MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM PRESENTATION.ppt
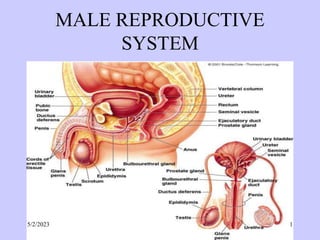
- 2. Introduction • It is comprised of a pair of testes, bilateral duct system, accessory sex glands, urethra and the penis. • The duct system includes tubuli recti, rete testis, efferent duct, epididymis duct, deferens duct, and ejaculatory duct. • Accessory sex gland include seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethral (Cowper’s) gland. 5/2/2023 2
- 3. The Testes • These are the primary male gonads that are suspended in the scrotum and their main function is production of spermatozoa and secretion of male hormones (Androgens). • The left testis is lower than the right and each testis measures about 4 to 5 cm long, 2.5 cm width and 3 cm in thickness and each weighs 10.5 to 14 gms. 5/2/2023 3
- 4. Testes cont…... • Structural organization – Each testis is contained in one compartment of the fibromuscular sac known as scrotum. – The scrotum has two right and left compartments that are separated externally by a cutaneous raphe that continues ventrally to the inferior surface of the penis and dorsally to the anus through the perineum. 5/2/2023 4
- 5. Testes cont…... – The scrotum is made up of the skin, smooth muscle (dartos muscle, cremaster muscle), external spermatic fascia, cremasteric fascia and the internal spermatic fascia which is associated with the external covering of the testis the tunica vaginalis – Testis is immediately surrounded by the testicular capsule, which is composed of three layers: –Outer layer or tunica vaginalis –Middle layer or tunica albuginea –Innermost layer or tunica vasculosa 5/2/2023 5
- 6. 5/2/2023 6
- 7. 5/2/2023 7
- 8. Tunica vaginalis • Is the lower end of the peritoneal processus vaginalis which precedes the descent of the fetal testes from the abdomen to the scrotum that has lost connection with the peritoneal cavity. • It covers the anterior and lateral surfaces of the testes. • Has visceral and parietal layers. 5/2/2023 8
- 9. • Visceral layer covers all aspects of the testes except the posterior border. • Parietal covers the posterior aspect of the testes. • In between them there is a cavity that contain small amount of fluid. • Sometimes during pathological situations abnormal fluid accumulation occurs in the cavity leading to hydrocoele. 5/2/2023 9
- 10. tunica albuginea • A thick layer of dense fibroelastic connective tissue that contains some smooth muscle cells concentrated predominantly on the posterior aspect of the testis adjacent to the epididymis to form the mediastinum testis from which arises septae (septula testis) that divides the testis into compartments or lobules. • Each lobule is pyramidal in shape with the apex directed towards mediastinum. 5/2/2023 10
- 11. • There are about 250 lobules each containing 1 to 4 seminiferous tubules and a connective tissue stroma in which intestitial cells (Leydig cells) are located. • Completely covers the testes. It lies internal to the tunica vaginalis. 5/2/2023 11
- 12. tunica vasculosa • The innermost layer of testicular capsule that consists of a network of blood vessels embedded within a delicate loose connective tissue. 5/2/2023 12
- 13. Histological aspect • Consist of many seminiferous tubules embedded in relatively sparse interstitial tissue. • The tubules are lined by a simple columnar epithelium of Sertoli cells. • Interspersed within the tubular epithelium are germ cells. • Meiotic cell divisions lead from spermatogonia through primary and secondary spermatocytes to cells called spermatids, which mature into spermatozoa. 5/2/2023 13
- 14. • Interstitial tissue between the tubules contains clusters of endocrine Leydig cells which secrete testosterone. • All of the seminiferous tubules converge onto a network of interconnecting tubules, the rete testis, which in turn lead through numerous small efferent ductules into the larger duct which extends through the epididymis. 5/2/2023 14
- 15. 5/2/2023 15
