Blunt Ocular trauma
- 9. Sports related eye Injury • Extrem risk- war, paintball,BB guns and air rifles, fencing. • High risk- boxing and full contact martial arts,ice hockey,racquet sports • Moderate risk-basketball, baseball ,field hockey,golf,soccer,rigby, polo,football, • Low risk-mountaineering, swimming, deep diving. • There is a poor prognosis in golf related eye injuries – golf ball travels at a high speed and can fit within the bony orbit
- 11. Prevention of ocular trauma • Wearing seat belt while driving and air bag facility in car • Wearing protective eye wear made up of polycarbonate lenses.(high- impact resistance) • Wearing helmet while playing sports along with glasses if required.
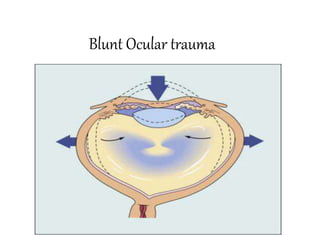
- 14. .Direct impact- produces maximum damage at point of impact .Compression wave force – transmitted through fluid contents in all directions , strikes angle of anterior chamber , pushes iris lens diaphragm posteriorly and strikes retina and choroid – contre coup damage eg commotio retina .Reflected compression wave – after striking the outer coats , the compression waves are reflected towards posterior pole and foveal damage .decompression wave force- after striking the posterior wall , it rebounds anteriorly. This damages retina choroid by forward pull and lens iris diaphragm by forward thrust from back .Coup injury- at the site of impact Countre coup- areas of the globe opposite to site of force application
- 15. • A-P diameter- decreases by 41%, cornea touches lens and iris. .Equatorial diameter increases by 128% .Distance b/w vitreous base and posterior pole of lens increases by 28%
- 16. Evaluation and initial management • In life threatening injuries - medical and neurosurgical stability ensured • Ocular surface lavaged immediately if history of chemical injury esp with alkali • Past medical history obtained • Ocular history and history of traumatic event obtained • Eye examination
- 17. Ocular examination • Visual acuity: snellens chart used. Lid retractors avoided in suspected glope rupture/perforation • Counting fingers/hand movements /detect light • External examination:skin,face,orbit/deformities noted • Ocular motility:ability to move eyes synchronously
- 18. • Pupils:size ,shape,symmetry,reaction to light(dirrect/consensual) • Presence/lack of afferent pupillary defect • Anterior segment: • Conjunctiva and sclera:chemosis/foreign body • Cornea:lack of clarity/irregularities/fluorescein/foreign body
- 19. • Anterior chamber:depth/hyphema/hypopyon • Iris:irregularities/defects • Lens:position/degree of cataract
- 20. Posterior segment • Vitreous :clarity • Optic disc:color,margins,cup disc ratio • Macula,retina,vessels • Presence of hemorrhage/foreign body/tears
- 21. • Intraocular pressure:avoided when obvious corneal laceration or prolapse of uveal tissue
- 22. ORBITAL HAEMARHAGE Orbital compartment syndrome Orbital trauma, hemorrhage into the orbit - forward movement of globe – increased orbital pressure - decreased orbital compliance - poor perfusion of orbital and intraocular structures If intraorbital pressure > central retinal artery pressure --- ischemia Classically in retrobulbar hematoma – post op, trauma Symptoms - elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) ,with or without a decrease in the visual acuity of the affected eye, proptosis, a tight orbit, decreased EOM Mx – medical – orbital massage, ice compresses,iv corticosteroids , iv mannitol if not C/I (head trauma), topical beta blockers
- 23. • Surgical - lateral canthotomy and • cantholysis of the inferior crus of the lateral canthal tendon (LCT). • If not reduced - superior crus also needs to be released. • AC paracentesis • If not reduced – orbital decompression
- 24. Diagnostic tests • X ray: • Advantage:documentation of presence and number of metallic foreign bodies in eye or orbit • Defines orbital wall and skull fractures • Cost effective
- 25. • Disadvantage:less helpful in locating foreign body • Doesnt identify radiolucent foreign body(glass/plastic/wood) • Fail to show existence and extent of penetrating or blunt orbitocranial injuries
- 26. • Ultrasonography: • Advantages:detection of posterior ocular lesions obscured by anterior segment disruption/hyphema • Detection/localization radiolucent foreign body in anterior orbit • Lens position
- 27. • Disadvantages: • Not reliable if foreign body located deep in orbit • Open globe injuries preclude time and manipulation • Extraocular muscles not well demonstrated esp massive facial trauma • Poor detection of scleral rupture
