What is Pulpitis?
Contents:
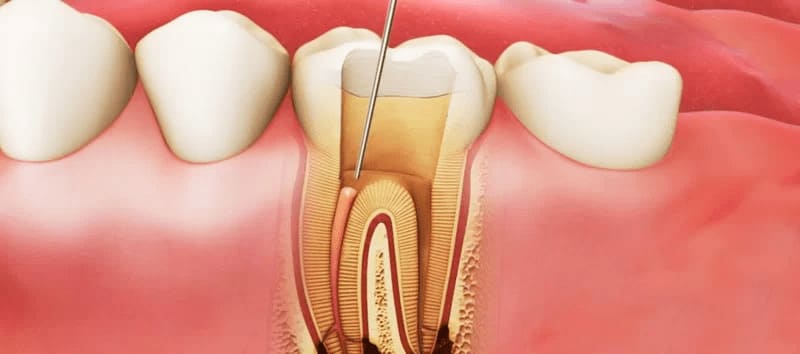
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the pulp. The pulp is a loose, fibrous connective tissue inside the tooth cavity. It includes many small vessels and nerve fibers and is responsible for the vital functions of the dentition elements.
Pathology requires an immediate visit to the dentist; the treatment is conservative, and sometimes it is necessary to remove the tooth nerve.
Causes of Pulpitis
Pulpitis is an inflammatory process of the tooth pulp, most often caused by streptococci and staphylococci.
Causes of the disease
- advanced caries, poor-quality filling – pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the carious cavity, and their toxic waste products lead to the development of inflammation;
- streptococcal sore throat;
- tooth injuries – enamel chipping, fracture of a dentition element with pulp injury;
- pathological abrasion of dentition elements.
The causes of pulpitis can be mistakes in dental treatment – if some procedures are performed incorrectly, the state of the pulp changes.
Pulpitis is a common dental disease found in 20-25% of patients with oral pathologies. The disease affects both the molars and primary teeth. Due to the physiological characteristics of children, the transition from caries to pulpitis occurs very quickly.
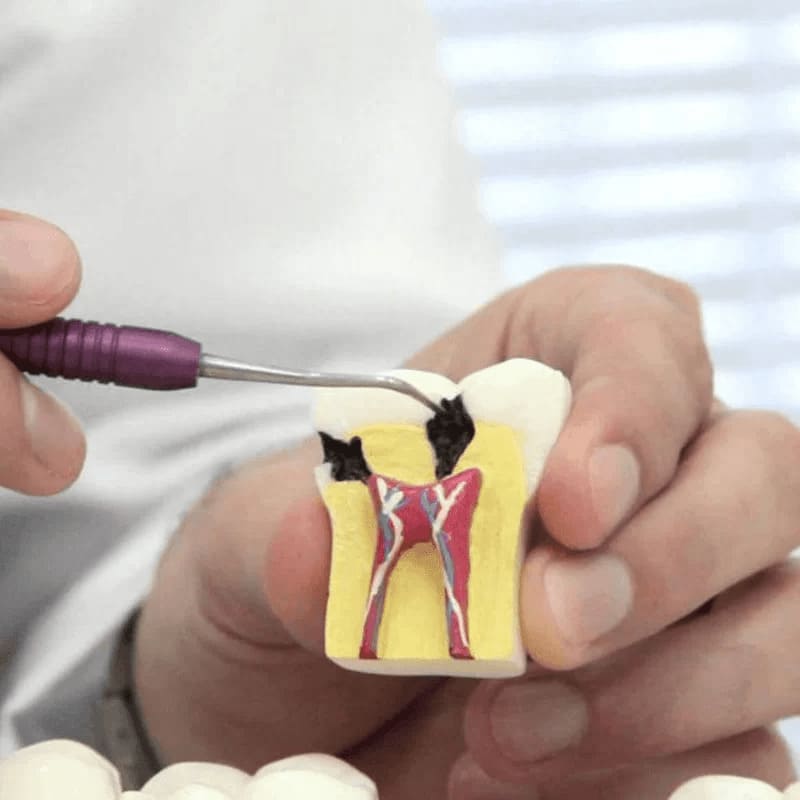
Forms of dental pulpitis
Pulpitis is classified according to various criteria. To establish the diagnosis, dentists use the International Classification of Diseases to Dentistry and Stomatology.
Types of pulpitis:
- Acute – serous limited or diffuse, focal sero-purulent.
- Purulent – a severe form of pathology accompanied by various complications.
- Chronic forms.
Sometimes lime deposits form in the pulp, which are painless; the dentist detects denticles during endodontic treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulpitis
The main symptom of pulpitis is severe pain. Unpleasant sensations occur at rest when cold or hot is applied to the affected tooth.
Pulpitis is one of the main causes of night toothache. In a horizontal position, blood rushes to the head; due to excessive pressure, nerve endings more actively transmit signals to the brain. The pain syndrome manifests itself most strongly from 12 am to 5 am.