- 16. Seminiferous tubule • Highly convoluted tubule about 0.2 mm in diameter and 30 to 40 cm long. • Are lined by seminiferous epithelium which is a modified stratified cuboidal epithelium consisting of spermatogenic cells and supporting cells (sertoli cells). • The tubules are surrounded by a basal lamina and by the thin 3 to 4 squamous smooth muscle cells invested by their own basal (external) lamina. 5/2/2023 16
- 17. • The connective tissue aspect of the smooth muscle cells is covered by the thin endothelium of a vast system of large lymphatic capillaries. • This system and smooth muscle sheath represent a physiological barrier to blood- borne substances intended to reach the spermatogenic cells. 5/2/2023 17
- 18. • Spermatogenic (Germ) cells • Comprises a stratified layer of epithelium 4 to 8 cells deep, lining the seminiferous tubule. • The cells differentiate progressively from the basal region of the tubule to the lumen. 5/2/2023 18
- 19. • Proliferation pushes the cells toward the lumen, and those nearest the lumen transform into spermatozoa and detach from the epithelium coming to lie free within the lumen. • The sequence of events is referred to as spermatogenesis (spermatocytogenesis and spermiogenesis). 5/2/2023 19
- 20. • Spermatogonia are the first cells of spermatogenesis. • They are always in contact with the basal lamina of the tubule. • Two types of spermatogonia can be distinguished: Type A spermatogonia – Have a rounded nucleus with very fine chromatin grains and one or two nucleoli. They are stem cells which divide to form new generations of both type A and type B spermatogonia. 5/2/2023 20
- 21. • Type B spermatogonia – Have rounded nuclei with chromatin granules of variable size, which often attach to the nuclear membrane, and one nucleolus. – Although type B spermatogonia may divide repeatedly, they do not function as stem cells and their final mitosis always results in the formation of primary spermatocytes. 5/2/2023 21
- 22. • Primary spermatocytes – Larger than the spermatogonia. – They are spherical or ovoid in outline, and are the largest germ cells seen within the seminiferous tubule where they occupy the middle zone of the epithelium. – A large number of primary spermatocytes is always visible in cross-sections through seminiferous tubules. 5/2/2023 22
- 23. • Secondary spermatocytes, – Are smaller than primary spermatocytes. They rapidly enter and complete the second meiotic division and are therefore seldom seen in histological preparations since they are short lived and divide quickly to produce Spermatids. 5/2/2023 23
- 24. • Spermatids, – Lie in the luminal part of the seminiferous epithelium. – They are small (about 10 µm in diameter) with an initially very light (often eccentric) nucleus. – The chromatin condenses during the maturation of the spermatids into spermatozoa, and the nucleus becomes smaller and stains darker. – The differentiation of the newly formed spermatids results into Spermatozoa. 5/2/2023 24
- 25. • Spermatozoa – The mature human spermatozoon is about 60 µm long and actively motile. It is divided into head, neck and tail. 5/2/2023 25
- 26. Sertoli cells • Constitute true epithelium of the seminiferous epithelium. • Relatively few in number spaced along the tubule at fairly regular intervals crowded between germ cells. • They are columnar, tall, pillar-like cells, with their bases resting on upon the basal lamina. • Do not migrate nor do they replicate after puberty. 5/2/2023 26
- 27. • Interstitial tissue – It’s the loose connective tissue between the seminiferous tubules contains interstitial endocrine cells (Leydig cells), blood, and lymphatic vessels, nerves, fibroblasts and mast cells. • Leydig cells (15-20 µm), located in the interstitial tissue between the convoluted seminiferous tubules, constitute the endocrine component of the testis. They synthesize and secrete testosterone. 5/2/2023 27
- 28. • Active Leydig cells are large ,irregularly polygonal, acidophilic cells often filled lipid droplets. • Have an elaborate smooth endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria with tubulovesicular cristae. • Inactive cells are difficult to distinguish from fibroblast. 5/2/2023 28