- 28. Computed tomography • Advantages: • Exact extent of orbital wall fractures associated soft tissue injury • Visualization of retroorbital space • Defines radiolucent foreign body • Exact location • Cerebral edema/hematoma • Contrast enhanced ct suspected vascular injuries
- 29. Disadvantages • Thick CT slices may miss small metallic foreign body • Multiple tightly clustered metallic foreign body may be obscured by artifacts
- 30. Magnetic resonance imaging • Advantages :improved soft tissue delineation • Sesitive tool for diagnosing small amount of blood • Better resolution of low density objects such as vegetable matter and wooden foreign body • Better detection of optic nerve lacerations or avulsion
- 31. Disadvantages • Less useful in analysing bone abnormalities • Longer scanning time impractical in traumatised patients • Cannot be used if metallic foreign body suspected
- 32. EYELID & CANALICULAR LACERATION 1.Periocular haematoma A) Trauma to globe or orbit Treatment: a. Cold compresses in the first 24 hours (leads to vasoconstriction). b. Hot compresses after 24 hours helps absorption. B)orbital roof fracture- SCH without visible posterior limit C)Basal skull fracture- bilateral ring haematoma(panda eyes) 2. Lid lacerations: a. Horizontal wounds: do not gape and produce a small scar. b. Vertical wounds: gape and need suturing. 3. Traumatic ptosis: a. Mechanical from blood or edema. b. Paralytic from injury of the levator muscle or its nerve supply.
- 33. Fig. (A) Periocular haematoma and oedema; (B) periocular haematoma and subconjunctival haemorrhage; (C) ‘panda eyes’
- 34. Lid margin lacerations . The tarsal plate is first sutured with partial –thickness lamellar 5’0 absorbable suture(vicryl). .Lid margins are sutured with vertical matress sutures in line with Meibomian gland orfices , about 2mm from the wound edges and 2mm deep. (far far near near tech)- 5’0 silk. . Skin sutures – interrupted sutures with 6’0 nylon or silk skin suture femove After 5-7day, margin sutures 2 weeks Lacerations with mild tissue loss- lateral cantholysis in order to increase lateral mobility. Lacerations with extensive tissue loss- tenzel semicircular. Posterior lamellar reconstruction- upper lid free tarsal graft, buccal muccossal graft, hard palate, hughes tarsoconjuctival flap. Anterior lamellar reconstruction-skin advancement, local or free skin graft. .
- 35. Fig. Repairing lid margin lacerations
- 36. Canalicular lacerations repair: - Repair within 24 hours - Locate & approximate ends -Bridge the defect with silicone tubing (eg-Crawford tube). Tied in nose - monocanalicular stent- Mini Monoka, suturing its footplate to lid using 8’0 suture - Leave the tube in situ for 3-6 months
- 38. Orbit floor blow out fracture
- 39. ORBITAL FRACTURES Orbit floor blow out fracture symptoms and signs Nausea , vomiting , Diplopia, limited EOM , enophthalmuus oculocardiac reflex, enophthalmus., force duction test. CT test of choice for bony structures but not good for soft tissue entrapment TREATMENT *Oral antibiotics, ice packs, nasal decongestan. Avoid nose blowing. ..no intervention required small crack- • involving upto ½ of orbital floor- with little or no herniation, no significant enophthalmus and improving diplopia. • Intervention required- more than half of orbital floor fractured • Fracture with entrapment of orbital contents, enophthalmus >2mm, persistent and significant diplopia . White eyed blow out fracture - Trap door fractures need surgical repair within first 24-48 hours
- 40. • Roof fracture- small fracture may not require treatment, but it is important to rule out CSF leak, which carries a risk of meningitis. Sizeable defects usually require reconstructive surgery. • Blow- out medial wall fracture- usually associated with floor fracture,subcutaneous emphysema develops on blowing the nose. • Lateral wall fracture- usually associated with extensive facial damage • Surgical Approaches • Transconjunctival approach • Transcarancular • Subciliary • Various implant material used – Autogenous bone and cartilage – Alloplastic material TEFLON (polytetrafuoroethylene) MEDPOR(high density polyethylene) SILASTIC(Polymeric silicone)
- 41. ORBITAL EMPHYSEMA Free air in the orbital soft tissue – seen in fractures of the orbital floor, medial wall, and roof If SEVERE - proptosis with decreased vision Mx – If minimal, the air will be absorbed by the tissues if severe the air should be released by technique of Hunts et al. A saline-filled syringe with a large-bore needle is introduced into the orbit toward the air seen on the CT scan. As the needle enters the air pocket, the escaping air bubbles through the saline, confirming release of the emphysema.
