OSOM® Ultra Strep A Test - Sekisui Diagnostics
OSOM® Ultra Strep A Test - Sekisui Diagnostics
OSOM® Ultra Strep A Test - Sekisui Diagnostics
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
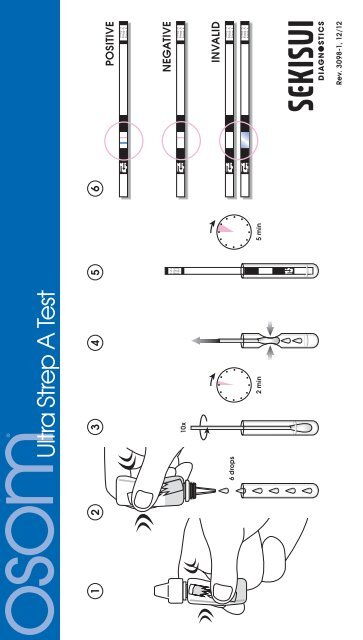
126 drops<strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong>34 5610x2 min 5 minPOSITIVENEGATIVEINVALIDRev. 3098-1, 12/12®
®<strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong>CLIA Complexity: WaivedINTENDED USEThe OSOM ® <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong> is a color immunochromatographic assay intended for the qualitativedetection of Group A <strong>Strep</strong>tococcal antigen directly from throat swab specimens.SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION OF TESTGroup A <strong>Strep</strong>tococcus is one of the most important causes of acute upper respiratory tract infection.Early diagnosis and treatment of Group A <strong>Strep</strong>tococcal pharyngitis has been shown to reduce theseverity of symptoms and further complications such as rheumatic fever and glomerulonephritis (1) .Conventional identification procedures for Group A <strong>Strep</strong>tococcus from throat swabs involve theisolation and subsequent identification of viable pathogens by techniques that require 18 to 24 hoursor longer (2) . The OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong> detects either viable or nonviable organisms directly from athroat swab, providing results within 7 minutes.PRINCIPLES OF TESTThe OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong> is a color immunochromatographic assay using Dual Label Technology(DLT)**. DLT uses antibody labeled color particles coated at two separate locations in the test device.DLT allows greater sensitivity than the conventional single label technology without sacrificing specificity.In the test procedure, a throat swab is subjected to a chemical extraction of a carbohydrate antigenunique to Group A <strong>Strep</strong>tococcus. The <strong>Test</strong> Stick is then placed in the extraction mixture and the mixturemigrates along the membrane. If Group A <strong>Strep</strong>tococcus is present in the sample, it will form complexeswith the anti-Group A <strong>Strep</strong>tococcus antibody conjugated color particles located at two separatelocations on the <strong>Test</strong> Stick. The complex will then be bound by the anti-Group A <strong>Strep</strong>tococcus captureantibody and a visible blue <strong>Test</strong> Line will appear to indicate a positive result. A red Control Line will alsoappear to indicate the test is valid.KIT CONTENTS AND STORAGEContents:25 <strong>Test</strong> Sticks Coated with Rabbit Anti-Group A <strong>Strep</strong>tococcus25 <strong>Test</strong> Tubes25 Sterile Swabs25 Extraction Reagent Bottles (2 M Sodium Nitrite and One Ampule with 0.3 M Acetic Acid)1 Positive Control (Nonviable Group A <strong>Strep</strong>tococci, 0.1% Sodium Azide)1 Negative Control (Nonviable Group C <strong>Strep</strong>tococci, 0.1% Sodium Azide)1 Workstation1 Directional InsertNote: extra components (swabs, tubes) have been provided for your convenience.• Store <strong>Test</strong> Sticks and reagents tightly capped at 15˚ – 30˚C (59˚– 86˚F).• Do not use <strong>Test</strong> Sticks or reagents after expiration date.• Store Extraction Reagent Bottles inside the box. Avoid exposure to light.• Avoid dropping Extraction Reagent Bottles as this may cause ampule breakage.MATERIALS REQUIRED BUT NOT PROVIDEDA timer or a watch.PRECAUTIONS• For in vitro diagnostic use.• Follow your laboratory safety guidelines in the collection, handling, storage and disposal of controls,patient specimens and all items exposed to patient specimens (3) .• Caution: The Extraction Reagent Bottle contains Sodium Nitrite and may be harmful if swallowed.Do not taste or swallow. Wash thoroughly after handling.• The Extraction Reagent Bottle contains a glass ampule. Crush the glass ampule with care.• Warning: The Extraction Reagent Bottle contains an acidic solution that will cause skin and eyeirritation. If the solution comes in contact with the skin or eyes, flush with large volumes of water.