- 29. 5/2/2023 29
- 30. 5/2/2023 30
- 31. Male genital ducts • Two types of ducts – Intratesticular genital ducts. Tubuli recti, rete testis, proximal part of efferent duct. – Extratesticular genital ducts. Distal part of efferent duct, epididymis duct, deferens duct, and ejaculatory duct. 5/2/2023 31
- 32. • Tubuli recti – The straight tubules which is a short terminal section of seminiferous tubule that lined solely by Sertoli cells. – As it narrows towards to rete testis the lining changes to a simple cuboidal epithelium. 5/2/2023 32
- 33. • rete testis – Complex series of interconnecting channels in a highly vascular of mediastinum testis. – Lined mainly by low cuboidal epithelium. – Each cuboidal cell has a single cilium on its apical surface with a few apical microvilli. 5/2/2023 33
- 34. Efferent duct • Approx 15 efferent ductules leaves the testis by penetrating tunica albuginea and connect the testis to ductus epididymis. • As it leaves the testis 15 to 20 cm long become highly coiled and tightly parked into 6 to 10 conical masses called Coni vasculosi. 5/2/2023 34
- 35. • At the base of the coni they empty into the single channel of ductus epididymis • They are lined with alternating clumps of tall and short pseudo stratified columnar cells thus giving rise to the saw-toothed appearance of the luminal surface. 5/2/2023 35
- 36. • Tall columnar cells are ciliated • Short non-ciliated columnar cells with numerous microvilli and canalicular invagination of apical surface. • Between the columnar cells there are few basal cells and intraepithelial lymphocytes. • Has circular smooth muscle layers in the wall of the ductule. • Elastic fibers are interspersed among the muscle cells. 5/2/2023 36
- 37. ductus epididymidis • About 6 m long. • It is lined by a very tall pseudostratified columnar epithelium. • Most cells of the epithelium, also called principal cells, have long stereocilia. • Stereocilia are non-motile structures, which in the EM resemble large microvilli. 5/2/2023 37
- 38. • Towards the basal lamina we see a number of small nuclei, which belong to the basal cells of the ductus epididymis. These cells regenerate the epithelium. • Peristaltic contractions of smooth muscle cells surrounding the ductus epididymis move the spermatozoa towards the middle segment of the duct, which is the site of final functional maturation of the spermatozoa - now they are motile. 5/2/2023 38
- 39. • The terminal segment of the ductus epididymis is the site of storage of the mature spermatozoa. • Smooth muscle fibers of the terminal part of the ductus epididymis do not contract spontaneously. • They contract during sexual stimulation concurrently with the contraction of the musculature of the duct into which it opens, the vas deferens. 5/2/2023 39
- 40. 5/2/2023 40
- 41. 5/2/2023 41
- 42. Vas deferens (ductus deferens) • Connects epididymis to the prostatic urethra • The mucosa of the vas deferens forms low longitudinal folds. • It is lined by a pseudostratified columnar epithelium. Similar to the epididymis, cells have long stereocilia. • The lamina propria is unusually rich in elastic fibres. 5/2/2023 42
- 43. • The muscularis is well developed (up to 1.5 mm thick) and consists of a thick circular layer of smooth muscle between thinner inner and outer longitudinal layers. • The muscularis is the structure which makes the vas deferens palpable in the spermatic cord. • The vas deferens is surrounded by an adventitia, which is slightly denser than usual. 5/2/2023 43
- 44. 5/2/2023 44
- 45. 5/2/2023 45
- 46. • Ejaculatory duct • The short duct (1 cm) formed by the union of the ductus deferens and duct of seminal vesicle. • It enters the urethra at the prostatic utricle. • Lined with a simple columnar and pseudostratified columnar epithelium • Has no muscle no muscle coat. • Supporting wall is fibrous connective tissue only. 5/2/2023 46
- 47. Male Accessory Reproductive Glands • Consists of – The seminal vesicles, – The prostrate and – The bulbourethral glands. 5/2/2023 47
