Info
benthic, inshore, detritus feeder, deposit feeder , almost circumtropical
Synonymised names:
Fistularia impatiens Forsskål, 1775 (synonym)
Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens bicolor Clark, 1938 (synonym)
Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens concolor Clark, 1921 (synonym)
Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens lutea Clark, 1921 (synonym)
Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens pulchra Clark, 1921 (synonym)
Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens var. bicolor Clark, 1938
Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens var. concolor Clark, 1921
Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens var. lutea Clark, 1921
Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens var. pulchra Clark, 1921
Holothuria botellus Selenka, 1867 (synonym)
Holothuria fulva Quoy & Gaimard, 1834
Holothuria impatiens (Forskål, 1775)· accepted, alternate representation
Holothuria impatiens var. bicolor Clark, 1938· accepted, alternate representation
Holothuria impatiens var. concolor Clark, 1921· accepted, alternate representation
Holothuria impatiens var. lutea Clark, 1921· accepted, alternate representation
Holothuria impatiens var. pulchra Clark, 1921· accepted, alternate representation
Holothuria ophidiana Quoy & Gaimard, 1834
Direct children (9):
Variety Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens var. ludingae Domantay, 1953 (nomen nudum)
Subspecies Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens bicolor Clark, 1938 accepted as Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens (Forsskål, 1775) (synonym)
Subspecies Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens concolor Clark, 1921 accepted as Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens (Forsskål, 1775) (synonym)
Subspecies Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens lutea Clark, 1921 accepted as Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens (Forsskål, 1775) (synonym)
Subspecies Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens pulchra Clark, 1921 accepted as Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens (Forsskål, 1775) (synonym)
Variety Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens var. bicolor Clark, 1938 accepted as Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens (Forsskål, 1775)
Variety Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens var. concolor Clark, 1921 accepted as Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens (Forsskål, 1775)
Variety Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens var. lutea Clark, 1921 accepted as Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens (Forsskål, 1775)
Variety Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens var. pulchra Clark, 1921 accepted as Holothuria (Thymiosycia) impatiens (Forsskål, 1775)
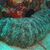
Sea cucumbers of the family Holothuriidae possess, exceptions confirm the rule, so-called Cuvier's tubes (named after the French naturalist Georges Cuvier, * August 23, 1769 † May 13, 1832).
These are long, thin tubes that are located on the rectum of the echinoderms and are flung towards potential predators for defense.
These released tubes form a sticky, tough and stretchy network in which fish, crustaceans or other prey predators can become entangled.
The adhesives may also contain toxins (holothurin).
Sea cucumbers are the vacuum cleaners of the oceans, continuously cleaning the sea floors, so it may be useful for aquarists to keep one or more sea cucumbers in the aquarium to avoid detritus rich zones.
Problem:
Many sea cucumbers of the family Holothuriidae can release their venom into the aquarium water when they are in danger or dying, corals are mostly not harmed by the venom, but fish usually die.
Holothurins can cause severe, burning pain when in contact with the skin and irritation and even blindness when in contact with the eyes. When ingested systemically, the toxins can cause paralysis, muscle spasms, and discomfort in the digestive system, and in larger quantities, death by respiratory paralysis.
Since sea cucumbers are considered a delicacy in many Asian countries, the Cuvier's tubes containing the toxins must be removed before preparation or consumption.







 Rafi Amar, Israel
Rafi Amar, Israel