- 42. ORBITAL APEX SYNDROME AND SUPERIOR ORBITAL FISSURE SYNDROME
- 43. ORBITAL APEX SYNDROME AND SUPERIOR ORBITAL FISSURE SYNDROME Fracture involving orbital roof Superior ophthalmic fissure syndrome (SOFS) is the combined dysfunction of CNs , III, IV and VI. .ophthalmoplegia, upper eye lid ptosis,proptosis; pupil is fixed and dilated. .spontaneous but gradual recovery usually occurs. nerve damage, trauma to the vascular structures of this area - carotid cavernous fistula or orbital compartment syndrome. Management of OAS and SOFS –based on the cause, and treatment is empiric if no specific cause is found. Orbital apex syndrome (OAS) is characterized by the combined dysfunction of CNs , ii,III, IV and VI.
- 44. SUB-CONJUNCTIVAL HEMORRHAGE Bright red patch of conjunctival tissue with distinct or feathered borders. If it is severe, the conjunctiva may become elevated and prolapse through the palpebral fissure Rule out intraocular foreign body Resolves spontaneously in 7 to 10 days, its color evolves from bright red to yellow green Can occur due to minor ocular trauma ,spontaneously , Valsalva maneuver, systemic hypertension antibiotic and lubricating eye drops and oral vit c
- 45. CONJUNCTIVAL TEAR / LACERATION Tears can occur due to various reasons such as poking a finger nail into the eye or dirt, sawdust, sand or any foreign particle entering the eye , rubbing the eyes aggressively & improper placement of contact lens or wearing dirty contact lens Symptoms - pain in the eye, ocular irritation , foreign body Sensation Signs –chemosis , SCH , torn conjunctiva Rx–prophylactic antibiotics for small lacerations Suturing for large lacerations >2mm
- 46. Cornea CORNEAL ABRASION Simple abrasion – superficial loss of epithelium caused by dust particles or foreign bodies that touch the cornea Small abrasion heals spontaneously Larger abrasion requires mild cycloplegic and pad bandaging of eye for 24 hours
- 47. Recurrent erosion ( Recurrent traumatic keratalgia ) spontaneously or scratches from babies fingernails Abrasion heals quickly but after some days Acute pain and lacrimation on waking up in the morning . Epithelium is loosely attached to the bowmans membrane and liable to be torn off by lid on waking Loose epithelium removed and eye padded for 48 hours • Treatment • Topical lubricants and hyperosmatic ointment(0.5%NaCl)-use nightly for eight weeks. • Bandage soft contact lens- 6 months • Epithelial debridemt- remove loose tissue • Stromal micropunctures • YAG laser Rx of Bowmans layer. • Excimer laser superficial keretectomy
- 48. CORNEAL EDEMA Delicate striae interlacing in different directions due to edema of the corneal stroma or occasionally to wrinkling of the descement s membrane. Due to post traumatic inflammation or raised IOP DESCEMETS MEMBRANE TEAR Ruptures in descemets membrane due to blunt trauma f/b acute edema of the stroma Mx- Prophylactic topical antibiotics. Topical steroids may be useful in cases of significant inflammatory reaction. Hypertonic saline or 5% NaCl ointment or drops to resolve corneal edema. •Corneal abrasion •Stromal oedema •Tears in Descemet membrane
- 49. Anterior Chamber Evaluate • Depth • Transparency • Angle recession • Abnormal tissue configuration(synechie) • depth
- 50. ANTERIOR CHAMBER Anterior synechiae Iris tissue that is adherent to the cornea or the angle, typically to an area of a former traumatic or surgical wound. Defective vision, pupil deformed , even cause secondary glaucoma Synechia lysed using spatula sweeping motion, cutting by scissors , vitrectomy probe If scar vascularized then diathermy first to avoid hemorrhage &synechiolysis
- 53. HYPHAEMA Blood in the AC commonly accumulates in case of(closed as well as open) globe trauma. Reabsorbs if fills less than half the anterior chamber. IOP to be evaluated Extensive if clots leads to pupillary block or trabecular block . Secondary rise of IOP in long term If hyphaema occupies more than half of anterior chamber – Eye patched and head elevated. Observe 72-96hours . Secondary hemorrhage risk Topical antiglaucoma, mydriatic ,steroids and oral antifibrinolytic Avoid NSAIDS as antithrombotic Avoid aspirin ,warfarin,ethanol