- 48. Seminal vesicles • They are paired. • Are elongate sacs (about 4 cm long and 2 cm wide), highly folded tubular glands with a muscular and fibrous coat. • They develop as evaginations of the vas deferens distal to ampulla. • They are situated posterior to prostate gland. • Each consists of one coiling tube (about 15cm long). 5/2/2023 48
- 49. • The mucosa is thrown into various primary, secondary and tertiary folds that increase the secretory surface. • The folds project into the lumen and merge with one another as a result different compartments of various sizes are formed. All communicate with the lumen. • The muscularis consists of inner circular and outer longitudinal layers of smooth muscle. 5/2/2023 49
- 50. • The epithelium is variable appearing as simple columnar or pseudostratified columnar (columnar cells and basal cells). • Pseudostratified columnar epithelium contains tall non ciliated columnar cells and short round cells that rest on basal lamina • The lamina propria of the mucosa is fairly thin and loose. 5/2/2023 50
- 51. • They are glands, whose secretion constitutes 60-70 % of the ejaculate. • The secretory product of the columnar cell, which may be seen in the lumen of the seminal vesicles, is strongly acidophilic. • It contains large amounts of fructose which the spermatozoa utilise as a source of energy. 5/2/2023 51
- 52. • The secretion also contains prostaglandins, flavins (yellow fluorescing pigment - of use in forensic medicine to detect semen stains) and several other proteins and enzymes. • The cocktail of compounds which is released by the seminal vesicles in addition to fructose has three main functions: 5/2/2023 52
- 53. 1. formation of the sperm coagulum, 2. regulation of sperm motility and 3. suppression of immune function in the female genital tract. 5/2/2023 53
- 54. 5/2/2023 54
- 55. 5/2/2023 55
- 56. Prostate • The prostate is the largest accessory sex gland in men (about 2 × 3 × 4 cm). • It surrounds the proximal urethra at its origin from the bladder • It contains 30 - 50 tubuloalveolar glands, which empty into 15 - 25 independent excretory ducts. These ducts open into the urethra. • The glands are embedded into a fibromuscular stroma, which mainly consists of smooth muscle separated by strands of connective tissue rich in collagenous and elastic fibers. 5/2/2023 56
- 57. • The muscle forms a dense mass around the urethra and beneath the fairly thin capsule of the prostrate. • The secretory alveoli of the prostate are very irregularly shaped because of papillary projections of the mucosa into the lumen of the gland. • The epithelium is cuboidal or columnar also patches of squamous. 5/2/2023 57
- 58. • Basal cells are again present, and the epithelium may look pseudo stratified where they are found. • The secretory cells are slightly acidophilic and secretory granules may be visible in the cytoplasm. 5/2/2023 58
- 59. • The secretion of the prostate contains citric acid, the enzyme fibrinolysin (liquefies the semen), acid phosphatase, a number of other enzymes and lipids. • The secretion of the prostate is the first fraction of the ejaculate. • The secretory ducts of the prostate are lined by a simple columnar epithelium, which changes to a transitional epithelium near the openings of the ducts into the urethra. 5/2/2023 59
- 60. • A characteristic feature of the prostate is the appearance of corpora amylacea in the secretory alveoli. • They are rounded eosinophilic bodies. • Their average diameter is about 0.25 to 2 mm). • They appear already in the seventh month of foetal development. • Their number increases with age - in particular past 50. • They may undergo calcification. Corpora amylacea may appear in semen. 5/2/2023 60
- 61. • Macroscopically the prostrate can be divided into lobes, but they are inconspicuous in histological sections. • In good histological sections it is possible to distinguish three concentric zones, which surround the prostatic part of the urethra. • The peripheral zone contains large, so- called main glands, whose ducts run posteriorly to open into the urethra. 5/2/2023 61