• If no glass ampule is inside the Extraction Reagent Bottle or the glass ampule appears to be brokenbefore use (reagent is colorless or yellow), discard and use another Extraction Reagent Bottle.• The Positive and Negative Controls contain sodium azide which may react with lead or copperplumbing to form potentially explosive metal azide. Large quantities of water must be used to flushdiscarded control material down a sink.• Do not interchange or mix components from different kit lots.SPECIMEN COLLECTION AND PREPARATION• Collect specimens with a sterile swab from the tonsils and/or the back of the throat (2) taking care toavoid the teeth, gums, tongue or cheek surfaces.• Do not use swabs with cotton tips, wooden shafts or calcium alginate swabs.• Do not use a collection system that contains charcoal or semisolid transport media.
• If your lab requires a culture result as well as the OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong> result, streak the culture platewith the swab before starting the OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong> procedure as the extraction reagents willcause the specimen to become nonviable.• Process the swab as soon as possible after collecting the specimen. If you do not perform the OSOM<strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A test immediately, store the swabs either at room temperature or refrigerated for up to 48hours. The swabs and the test kit must be at room temperature prior to running the test.• Sample Transport:• Because the performance characteristics of this product were established with the sterile rayonswabs supplied with the kit, we recommend using these swabs to assure optimal performance.You may purchase the kit swabs in a double swab/dry tube format as an accessory(<strong>Sekisui</strong> <strong>Diagnostics</strong> Part #7784).• Because the test does not require live organisms for processing, a rayon transport swabcontaining Stuart’s or Amies media may also be used; however, swabs from other suppliers havenot been validated.QUALITY CONTROLInternal Procedural ControlsThe OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong> provides three levels of procedural controls with each test run:• The color of the liquid changes from pink to light yellow after the glass ampule is crushed and theextraction reagents are mixed. This is an internal extraction reagent control. The color change meansyou have mixed the extraction reagents properly. The color change also means that the reagents arefunctioning properly.• The red Control Line is an internal positive procedural control. For the <strong>Test</strong> Stick to be working properly,capillary flow must occur. The <strong>Test</strong> Stick must absorb the proper amount of sample and the <strong>Test</strong> Stickmust be working properly for the red Control Line to appear.• A clear background is an internal background negative procedural control. If no interferingsubstances are in the specimen and the <strong>Test</strong> Stick is working properly, the background willclear. A discernible result will be seen.If the red Control Line does not appear the test is invalid. If the background does not clear and interfereswith the test result, the test is invalid. Call <strong>Sekisui</strong> <strong>Diagnostics</strong> Technical Service if you experienceeither of these problems.External Quality Control <strong>Test</strong>ingEach kit contains Positive and Negative Control material. The controls are for external quality controltesting. Use the Controls to test that the extraction reagents and the <strong>Test</strong> Sticks are working properly.Also use the Controls to test that you are able to correctly perform the test procedure, including theantigen extraction portion of the test procedure. If you choose, you may use Group A and non GroupA <strong>Strep</strong>tococcus ATCC reference strains as external controls. Some commercial controls may containinterfering additives. Therefore <strong>Sekisui</strong> <strong>Diagnostics</strong> recommends that you do not use commercialcontrols with the OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong>.Quality Control requirements should be established in accordance with local, state and federalregulations or accreditation requirements. Minimally, <strong>Sekisui</strong> <strong>Diagnostics</strong> recommends that positive andnegative external controls be run with each new lot and with each new untrained operator.QC <strong>Test</strong>ing Procedure:Positive Control• Follow Steps 1 and 2 in the TEST PROCEDUREsection to dispense the Extraction Reagentinto the <strong>Test</strong> Tube.