Profit Before Tax Definition
Profit before tax (PBT) is a line item in a company’s income statement that measures profits earned after accounting for operating expenses like COGS, SG&A, Depreciation & Amortization, etc non-operating expensesNon-operating ExpensesNon operating expenses are those payments which have no relation with the principal business activities. These are the non-recurring items that appear in the company's income statement, along with the regular business expenses.read more like interest expense, but before paying off the income taxes. This is a significant measure because it gives the company’s overall profitability and performance before making corporate taxesCorporate TaxesCorporate tax is a tax levied by the government on the profits earned by a company at a fixed rate each year and is calculated in accordance with specific tax regulations.read more payments.
PBT is further used to calculate net profits by deducting income tax.
Table of contents
The formula of Profit Before Tax
The following formula can simply calculate PBT:
PBT = Revenue – (Cost of Goods Sold – Depreciation Expense – Operating Expense –Interest Expense)

You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkHow to Provide Attribution?Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Profit Before Tax (PBT) (wallstreetmojo.com)
An income statement that starts with revenue or sales goes on to calculate PBT as follows:
Format of Profit Before Tax
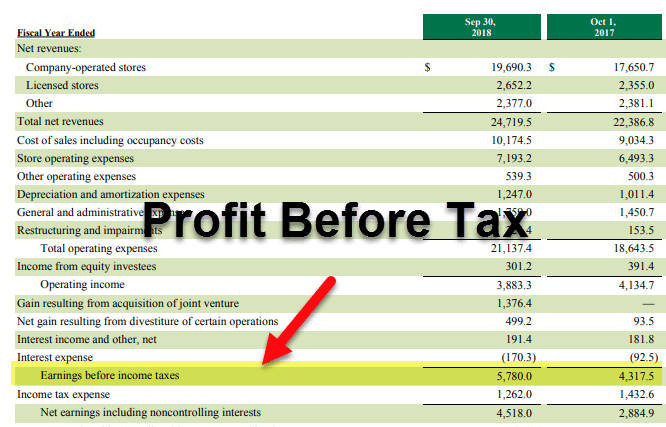
Revenue or Sales
Less: Cost of goods soldCost Of Goods SoldThe Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is the cumulative total of direct costs incurred for the goods or services sold, including direct expenses like raw material, direct labour cost and other direct costs. However, it excludes all the indirect expenses incurred by the company. read more
Gross profit
Less: Operating expense
Operating incomeOperating IncomeOperating Income, also known as EBIT or Recurring Profit, is an important yardstick of profit measurement and reflects the operating performance of the business. It doesn’t take into consideration non-operating gains or losses suffered by businesses, the impact of financial leverage, and tax factors. It is calculated as the difference between Gross Profit and Operating Expenses of the business.read moreLess: Interest expense
Note
This is a simple format for PBT calculation and can vary in complexity.
Examples of Profit Before Tax
Below are some examples of PBT
Example #1
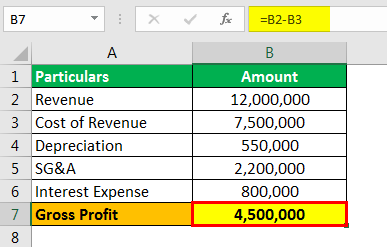
Company XYZ limited has US $12 million in Sales and wants to measure its PBT. The table below gives insight into different costs/expenses.
From the above data, we get the following information.
- Revenue: 12,000,000
- Cost of Revenue: 7,500,00
- Depreciation: 550,00
- SG&A: 2,200,000
- Interest Expense: 800,000
Subtract the Cost of revenue to get Gross profitGross ProfitGross Profit shows the earnings of the business entity from its core business activity i.e. the profit of the company that is arrived after deducting all the direct expenses like raw material cost, labor cost, etc. from the direct income generated from the sale of its goods and services.read more.
Gross Profit will be –
- =12000000-7500000
- Gross Profit = 4500000
Subtract depreciation, SG&A expenses, and interest expenseInterest ExpenseInterest expense is the amount of interest payable on any borrowings, such as loans, bonds, or other lines of credit, and the costs associated with it are shown on the income statement as interest expense.read more further to obtain profit before tax.