- 62. • The internal zone consists of the so-called submucosal glands, whereas • The innermost zone contains mucosal glands. • This subdivision of the prostate is of clinical importance. • With age the prostate becomes enlarged due to benign nodular hyperplasia or benign prostatic hypertrophy. • The onset age of these hyperplastic changes is 45. About 3/4 of the males above 60 are affected of which half will be symptomatic. 5/2/2023 62
- 63. • This condition affects the mucosal glands. • Cancer of the prostate, which is the second most common malignant tumor in western males, involves the peripheral zone. • It affects approximately 1 in 20 • It is often not detected early because the abnormal growth may not impinge on the urethra and produce symptoms that demand prompt attention 5/2/2023 63
- 64. 5/2/2023 64
- 65. 5/2/2023 65
- 66. 5/2/2023 66
- 67. Bulbourethral gland (Cowper’s glands) • Are paired bodies, each the size of a pea, located in the connective tissue behind the membranous urethra and joins the initial portion of penile urethra • The glands are compound tubuloalveolar glands that structurally resemble mucus secretory glands • Is surrounded by thin connective tissue capsule, external to which are skeletal muscle fibers 5/2/2023 67
- 68. • The septa pas into the gland to divide it into lobules • The secretory end pieces are variable, being either alveolar, saccular or tubular • The secretion is clear, mucus like containing considerable amounts of galactose, galactosamine, galacturonic acid, sialic acid and methylpentose. • They constitute major portion of preseminal fluid and probably serves as a lubricant of the penile urethra 5/2/2023 68
- 69. semen • Is a combined product of all of the glandular elements of the male reproductive system • It contains fluid and sperm from the testis and secretory products from epididymis, vas deferens, prostate, seminal vesicle and bulbourethral glands • It is alkaline in nature 5/2/2023 69
- 70. • May help to neutralize the acid environment of the urethra and vagina • Also contains prostaglandins that may influence sperm transit in both male and female reproductive tracts, and also may have a role in implantation of a fertilized ovum 5/2/2023 70
- 71. • The volume of average ejaculate of semen is about 3mL. This is normally contains up to 100million sperm/mL. • Of which it is estimated that 20% are morphologically abnormal; and nearly 25% are immotile 5/2/2023 71
- 72. PENIS • An elongated organ which is common termination of both the urinary and genital extratesticular duct system • Urethra carries both semen and urine to the exterior • It consist primarily of two dorsal masses of erectile tissue; the corpora cavernosa, and a ventral mass of erectile tissue that surrounds the urethra; corpus spongiosum (corpus cavernosum spongiosum urethrae) 5/2/2023 72
- 73. • A dense fibroelastic layer , the tunica albuginea, binds the three cavernosa together as well as forming capsule around each one • Corpora cavernosa are lined with vascular endothelium thus increase in size and rigidity by filling with blood principally derived from helicine arteries 5/2/2023 73
- 74. • These arteries dilate under sexual stimulation to increase blood flow to the penis • Helicine arteries(dilate) and arteriovenous anastomosis (closes) • As erectile tissue fills, the peripheral veins that drain it are increasingly compressed, this may amplify erectile response 5/2/2023 74
- 75. • Thin skin of penis is loosely attached to the underlying connective tissue which contain no adipose tissue. Only at the glans penis skin is firmly attached • Thin layer of smooth muscle in the skin is continuous with dartos layer of scrotum • In uncircumcised male, glans is covered with a fold of skin, prepuce, which has characteristic of mucous membrane on its inner aspect 5/2/2023 75
- 76. • Skin contains small sweat glands and infrequent sebaceous glands unassociated with hair follicles. No hair follicles on the distal part of the penis • On the glans penis and inner surface of prepuce there are numbers of modified sebaceous glnds , the Glands of Tyson 5/2/2023 76
- 77. • Innervation; spinal, sympathetic, and parasympathetic 5/2/2023 77