Chemosynthesis
Most life on Earth relies on sunlight as their primary energy source to make their own food by photosynthesis. However, in deep-subsurface ecosystems such as hydrothermal vents where sunlight is absent, organisms use a completely different process known as chemosynthesis to produce their food.
What is Chemosynthesis
Chemosynthesis is the process by which specific microorganisms prepare food (glucose) using inorganic substances without sunlight. They rely on the oxidation of sulfur, hydrogen, hydrogen sulfide, and methane for their energy source.
Such microbes called chemoautotrophs can survive extremely harsh conditions like high temperature and osmotic pressures. Sulfur-oxidizing gamma proteobacteria, neutrophilic iron-oxidizing bacteria, epsilon proteobacteria, and methanogenicarchaea are typical chemoautotrophs.
Besides hydrothermal vents, chemosynthesis also happens in hot springs and cold seeps.
When was it Discovered
Chemosynthesis was discovered in 1977 when a group of scientists on an ocean research expedition near the Galápagos Islands found hot hydrothermal vents emitting a hot chemical fluid on the ocean floor. They found a community of several new animal species living in absolute darkness without sunlight.
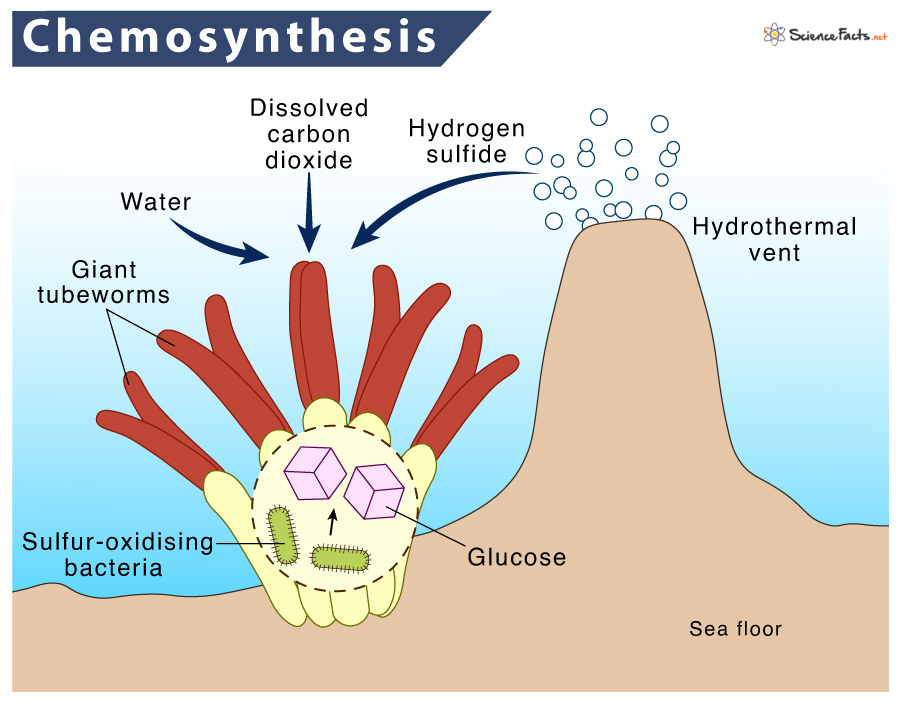
We will now discuss the process of chemosynthesis using hydrogen sulfide (H2S) as the energy source.
Why is Chemosynthesis Important
Chemosynthesis forms an alternative life form on Earth without sunlight. It helps to sustain life in extreme environments where oxygen is insufficient or absent. Thus, chemosynthesis forms the basis of the marine food chain sustaining shrimp, tubeworms, clams, crabs, fish, and octopods.
Certain eukaryotes build a symbiotic relationship with chemoautotrophs to get food. For example, tubeworms have these chemoautotrophic bacteria in their trophosome, sheltering them. The bacteria, in turn, convert the chemicals from the hydrothermal vents into food for the worm.
How does Chemosynthesis Work
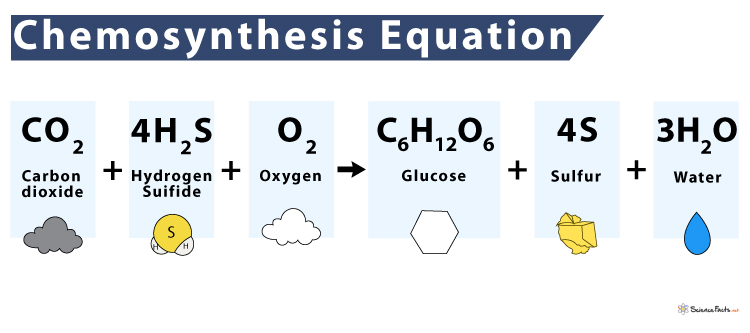
Chemoautotrophs, with the help of carbon dioxide and oxygen and using the energy released from the oxidation of hydrogen sulfide (H2S), produce glucose, sulfur, and water.
Equation
Chemical Equation
Word Equation
Carbon dioxide + Hydrogen sulfide + Oxygen → Glucose + Sulfur + Water
Reactants
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Hydrogen sulfide (H2S)
- Oxygen (O2)
Substances Produced
- Glucose (C6H12O6)
- Sulfur (S)
- Water (H2O)
Chemosynthesis vs Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis and chemosynthesis are two different ways of producing food for organisms living on Earth. Photosynthesis requires sunlight, whereas chemosynthesis makes use of chemical energy.
FAQs
Ans. No, bacteria that perform chemosynthesis are primary producers or autotrophs. They use the energy stored in inorganic molecules and convert them into glucose.
Ans. No.
-
References
Article was last reviewed on Friday, February 17, 2023