- 54. Surgical Ant chamber I/A done when A – IOP> 50 mmHg for 2 days or > 35 mmHg for 7 days. B – Early corneal blood staining because it can progress to a dense opacity within a few hours. C – Total hyphema for more than 5 days to prevent the development of PAS and chronic elevation of IOP Bleeding generally occurs from tears in the: major arterial circle and branches of the ciliary body; Choroidal arteries; Ciliary body vein; Iris vessels at the pupillary margin or in the angle. Complications - IOP elevation, corneal blood staining, the formation of anterior/posterior synechiae, cataract
- 55. IRIS AND PUPIL • Vossius ring • Radial sphincter tears •Iridodialysis
- 56. Radiating lacerations of the iris sometimes extending to the ciliary margin are rare Iridodialysis–iris root is torn away from its ciliary body attachement – black biconvex area seen at periphery and pupillary edge bulges slightly inwards forming D shaped pupil Uniocular diplopia- red reflex and lens zonules seen through peripheral gap
- 57. Extensive iridodialysis detached portion of iris completely rotated and pigmented back of iris faces forward ( anteflexion of the iris ) Total inversion or retroflexion of the iris --the whole iris doubled back into the cilirary region Traumatic aniridia - iris is completely torn away from its ciliary attachement contracts into minute ball and sinks to bottom of the anterior chamber
- 58. Treatment is anti inflammatory medications given locally . Atropine instilled in iridodialysis but avoided in ruptures of the iris or if lens is subluxated Surgical repair of iris is done by 10-0 prolene suture taking base of iris avulsion and suturing to the scleral spur and ciliary body junction. Traumatic aniridia – special scleral fixating iris lens , pupillary prosthesis and lens implantation,
- 63. Ciliary Body • Ciliary body detachment • Ciliary body damage • Cyclodialysis cleft
- 64. Ciliochoroidal Detachment • It Causes hypotony Medical treatment • Topical and systemic corticosteroids to rx concurrent iridocyclitis. • Topical cycloplegic agents(eg. 1% Atropine BD/TID) • Systemic CAI may help improve suprachoroidal fluid absoption. • Surgical rx if no response to medical regimen for 3-4 weeks, with flat A/C and/or PAS formation. Surgical treatment of a ciliochoroidal detachment by means of supraciliary/suprachoroidal fluid drainage is achieved by creating a fornix based conjunctival flap, followed by the dissection of a partial-thickness scleral flap extending over the supraciliary and the suprachoroidal spaces . A stab incision is then made into the supraciliary space, and fluid is subsequently drained. Multiple incisions are usually made. • The ciliary body is sutured to the scleral spur using a permanent 10–0 polypropylene or nylon suture,
- 65. Cyclodialysis cleft It is a separation of the ciliary body from the scleral spur, creating a direct connection between the anterior chamber and the suprachoroidal space. Many will spontaneously close, but those that do not can cause chronic hypotony, resulting in hypotony maculopathy, optic disc edema, choroidal effusion and detachement and decreased visual acuity. conservative medical therapy first(cycloplegic – mydriatic afents-1% Atropine BD) , if fails then argon laser photocoag ,diathermy , cryotherapy . Surgery repair is the Rx of choice for medium to large- sized clefts after initial Rx fails
- 67. Angle recession glaucoma • Tear b/w the longitudinal and circular muscles of the ciliary body • However, the cause for raised IOP is not the angle recessio. • trabecular meshwork proliferative and degenerative changes- leads to obstruction of aqueous flow • Extension of endothelial layer with a descements – like membrane from the cornea over anterior chamber angle • Angle recession more than 180 degree generally cause rise in IOP. • When medical and trabeculoplasty treatment fails • Trabeculectomy with antimetabolites, and the implantation of a Molteno device (IOP Ophthalmics) in the eyes of patients with uncontrolled ARG • • Trabeculectomy with antimetabolites is effective but there is a risk of bleb-related infection was also highest in this
- 68. Angle recession glaucoma on gonioscopy increase ciliary band width
