Abstract
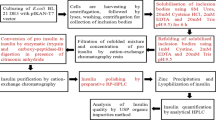
Bilirubin, a natural intermediate in heme degradation, is a valuable Chinese medicine used in more than 50 traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) preparations. At present, bilirubin is mainly produced by extraction from pig bile, but a shortage of the raw material has increased the price, to about US$10,000/kg in the Chinese market. Biliverdin, the precursor of bilirubin, is more abundant and less expensive than bilirubin, but it is not used in TCM. Thus, the biotransformation of biliverdin by biliverdin reductase (BvdR) may be a practical way to produce bilirubin. In this study, the codon-optimized gene of biliverdin reductase (mbvdR) from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis was cloned into Escherichia coli BL21(DE3), and the conditions for BL21-mBvdR expressing BvdR were optimized. Resting BL21-mBvdR cells were employed as biocatalysts to biotransform biliverdin to bilirubin. At a concentration of biliverdin substrate of 450 mg/L in the reaction mixture, the bilirubin content in dry cells reached 20.8 ± 0.8 mg/g, with a conversion yield of 72.3%. Therefore, recombinant E. coli expressing BvdR can be applied to biotransform biliverdin to bilirubin, providing a potential alternative process for bilirubin production.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data generated during this study are included in the article.
References
McDonagh AF (2001) Turning green to gold. Nat Struct Biol 8:198–201. https://doi.org/10.1038/84915
Creeden J, Gordon D, Stec D, Hinds JT (2020) Bilirubin as a metabolic hormone: the physiological relevance of low levels. Am J Physiol: Endocrinol Metab 320:E191–E207. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00405.2020
Shapiro SM (2005) Definition of the clinical spectrum of kernicterus and bilirubin-induced neurologic dysfunction (BIND). J Perinatol 25:54–59. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211157
Shiels RG, Hewage W, Pennell EN, Vidimce J, Grant G, Pearson AG, Wagner KH, Morgan M, Bulmer AC (2020) Biliverdin and bilirubin sulfonate inhibit monosodium urate induced sterile inflammation in the rat. Eur J Pharm Sci 155:105546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105546
Thakkar M, Edelenbos J, Doré S (2019) Bilirubin and ischemic stroke: rendering the current paradigm to better understand the protective effects of bilirubin. Mol Neurobiol 56:5483–5496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1440-y
Tran D, Jeong Y, Kim J, Bae H, Son S, Kwak S (2020) The anti-inflammatory role of bilirubin on “two-hit” sepsis animal model. Int J Mol Sci 21:8650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228650
Yao Q, Jiang X, Huang ZW, Lan QH, Wang LF, Chen R, Li XZ, Kou L, Xu HL, Zhao YZ (2019) Bilirubin improves the quality and function of hypothermic preserved islets by its antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effect. Transplantation 103:2486–2496. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000002882
Kim J, Yoon SJ, Woo MH, Kim SH, Kim NK, Kim J, Kim OJ, Oh SH (2017) Differential impact of serum total bilirubin level on cerebral atherosclerosis and cerebral small vessel disease. PLoS ONE 12:e0173736. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0173736
Lapenna D, Ciofani G, Pierdomenico SD, Giamberardino MA, Ucchino S, Davì G (2018) Association of serum bilirubin with oxidant damage of human atherosclerotic plaques and the severity of atherosclerosis. Clin Exp Med 18:119–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-017-0470-5
Doré S, Snyder SH (1999) Neuroprotective action of bilirubin against oxidative stress in primary hippocampal cultures. Ann NY Acad Sci 890:167–172. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb07991.x
Mancuso C (2017) Bilirubin and brain: a pharmacological approach. Neuropharmacology 118:113–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.03.013
Vítek L, Tiribelli C (2021) Bilirubin: the yellow hormone? J Hepatol 75:1485–1490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2021.06.010
Yu ZJ, Xu Y, Peng W, Liu YJ, Ji Z, Li JS, Sun T, Wang P (2020) Calculus bovis: a review of the traditional usages, origin, chemistry, pharmacological activities and toxicology. J Ethnopharmacol 254:112649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2020.112649
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission (2020) Pharmacopoeia of People’s Republic of China. China Medical Science Press, Beijing
Huang SY, Hsu RP (1992) Separation and purification of bilirubin from hog bile. In: Furusaki S, Endo I, Matsuno R (eds) Biochemical engineering for 2001. Springer, Japan, Tokyo, pp 551–553
Cao H (2011) Production method for extracting bilirubin by promoting degradation by animal blood in vitro enzyme. China Invention Patent CN101487032A
Zhao R, Xu GY, Liu ZZ, Li JY, Yang N (2006) A study on eggshell pigmentation: biliverdin in blue-shelled chickens. Poultry Sci 85:546–549. https://doi.org/10.1093/ps/85.3.546
Ding ZK, Xu YQ (2002) Purification and characterization of biliverdin IXα from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) bile. Biochemistry (Mosc) 67:927–932. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1019974822667
Morales J (2020) Eggshell biliverdin as an antioxidant maternal effect. BioEssays 42:2000010. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.20200133
Chen D, Brown JD, Kawasaki Y, Bommer J, Takemoto JY (2012) Scalable production of biliverdin IXα by Escherichia coli. BMC Biotechnol 12:89. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6750-12-89
Pendrak ML, Roberts DD (2005) Methods for the production of biliverdin. US Patent Application Publication, USA, US2005/0209305A1
Kikuchi A, Park SY, Miyatake H, Sun D, Sato M, Yoshida T, Shiro Y (2001) Crystal structure of rat biliverdin reductase. Nat Struct Biol 8:221–225. https://doi.org/10.1038/84955
Schluchter WM, Glazer AN (1997) Characterization of cyanobacterial biliverdin reductase: conversion of biliverdin to bilirubin is important for normal phycobiliprotein biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 272:13562–13569. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.21.13562
Hayes JM, Mantle TJ (2009) The effect of pH on the initial rate kinetics of the dimeric biliverdin-IXα reductase from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC6803. FEBS J 276:4414–4425. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07149.x
Brunelle JL, Green R (2014) Chapter twelve: One-dimensional SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (1D SDS-PAGE). In: Lorsch J (ed) Methods enzymol, vol 541. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 151–159
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by Shanghai Hebutong Technology Co., Ltd. and the Science and Technology Department of Zhejiang Province (Grant No. 2021C03088).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JM: conceptualization, methodology, and writing (review and editing) XW: investigation, methodology, and writing (original draft preparation). SZ: investigation. YY: methodology and validation. XW: resources and validation. GY: project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent for publication
The authors approved the manuscript submission to Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mei, J., Wu, X., Zheng, S. et al. Production of bilirubin by biotransformation of biliverdin using recombinant Escherichia coli cells. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 45, 563–571 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-021-02679-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-021-02679-4