Therefore, the calculation of PBT as per the formula
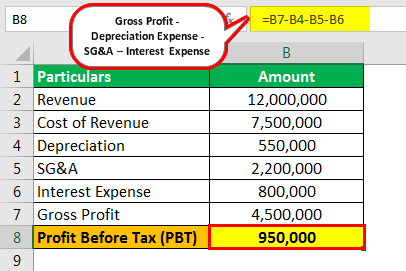
- = 4500000-550000-2200000-800000
- PBT = 950000
Example #2
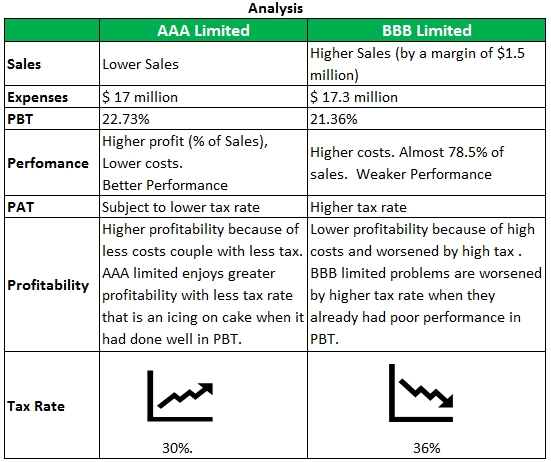
AAA Limited and BBB Limited operate in similar industries with similar scales and product linesProduct LinesProduct Line refers to the collection of related products that are marketed under a single brand, which may be the flagship brand for the concerned company. Typically, companies extend their product offerings by adding new variants to the existing products with the expectation that the existing consumers will buy products from the brands that they are already purchasing.read more. A team of analysts wants to make a comparative analysis of the PBTs of these two companies, and they have the following information-
From the above data, we get the following information.
| Company | AAA Limited | BBB Limited |
|---|---|---|
| Sales | $22,000,000 | $235,000,000 |
| Cost of Goods Sold | $14,000,000 | $14,800,000 |
| Operating Expenses | $3,000,000 | $2,500,000 |
| Profit Before Tax | ? | ? |
| Income Tax Rate | 30% | 36% |
| Profit After Tax | ? | ? |
Calculation of Profit Before Tax
Therefore, the calculation of PBT of AAA limited as per the formula is as follows,
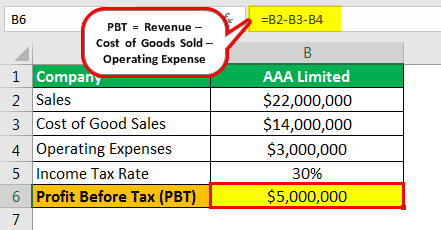
- =$22000000-$14000000-$3000000
- PBT = $5000000
Therefore, the calculation of PBT of BBB limited as per the formula is as follows,
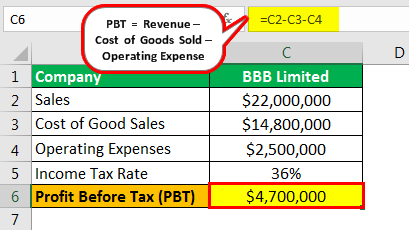
- =$22000000-$14800000-$2500000
- PBT = $4700000
Calculation of Profit After Tax
Therefore, the calculation of PAT of AAA limited as per the formula is as follows,
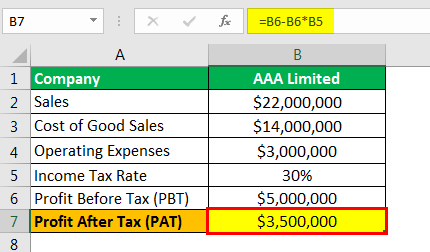
- =$5000000-$5000000*30%
- PAT = $3500000
Therefore, the calculation of PAT of BBB limited as per the formula is as follows,
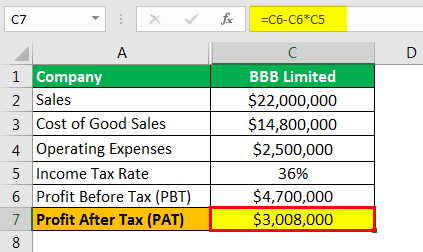
- =$4700000-$4700000*36%
- PAT = $3008000
This shows that while profit before tax measures performance, it does not reflect correctly on the profitability. PBT, on the other hand, better gauges profitability but falls short of giving insights on parameters like productivity, efficiencies, and performance levels.
Advantages of PBT Measure
Companies with similar business, characteristics, and scale can be analyzed on a comparative basis about their Profits before tax:
- PBT can mislead companies’ comparative performances because of its subjectivity to different tax systems. Hence, a preceding line item, PBT, better considers the comparability by eliminating the varied nature of taxes.
