UNFSA Overview
The United Nations Fish Stocks Agreement
The United Nations Agreement for the Implementation of the Provisions of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea of 10 December 1982 relating to the Conservation and Management of Straddling Fish Stocks and Highly Migratory Fish Stocks (UNFSA) is an international agreement that regulates key fisheries that, because of their transboundary nature, require international cooperation for their conservation and management. Its objective is to ensure the long-term conservation and sustainable use of straddling fish stocks and highly migratory fish stocks through effective implementation of the relevant provisions of the Convention. The Agreement sets out principles for the conservation and management of those fish stocks and establishes that such management must be based on the precautionary approach and the best available scientific information.

Related instruments
Documentation
Status of the Agreement
Bodies and processes
UNFSA Toolkit
Find a compilation of legal resources related to UNFSA available for fisheries managers, policy makers, and the general public.

Key data
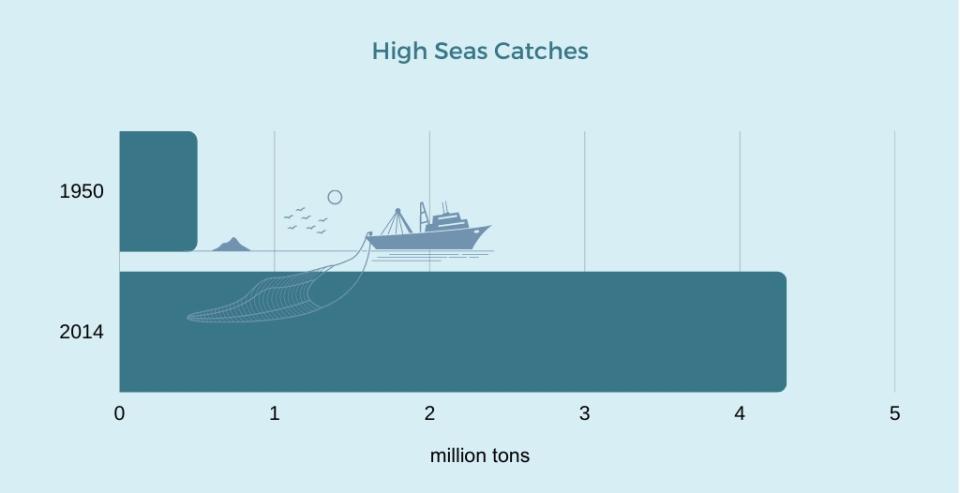
Pressures on highly migratory fish stocks and straddling fish stocks have been rapidly increasing during the last decades. High seas fish catches grew from 0.5 million tons to 4.3 million tons between 1950 and 2014.
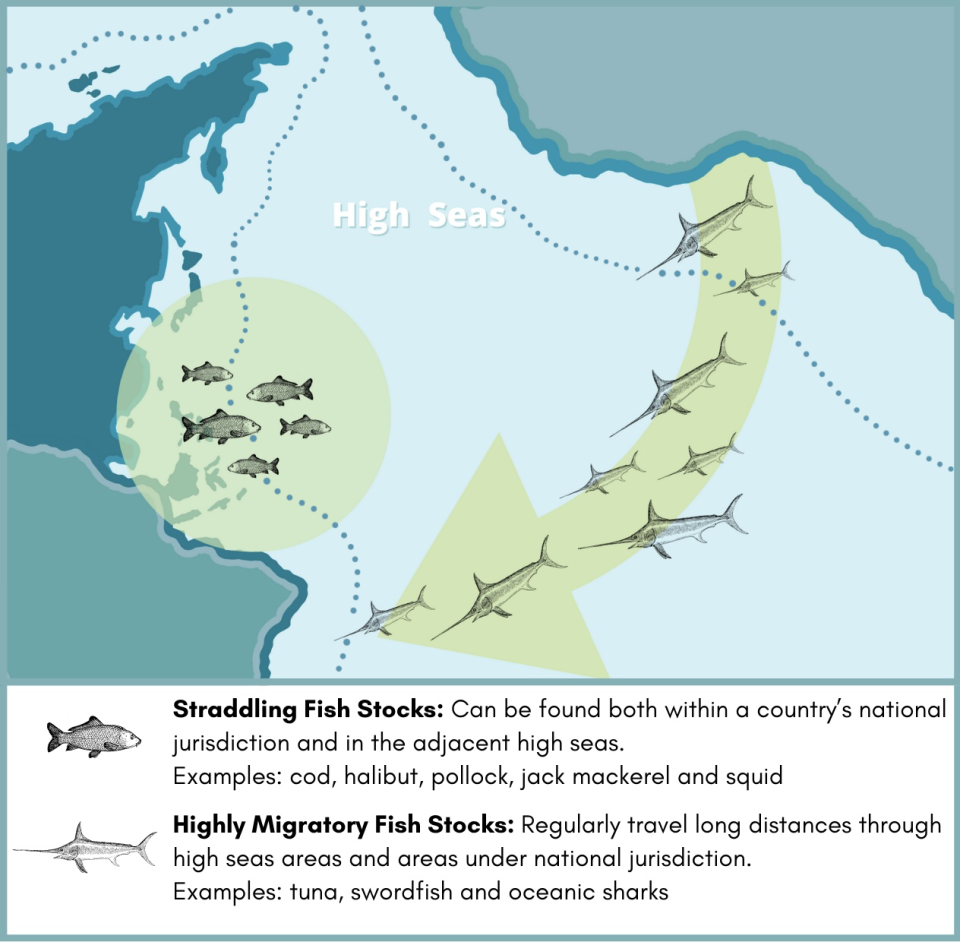
The exponential growth in fisheries catches has had an impact on those fish stocks covered by the Fish Stocks Agreement.

Full and effective implementation of UNFSA can help States manage fisheries resources, cooperate with each other, and fulfil their obligations, resulting in various benefits.