Features of Pain Syndrome in Various Forms of Pulpitis
There are characteristic signs of pulpitis, but the symptoms may differ in different forms of pathology.
Signs of different forms of the disease:
- Acute focal pulpitis. Sudden, short-term pain attacks with long breaks characterize it. Unpleasant sensations are most often associated with exposure to temperature stimuli. The pain has a precise localization, which worsens at night. During the examination, the bottom of a deep carious cavity is painful.
- Acute diffuse pulpitis. Pain attacks are long with short intervals. The pain syndrome is intense, especially at night. Discomfort from the diseased tooth radiates to the jaw, ear, and eye. The carious cavity is deep; the entire bottom surface is painful.
- Purulent pulpitis. Severe pain appears suddenly, most often at night, and the patient cannot pinpoint which tooth hurts. High temperatures aggravate unpleasant sensations; cold helps to reduce the pain a little. There are signs of intoxication – weakness, headache, fever, lack of appetite.
- Chronic pulpitis. Clinical manifestations are erased. The tooth hurts slightly and for a short time.
- Chronic gangrenous form. Toothache occurs after eating hot, cold food or drinks. Additionally, there is an unpleasant rotten breath. Acute pain often spreads in the direction of the trigeminal nerve.
- Chronic hyperplastic form. The pain syndrome is practically absent, but the inflamed pulp bleeds.
In acute conditions of any form of pulpitis, patients complain of sharp, prolonged attacks of intense pain. At rest, the tooth hurts a little, but when biting down on the antagonist’s tooth, the discomfort increases.
How Does a Doctor Diagnose Pulpitis?
If you have signs of pulpitis, you should visit a dental clinic. The doctor makes a diagnosis based on a checkup, analysis of patient complaints, and imaging.
Signs of pulp inflammation on examination:
- carious tooth with altered dentin;
- the affected element reacts painfully to temperature changes;
- percussion is painful.
The main diagnostic methods:
- Probing. A procedure to assess the condition of hard tissues, dentin, the integrity of the tooth cavity, and detect pain. The dentist assesses the depth of periodontal pockets and the quality of the adjacent filling material.
- Percussion. In the acute form of the disease, pain occurs.
- Assessment of the reaction to temperature stimuli. A diseased tooth reacts to heat, cold, and the pain does not disappear after removing the trigger.
- Measurement of pulp electrical excitability with a special device. In the case of pulp inflammation, the indicators are 18-60 μA.
- X-ray. It is prescribed to detect a hidden carious cavity and assess the fit of the filling. Sometimes with pulpitis in the area of the tooth root, an enlarged periodontal gap is observed.
The dentist conducts a differential diagnosis to exclude deep caries and chronic periodontitis. Additionally, a consultation with a neurologist may be required to exclude trigeminal nerve damage, and the patient may need an ENT specialist if suppurative otitis media or sinusitis is suspected.
How Is Pulpitis Treated?
In treating pulpitis, they try to fully or partially preserve the pulp and restore the tooth’s functionality, so conservative methods are used. In advanced cases, it is necessary to remove the pulp.
Without proper and timely treatment of pulpitis, pulp necrosis, periodontitis, periostitis, and osteomyelitis develop.
Complications can arise during the treatment of root canals of teeth – breakage of the instrument inside the canal, perforation of the bottom or walls of the tooth cavity. Negative consequences can occur due to non-compliance with the rules for using temporary pastes, extruding the filling material beyond the upper part of the root.
Conservative Methods of Pulpitis Treatment
Biological method
It is used to preserve the pulp ultimately. It is performed in case of partial acute or reversible pulpitis to eliminate the inflammatory process and dentin formation and prevent the penetration of bacteria.
The method is most often used to treat patients under 29. In this case, the electrodiagnostic testing should give more than 25 μA, and no pathologies should exist on the X-ray image.
Vital puncture
Partial preservation of the pulp. It is used in acute focal, chronic pulpitis with electrodiagnostic testing results up to 40 μA in treating elements of the dentition with an unformed root or multi-rooted teeth. Periodontal and periodontal tissues mustn’t be inflamed.
Pulp Removal Methods
Pulpectomy – removal of the entire pulp, used in treating all types of pulpitis.
Stages of endodontic treatment:
- Anesthesia.
- Preparation of the carious cavity.
- Removal of affected pulp tissue. Root canals are expanded and shaped into a cone.
- Canal treatment to eliminate pulp residues, toxic tissue decay products, and canal expansion.
- Rinsing the canals with an antiseptic.
- An antibiotic, anti-inflammatory paste, is placed in the canals, and a temporary filling is placed for 1-2 days. In some forms of pulpitis, this stage is skipped; the canals are dried after irrigation.
- Root canal filling. Materials based on zinc oxide and eugenol, epoxy resins, and gutta-percha are used.
Pulpitis can lead to losing an element of dentition and other complications. To prevent pulp inflammation, it is necessary to visit the dentist twice a year and take proper care of the oral cavity.
You can make an appointment at the KES clinic for a routine checkup or to treat pulpitis. Our experienced dentists will help with any form of the disease.