- PBT, as opposed to PAT (Profit after tax), is a measure of performance. Regarding varied tax policies, PAT is more inclined toward profitability calculationProfitability CalculationProfitability refers to a company's ability to generate revenue and maximize profit above its expenditure and operational costs. It is measured using specific ratios such as gross profit margin, EBITDA, and net profit margin. It aids investors in analyzing the company's performance.read more than performance measurement.
- Profit before tax also acknowledges the debt obligations of a company. The long-term debtLong-term DebtLong-term debt is the debt taken by the company that gets due or is payable after one year on the date of the balance sheet. It is recorded on the liabilities side of the company's balance sheet as the non-current liability.read more and lease obligations in a company’s balance sheet are reflected in its income statementIncome StatementThe income statement is one of the company's financial reports that summarizes all of the company's revenues and expenses over time in order to determine the company's profit or loss and measure its business activity over time based on user requirements.read more interest expense column.
Disadvantages of PBT Measure
- Profits that are not taxed do not give a true account of companies’ free cash flows (FCFFCFThe cash flow to the firm or equity after paying off all debts and commitments is referred to as free cash flow (FCF). It measures how much cash a firm makes after deducting its needed working capital and capital expenditures (CAPEX).read more). This makes for a skeptical valuation of a companyValuation Of A CompanyDiscounted cash flow, comparable company analysis, comparable transaction comps, asset valuation, and sum of parts are the five methods for valuing a company.read more if FCF methods are used.
- PBT is not a complete measure for comparison purposes if the operations of the companies under consideration are not similar – in nature and scale.
Limitation of PBT as a Measure of Profitability/Performance
Although PBT gives a clear picture of how companies have performed in terms of their sales and costs, both operating and non-operating, it becomes difficult to gauge the bottom lineBottom LineThe bottom line refers to the net earnings or profit a company generates from its business operations in a particular accounting period that appears at the end of the income statement. A company adopts strategies to reduce costs or raise income to improve its bottom line. read more of companies operating in different business settings.
- Taxation policies vary significantly across the world.
- The company’s profits might be eligible for tax benefitsTax BenefitsTax benefits refer to the credit that a business receives on its tax liability for complying with a norm proposed by the government. The advantage is either credited back to the company after paying its regular taxation amount or deducted when paying the tax liability in the first place.read more.
These conditions make a substantial difference in companies’ bottom line and redefine profitability if not performance.
Significance of PBT and Points to Note
While there are many other factors based on which a company’s performance can be evaluated, profit before tax becomes important because it takes note of all the expenses incurred by the company. As we go into finer details, the analysis becomes better and provides greater insights into the business’s health.
However, any analysis that overlooks qualitative factors concerning the business is incomplete. For that matter, even Profit after taxProfit After TaxProfit After Tax is the revenue left after deducting the business expenses and tax liabilities. This profit is reflected in the Profit & Loss statement of the business.read more will be rendered futile if analysts neglect the qualitative analysis of the company. It should be noted that companies are not evaluated on the numerical values of their respective PBTs. Therefore, underlying assumptions and reasons are equally important to drawing near-complete analyses of companies.
Profit before tax can also represent as Earnings before tax:
Earnings before tax, EBT = EBIT – interest expense = PBT
Conclusion
PBT is an important concept in business. It measures business performance in so far as everything except taxes. Unlike gross and operating profit, where expenses are not included, PBT analysis should always consider different expense recognition principlesExpense Recognition PrinciplesThe Expense Recognition Principle is an accounting principle that states that expenses should be recorded and compiled in the same period as revenues.read more followed by different businesses.
A company’s interest payments will capture its high leverage and give analysts a true picture of its indebtedness. Unfortunately, while PBT is a good indicator measure, EBITDAEBITDAEBITDA refers to earnings of the business before deducting interest expense, tax expense, depreciation and amortization expenses, and is used to see the actual business earnings and performance-based only from the core operations of the business, as well as to compare the business's performance with that of its competitors.read more and EBITEBITEarnings before interest and tax (EBIT) refers to the company's operating profit that is acquired after deducting all the expenses except the interest and tax expenses from the revenue. It denotes the organization's profit from business operations while excluding all taxes and costs of capital.read more fail to sense the same.
From an investor’s perspective, PBT is a useful measure for comparing businesses located in different economies, thus subject to different taxes. The extent to which PBT reflects performance in such cases is probably the finest of all – Sales, EBITDA, and EBIT.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Profit Before Tax and its definition. Here we discuss the formula to calculate PBT along with examples, advantages, and disadvantages. You can learn more about accounting from the following articles –