• Vigorously mix the Positive Control material.Add 1 free falling drop of the Positive Controlfrom the dropper bottle into the <strong>Test</strong> Tube.• Using a clean swab, follow steps 3 – 6 in theTEST PROCEDURE section to test the swab.Negative Control• Follow Steps 1 and 2 in the TEST PROCEDUREsection to dispense the Extraction Reagentinto the <strong>Test</strong> Tube.• Vigorously mix the Negative Control material.Add 1 free falling drop of the Negative Controlfrom the dropper bottle into the <strong>Test</strong> Tube.• Using a clean swab, follow steps 3 – 6 in theTEST PROCEDURE section to test the swab.LIMITATIONSAs with all diagnostic assays, the results obtained by this test yield data that must be used only as anadjunct to other information available to the physician. The following factors must be considered toobtain reliable results:• The OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong> is a qualitative test for the detection of Group A <strong>Strep</strong>tococcal antigen.This test detects both viable and non-viable Group A <strong>Strep</strong>tococci, and may yield a positive resultin the absence of living organisms.• The quality of the test depends on the quality of the sample; proper throat swab specimens must beobtained. Negative results can occur from inadequate specimen collection or antigen level whichis below the detection limit of the test.• The OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong> should be used only with throat swab specimens. The use of swabspecimens taken from other sites or the use of other samples such as saliva, sputum or urine hasnot been established.• This test does not differentiate between carriers and acute infection.• Pharyngitis may be caused by viral or bacterial pathogens other than Group A <strong>Strep</strong>tococcus (1,2) .• If the test result is inconsistent with the clinical symptoms, a second throat swab should be collectedfor repeat testing.The American Academy of Pediatrics states (4) : “Several rapid diagnostic tests for GAS pharyngitis areavailable... The specificities of these tests generally are very high, but the reported sensitivities varyconsiderably. As with throat cultures, the accuracy of these tests is most dependent on the quality of thethroat swab specimen, which must contain pharyngeal and tonsillar secretions, and on the experienceof the person who is performing the test. Therefore, when a patient suspected of having GAS pharyngitishas a negative rapid streptococcal test, a throat culture should be obtained to ensure that the patient
does not have GAS infection.” It also states: “Cultures that are negative for GAS infection after 24 hoursshould be incubated for a second day to optimize isolation of GAS.”EXPECTED RESULTSApproximately 19% of all upper respiratory tract infections are caused by Group A <strong>Strep</strong>tococci (5) .<strong>Strep</strong>tococcal pharyngitis displays a seasonal variation and is most prevalent during winter and earlyspring. The highest incidence of this disease is found in crowded populations such as military basesand in school-age children (6) .PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICSSummaryThe study results in this section show that the sensitivities of the OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong> and the standardsingle swab culture method are not statistically different. The study also compared the OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong>A <strong>Test</strong> to Rigorous