- 70. Lens
- 71. CONCUSSION CATARACT It is due to mechanical effects of the injury on the lens fibres due to entrance of aqueous into the damaged lens capsule . The tears frequently occur on the thinnest part of the posterior pole of the lens If they are covered by iris such tears rapidly seals , at first by fibrin and later by proliferation of the subcapsular epithelium which secretes a new capsule and the entrance of the aqueous is stopped Sometimes the tear in the lens capsule remains open and opacification may progress to involve the entire lens Rosette shaped cataract – in posterior cortex sometimes in anterior cortex Rosette cataract may disappear or remain stationary or progress to total opacification of the lens which may appear rapidly within a few hours after injury or may be delayed for many months
- 72. SUBLUXATED LENS When the crystalline lens is partially displaced but contained within the lens space Defective vision due to astigmatism and decreased accommodation Uniocular diplopia Signs – irregular depth of AC, tremulous iris T/T – miotics pilocarpine Severe – lens removal and iol implantation
- 73. DISLOCATED LENS When the lens lies completely outside the lens patellar fossa in the anterior chamber , free floating in the vitreous or directly over the retina In AC dislocation of the lens – should be extracted with cryoprobe or Vectis combined with anterior vitrectomy Complications- iridocyclitis , secondary glaucoma Lens dislocated into vitreous- Non complicated cases- contact lens or iris claw Complicated cases – lens extraction along with vitrectomy
- 75. VITREOUS Anterior or posterior detachement of vitreous or both Equatorial expansion disrupt the anterior hyaloid face, allowing vitreous to enter the anterior chamber through the disrupted zonules. Appearance of clouds of fine pigmentary opacities- innumerable golden brown dots derived from uvea 1. Vitreous hemorrhage. 2. Vitreous opacities or floaters. 3. Vitreous prolapse through a ruptured globe with traction on the retina. 4. Avulsion of the vitreous base causing retinal disinsertion. Bucket handle appearance- stripe of translucent vitreous over the retina
- 76. CHOROID 1. Rupture of choroid (choroid,bruchs membrane,RPE ) Usually concentric with disc and on its temporal side- a curved white streak( due scleral thinning ) over which retinal vessels pass and rapidly becomes pigmented along its edge If macula involve – loss of central vision Non involvement of macula in periphery- causes little impairment of vision Rupture of choroid and retina – chorioretinitis sclopetaria T/t - steroids to decrease inflammatory changes and extent of later chorioretinal scarring Late complication – choroidal neovascularization
- 77. 2. Hemorrhagic choroidal effusion Accumulation of blood in suprachoroidal space between sclera and choroid- mainly due to rupture of choroidal vessels. Painful, high IOP for prolonged period (mass effect).Fundus – dome shaped elevations more posterior to equator. Poor prognosis - visual loss Mx -atropine 1% e/d qid, prednisolone qid,beta blockers , alpha agonists and topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitors Surgery –not done until autolysis of clot (7days ) then surgical drainage complete. Surgical stab incisions (2mm long) 5-8mm posterior to limbus where CD prominent 3. Spontaneous choroidal detachment from hypotony
- 78. RETINA 1.COMMOTIO RETINAE (BERLINS EDEMA) Milky white cloudiness due to edema over considerable area at posterior pole which may disappear after few days when vision restored Pigmentary deposits at macula - Vision may be good at first , central vision gradually diminishes Presence of intraretinal hemorrhage signals more severe involvement 2. Hemorrhages: retinal (superficial or deep) or subhyaloid
- 79. 3.Retinal Dialysis Disinsertion of the retina from non-pigmented pars plana epithelium at the ora serrata Retina remains attached to vitreous base MC location- superonasal and Inferotemporal quadrants May remain undiagnosed for long periods d/t minimal symptoms Vitreous avulsion -Overhanging bucket handle Appearance. *treatment –retinal dialysis without RD- cryotherapy or laser prophylactic therapy With RD-scleral buckling Retinal dialysis Retinal subhyaloid Hrhge
