces to enhance network efficiency and reduce conflicts.