Gold Standard and another commercially available rapid test, Inverness Medical –BioStar’s <strong>Strep</strong> A OIA ® Max <strong>Test</strong>***.Comparison of the Performances of OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong>, <strong>Strep</strong> A OIA Max <strong>Test</strong> and Standard SingleSwab Culture Method, by Using Rigorous Gold Standard (“RGS”; Multiple Sample Swab Culture plus BrothEnhanced Pledget Culture) as the Gold StandardIn a hospital clinical lab field evaluation, two swabs (A and B) were collected from each of 302 patientspresenting with pharyngitis. Swabs were held in transport tubes with Stuart’s modified transport mediumuntil testing. Swabs A and B from each patient were inoculated on separate selective sheep blood agarplates. One swab (Swab A) was then tested by the OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong> and the other swab (SwabB) was tested by the <strong>Strep</strong> A OIA Max <strong>Test</strong>. Plates were incubated for 24 – 48 hours at 35˚C with 5 – 10%CO2. All pledgets from the transport tubes were placed aseptically in modified Todd Hewitt Broth (THB)for 16 – 24 hours at 35˚C with 5 – 10% CO2. After the initial incubation, the inoculated THB was sub-culturedon SXT agar plates and incubated for 24 – 48 hours at 35˚C with 5 – 10% CO2. All presumptive GAS colonieswere confirmed with commercially available <strong>Strep</strong> A test kits. A positive culture from either one of thetwo swabs or the pledget was considered a Rigorous Gold Standard (RGS) positive.Of 302 total patients sampled, 94 were found RGS positive and 208 were RGS negative, with a positiverate of 31.1%. The sensitivity of the OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong>, 92.6% (95% confidence interval (CI): 84.8 – 96.0%)was the same as the corresponding standard single swab culture, 92.6% (95% CI: 84.8 – 96.0%). In thesestudies, the two test methods’ sensitivities were not statistically different (p = 0.7811). The sensitivity of theOSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong> was 92.6% and the sensitivity of the <strong>Strep</strong> A OIA Max <strong>Test</strong> was 75.5%, with p valueof 0.0021. The results are summarized below:Individual <strong>Test</strong> Results Compared to the RGS:Swab A - Culture vs RGSRGS + RGS - TotalCulture + 87 0 87Culture - 7 208 215Total 94 208 302Sensitivity: 87 / 94 = 92.6%Specificity: N/A aSwab B - Culture vs RGSRGS + RGS - TotalCulture + 82 0 82Culture - 12 208 220Total 94 208 302Sensitivity: 82 / 94 = 87.2%Specificity: N/A aSwab A - OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong> vs. RGSRGS + RGS - Total<strong>Ultra</strong> + 87 15 102<strong>Ultra</strong> - 7 193 200Total 94 208 302Sensitivity: 87 / 94 = 92.6%Specificity: 193 / 208 = 92.8%Swab B - <strong>Strep</strong> A OIA Max <strong>Test</strong> vs RGSRGS + RGS - TotalOIA + 71 6 77OIA - 23 202 225Total 94 208 302Sensitivity: 71 / 94 = 75.5%Specificity: 202 / 208 = 97.1%Summary of the <strong>Test</strong> Method Sensitivity and Specificity When Compared to the Rigorous Gold Standard:<strong>Test</strong> Method Sensitivity SpecificitySingle Swab Culture A (SSC A) 87 / 94 (92.6%) N/A aSingle Swab Cuture B (SSC B) 82 / 94 (87.2%) N/A aOSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong> (Swab A) 87 / 94 (92.6%) 193 /208 (92.8%)<strong>Strep</strong> A OIA Max <strong>Test</strong> (Swab B) 71 / 94 (75.5%) 202 / 208 (97.1%)Statistical Analysis b for the Sensitivity of the Various <strong>Test</strong> Methods:<strong>Test</strong> Method Sensitivity pSSC A vs. SSC B 87 / 94 (92.6%) vs. 82 / 94 (87.2%) 0.3312OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> vs. SSC A 87 / 94 (92.6%) vs. 87 / 94 (92.6%) 0.7811OIA Max vs. SSC B 71 / 94 (75.5%) vs. 82 / 94 (87.2%) 0.0581OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> vs. OIA Max 87 / 94 (92.6%) vs. 71 / 94 (75.5%) 0.0021a. N/A, Not applicable, all culture positives are true-positive by definition.b. A statistical analysis using “The Difference Between Two Independent Proportions” by Fleiss (7) was used.