- 80. 4.Giant Retinal Tears Extends from min 90 degrees/ 3 clock hours Typically located in inferotemporal and superonasal quadrants a/w posterior vitreous detachment 5.Horseshoe Tears Areas of strong vitreoretinal adhesion cause retinal break during traumatic/spontaneous PVD They take shape of a horseshoe Globe deformations and torsion leading to PVD and fluid collects subsequently in the subretinal space
- 81. 6.Necrotic Retinal Breaks Seen posterior to ora serrata Direct contusive damage, retinal vascular damage and retinal capillary necrosis leads to weakened retina and irregularly shaped retinal breaks Detachment tends to form within 24 hours
- 82. Treatment Prophylactic laser retinopexy/ trans-scleral cryopexy- peripheral retinal breaks Close all retinal breaks and relieve vitreoretinal traction Surgical techniques- pneumatic retinopexy, scleral buckling and/or PPV Giant retinal tears- PFC stabilization, lensectomy, silicon oil tamponade RD with pars plana tears/ retinal dialysis- scleral buckling with trans-scleral cryotherapy or PPV,air-fluid exchange, internal drainage of SRF and endolaser photocoagulation
- 83. 7.Retinal detachment may be weeks or months later , more in myopic eyes or peripheral retinal degenerations i. Rhegmatogenous due to retinal tears, ii. Exudative due to severe hypotony, or iii. Tractional due to vitreous prolapse and incarceration in a scleral wound. Treatment- pneumatic retinopexy, scleral buckling, or vitrectomy d
- 84. TRAUMATIC MACULAR DEGENERATION Fine pigmentary changes at macula- tendency to increase progressively Submacular hemorrhage – accumulation of blood between the neurosensory retina and (RPE) arising from the choroidal or retinal circulation. pneumatic displacement with C3F8 and intravitreal tPA injection done within 3 weeks Macular Edema – cystic changes at macula and on rupture of a cyst Macular hole may form- round or oval deeply red patch Mechanical energy – vitreous fluid wave –and contrecoup macular necrosis or laceration
- 85. OPTIC NERVE 1. Hemorrhage of the optic nerve sheaths. 2. Edema of the optic nerve with hypotony. 3. Avulsion of the optic nerve with twisting injuries. 4. Traumatic optic atrophy usually of the primary type.
- 86. OPTIC NERVE AVULSION Head trauma - many - Penetrating injury - between the globe & orbital wall- disinsertion of the nerve at the level of the lamina cribrosa. Nonpenetrating injury sports injury - finger is pushed into the orbitextreme forward movt of the globe with shearing of the optic nerve fibers -the nerve sometimes only partially avulsed. No-light-perception (NLP) vision, afferent pupillary defect. Fundus- vitreous and retinal hemorrhages, an empty cavity at the nerve head is seen Mx -The transected nerve fibers are irreversibly damaged Partial avulsion, management aimed at preservation of the remaining intact nerve.
- 87. TRAUMATIC OPTIC NEUROPATHY (TON) *Cause –ocular, orbital or head trauma *Direct-optic nerve damage due to bony fragments, projectiles or local haematoma *Indirect- impact on eye,orbit and cranium transmitted to optic nerve. *Mechanism- contusion, deformation, compression,transection, intraneural haemmarhage,shearing,secondary vasospasm,and oedema *Ix- CT,MRI Mx- medical – Iv high dose corticosteroids Surgical – optic canal decompression -optic nerve sheath fenestration
- 88. Globe Rupture • Associated with poor visual prognosis • The rupture is usually anterior, in the vicinity of schlemm canal. • Associated with prolapse of lens, iris, ciliary body, vitreous • Rupture at the site of a surgical wound • Occult posterior rupture a/w- asymmetry of anterior chamber(classically deep),low iop, • Gentle Bscan may demonstrate posterior rupture. • Surgical repair of corneal and scleral wound and topical and systemic antibiotics
- 89. Traumatic endophthalmitis • Ocurs in 2 to 7% in penetrating injuries • 7to 31% with retained intraocular foreign body • Eyes at risk are those injured by foreign bodies contaminated by soil or vegetable matter in rural setting • Intravenous and intraocular antibiotics
- 90. • Staphylococcal,streptococcal,and bacillus species commonly involved