Comparison of the Performances of OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong> andStandard Single Swab Culture Method, by Using Combined Culture Standard(“CCS”; Single Swab Culture plus Broth Enhanced Pledget Culture) as the Gold StandardIn a field evaluation conducted by a clinical lab for a pediatric group practice, a total of 490 throatswabs were collected from patients presenting with pharyngitis. Swabs were held in transport tubeswith modified Stuart’s transport media until testing.Each swab was inoculated on a sheep blood agar plate, then tested by the OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong>.The plate methods were the same as previously described. All pledgets from the transport tubes werealso tested following the enhanced pledget culture method described previously. A positive culturefrom either the swab or the pledget was considered a Combined Culture Standard (CCS) positive.Of 490 total specimens, 164 were found CCS positive and 326 were CCS negative, with a positiverate of 33.5%. Of the 326 CCS negative specimens, 326 were also negative by the OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong>A <strong>Test</strong>, for a specificity of 100% (95% CI: 98.5 – 100%). Of the 164 CCS positive specimens, 161 and 157were also positive by the standard single swab culture and the OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong>, respectively.These equal to sensitivities of 98.2% (95% CI: 94.3 – 99.2%) and 95.7% (95% CI: 91.1 – 97.7%) for the standardsingle swab culture and the OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong>, respectively. A statistical analysis comparing thesensitivity of the standard single swab culture and the OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong>, using “The DifferenceBetween Two Independent Proportions” by Fleiss (7) , showed these two methods were not statisticallydifferent (p = 0.3341).Sensitivity: 157 / 164 = 95.7%The results are summarized below:<strong>Test</strong> Results:Single Swab Culture vs. CCSOSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong> vs. CCSCCS + CCS - TotalCCS + CCS - TotalCulture + 161 0 161<strong>Ultra</strong> + 157 0 157Culture - 3 326 329<strong>Ultra</strong> - 7 326 333Total 164 326 490Total 164 326 490Sensitivity: 161 / 164 = 98.2%Specificity: N/A a Specificity: 326 / 326 = 100%Sensitivity Analysis:<strong>Test</strong> Method Sensitivity SpecificitySIngle Swab Culture 161/164 (98.2%) N/A aOSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong> 157/164 (95.7%) 326/326 (100%)p = 0.3341 N/A aa N/A, Not applicable, all culture positives are true-positive by definition.Evaluation of the Performance of OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong>by Using Standard Single Swab Culture Method as the Gold StandardIn a two site field evaluation, throat swabs were collected from patients presenting with pharyngitis. Eachswab was inoculated on a sheep blood agar plate, then tested by the OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong>. Plateswere incubated for 24 – 48 hours at 35˚C with 5 – 10% CO2. Presumptive GAS colonies were confirmed withcommercially available <strong>Strep</strong> A test kits. When the standard single swab culture method was used as thegold standard, the combined results from these two sites showed that the OSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A <strong>Test</strong> had asensitivity of 96.4% (239/248; 95% CI: 93.0 – 97.9%), a specificity of 96.3% (524/544; 95% CI: 94.3 – 97.5%), andan overall agreement of 96.3%. The results are summarized below:Culture DensityOSOM <strong>Ultra</strong> <strong>Strep</strong> A Results4+ (predominant grwoth) 89/89 (100%)3+ (>50 colonies) 90/91 (98.9%)2+ (11 – 50 colonies) 45/46 (97.8%)1+ (
TEST PROCEDUREAbsorbent End Result Window Handle EndSTEP 1Just before testing, squeeze the Extraction Reagent Bottleto crush the ampule inside. Note: The ampule must becrushed before proceeding to the next step.STEP 2Vigorously shake the Extraction ReagentBottle 3 – 5 times to mix the contents. Theliquid in the Extraction Reagent Bottleshould turn from pink to light yellow.6 dropsAdd 6 drops of the Extraction Reagentto the <strong>Test</strong> Tube.STEP 3Immediately put the swab into the <strong>Test</strong> Tube.10xVigorously mix the solution by rotating the swab forcefullyagainst the side of the <strong>Test</strong> Tube at least ten (10) times.Best results are obtained when the specimen is vigorouslyextracted in the solution.Let stand for 2 minutes.2 minSTEP 4Express as much liquid as possible from the swab bysqueezing the sides of the tube as the swab is withdrawn.Discard the swab.STEP 5Remove the <strong>Test</strong> Stick(s) from the container;re-cap the container immediately.Place the Absorbent End of the <strong>Test</strong> Stick into theextracted sample.STEP 6Read results at 5 minutes. Positive results may be readas soon as the red Control Line appears. Negative resultsmust be confirmed at 5 minutes.5 minResults are invalid after the read time.The use of a timer is recommended.